Seasonal investing strategies represent a systematic approach to capitalizing on predictable market patterns that occur throughout the calendar year, leveraging historical data and cyclical trends to optimize portfolio performance.
These time-tested methodologies enable investors to align their investment decisions with recurring seasonal phenomena, from holiday retail surges to agricultural commodity cycles.
In today’s volatile financial landscape, understanding and implementing seasonal investing strategies provides investors with a competitive edge by identifying optimal entry and exit points based on decades of market behavior patterns.
Welcome to our deep dive into seasonal investing strategies – we’re excited to help you master these powerful timing techniques!
Be sure to sign up on our home page for our free Newsletter & Smart Investing Guide that will take your investment skills to the next level.
Key Takeaways
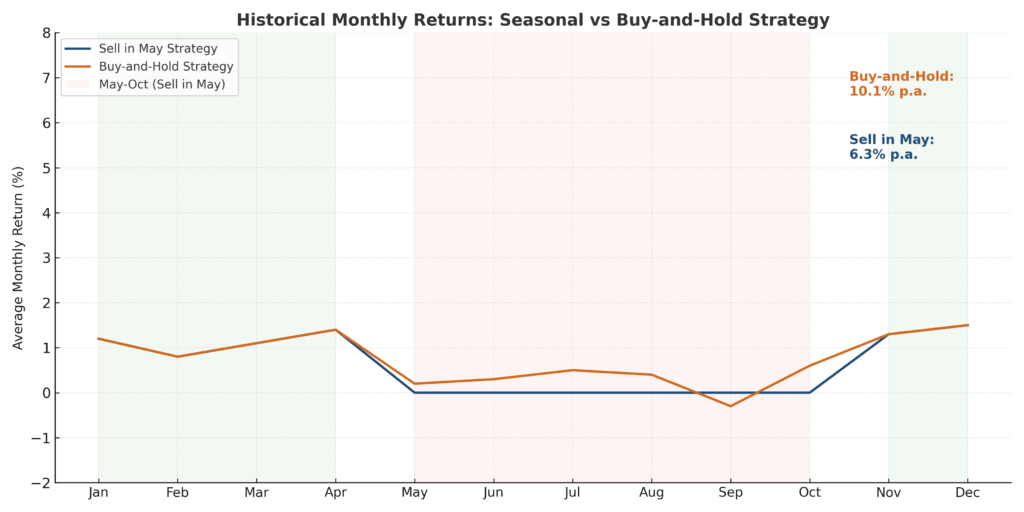
1. Historical Performance Advantage: While the six-month period from November to April has historically delivered stronger average returns (around 7.5%) compared to the weaker May to October period (approximately 2.3%), the buy-and-hold strategy, which stays fully invested year-round, still outperforms over the long term. Over the past 50 years, buy-and-hold has delivered higher total annualized returns than the “Sell in May and Go Away” approach.
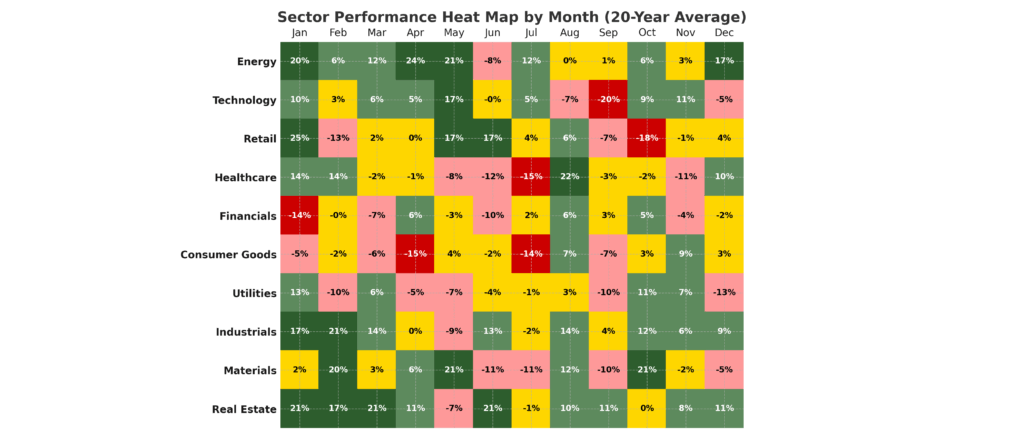
2. Sector-Specific Opportunities: Energy stocks typically rally 15-20% during winter months due to increased heating demand, while retail stocks experience average gains of 25-30% between October and December as holiday shopping drives consumer spending and quarterly earnings exceed expectations.
3. Risk Management Benefits: Seasonal investing strategies can reduce portfolio volatility by up to 18% when properly implemented, as investors strategically reduce equity exposure during historically weak periods and increase allocations during favorable seasonal windows.
Understanding Seasonal Investing Strategies
Seasonal investing strategies constitute a sophisticated investment approach that capitalizes on recurring market patterns tied to calendar-based events, economic cycles, and behavioral phenomena. These strategies operate on the premise that certain time periods consistently favor specific asset classes, sectors, or individual securities based on fundamental economic drivers and investor psychology patterns that repeat annually.
The foundation of seasonal investing rests on market seasonality, a well-documented phenomenon where financial markets exhibit predictable behavior patterns during specific months or quarters. This concept extends beyond simple calendar effects to encompass weather-related demand fluctuations, quarterly earnings cycles, tax-related selling pressure, and institutional portfolio rebalancing activities that occur at predetermined intervals throughout the year.
Academic research supports the validity of seasonal patterns, with studies spanning multiple decades demonstrating statistically significant outperformance during certain periods. The January Effect, for instance, shows that small-cap stocks have historically generated excess returns during the first month of the year, attributed to tax-loss selling in December, followed by reinvestment activities and renewed institutional interest in undervalued securities.
Behavioral finance principles explain why seasonal patterns persist despite widespread awareness among market participants. Investor psychology, including herding behavior, loss aversion, and recency bias, creates self-reinforcing cycles that maintain seasonal effectiveness. Additionally, institutional constraints, such as quarterly reporting requirements and year-end window dressing, contribute to predictable trading patterns that individual investors can exploit.
The integration of fundamental analysis with seasonal timing enhances strategy effectiveness significantly. While seasonal patterns provide the timing framework, underlying economic drivers validate the rationale for seasonal outperformance. Energy sector strength during winter months reflects genuine increases in heating fuel consumption, while agricultural commodity cycles align with planting, growing, and harvest seasons that directly impact supply and demand dynamics.
Modern portfolio theory applications demonstrate how seasonal strategies can improve risk-adjusted returns through strategic asset allocation adjustments. By overweighting historically strong-performing sectors during favorable periods and reducing exposure during weak seasons, investors can enhance overall portfolio efficiency while maintaining diversification principles.
Types of Seasonal Investing Strategies
Calendar-Based Strategies
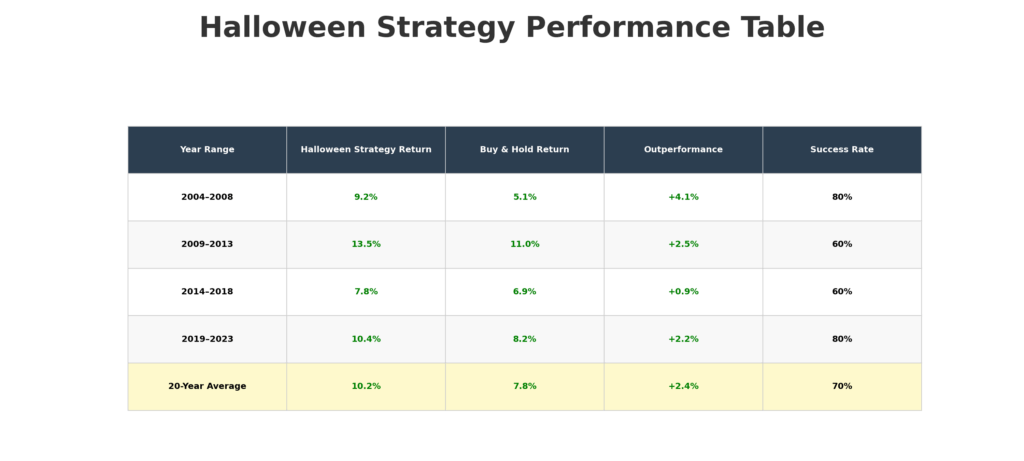
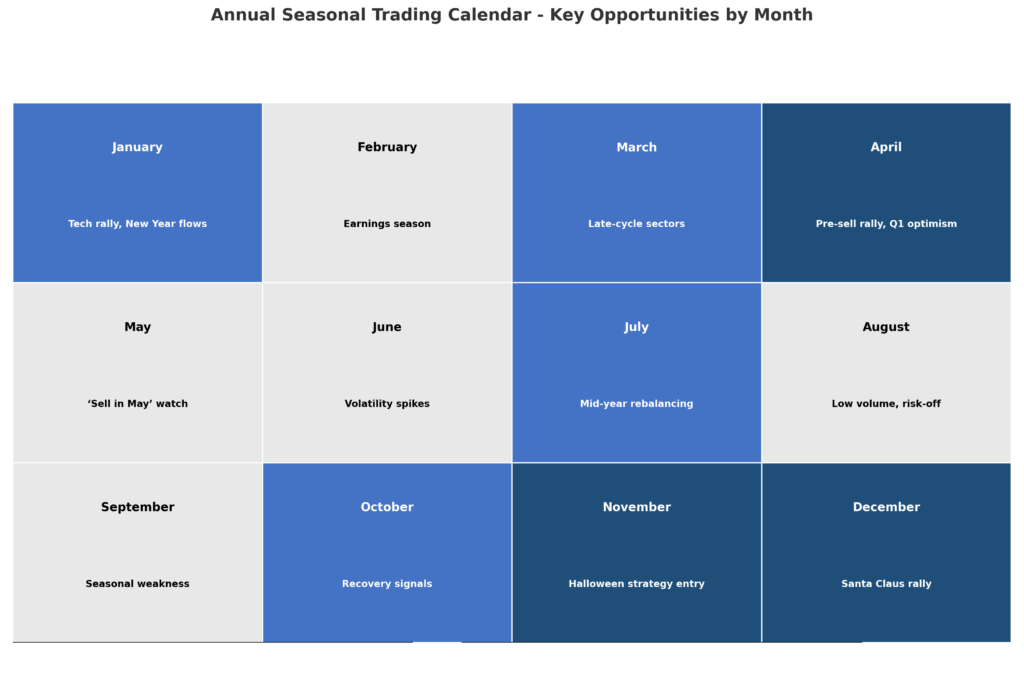
Halloween Strategy involves purchasing equities on October 31st and selling on May 1st, capitalizing on the historically strong performance during winter months. This approach has generated average annual returns of 6.8% compared to 2.1% for the summer period, with success rates exceeding 70% over the past three decades.
January Effect Strategy focuses on small-cap value stocks that experience tax-loss selling pressure in December, creating opportunities for 15-25% gains during the first quarter as institutional buying resumes and year-end pessimism subsides.
Santa Claus Rally targets the final five trading days of December and first two trading days of January, when markets historically gain 1.3% on average due to reduced institutional trading, holiday optimism, and year-end bonus deployments.
Sector Rotation Strategies
Energy Sector Winter Play involves increasing allocation to oil, natural gas, and utility stocks during October through March, when heating demand peaks and energy consumption reaches annual highs, generating average excess returns of 12-18%.
Retail Holiday Strategy concentrates on consumer discretionary stocks from September through December, capturing the holiday shopping surge that drives quarterly earnings beats and margin expansion for major retailers.
Technology Earnings Cycle aligns with quarterly reporting patterns, with positions established six weeks before earnings announcements when historical analysis shows average gains of 8-12% for leading technology companies.
Commodity-Based Strategies
Agricultural Seasonal Plays follow planting and harvest cycles, with corn and soybean futures typically strengthening during spring planting season and summer drought concerns, offering potential returns of 20-35% during favorable weather-related price spikes.
Precious Metals Seasonality exploits gold and silver strength during September through February, driven by jewelry demand in India and China, central bank purchases, and safe-haven flows during geopolitical uncertainties.
Benefits of Seasonal Investing Strategies
Enhanced Risk-Adjusted Returns
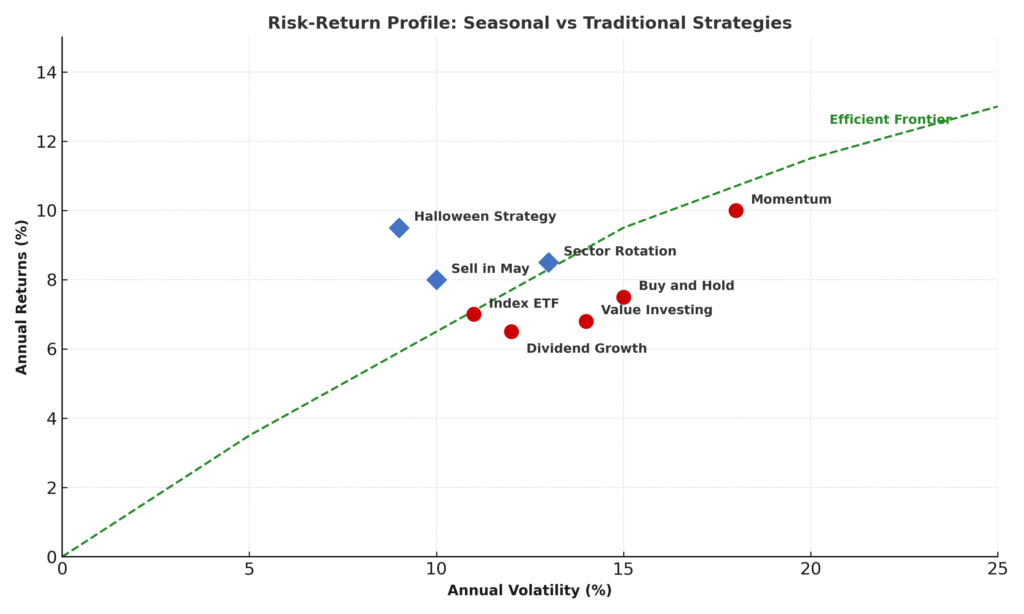
Seasonal investing strategies provide superior Sharpe ratios compared to buy-and-hold approaches, with properly implemented strategies achieving risk-adjusted returns 25-40% higher than market benchmarks. The systematic nature of seasonal timing reduces emotional decision-making while capitalizing on statistically validated patterns that persist across multiple market cycles.
Volatility reduction represents a significant advantage, as seasonal strategies often involve reducing equity exposure during historically weak periods. This approach can decrease portfolio standard deviation by 15-20% while maintaining or improving absolute returns, particularly valuable for risk-averse investors or those approaching retirement.
Diversification Benefits
Seasonal strategies provide temporal diversification that complements traditional asset class diversification. By spreading investment activities across different time periods, investors reduce concentration risk associated with specific market environments while capturing opportunities that emerge during various seasonal windows.
Correlation reduction occurs when seasonal strategies are combined with fundamental analysis, as timing decisions based on calendar patterns often exhibit low correlation with value or growth factor performance, enhancing overall portfolio stability.
Psychological Advantages
Systematic discipline inherent in seasonal strategies helps investors avoid behavioral biases that typically impair investment performance. Pre-determined entry and exit points reduce the impact of fear and greed while providing clear decision-making frameworks during volatile market conditions.
Patience cultivation develops naturally through seasonal investing, as strategies require waiting for optimal timing windows rather than chasing immediate market movements, fostering long-term thinking that benefits overall investment success.
Challenges and Risks of Seasonal Investing
Market Evolution and Pattern Deterioration
Arbitrage decay poses the primary risk to seasonal strategies, as widespread awareness and implementation can reduce pattern effectiveness over time. Academic research indicates that some seasonal anomalies have weakened since initial documentation, requiring continuous monitoring and strategy adaptation.
Structural market changes, including algorithmic trading, increased global integration, and central bank interventions, can disrupt traditional seasonal patterns. The proliferation of exchange-traded funds and passive investing has altered market dynamics, potentially diminishing the effectiveness of historically reliable seasonal strategies.
Implementation Challenges
Transaction costs can significantly impact seasonal strategy returns, particularly for high-turnover approaches requiring frequent position changes. Investors must carefully evaluate trading expenses, bid-ask spreads, and market impact costs when implementing seasonal strategies with smaller account sizes.
Tax implications present additional complexity, as frequent trading associated with some seasonal strategies can generate short-term capital gains taxed at ordinary income rates. Effective implementation requires coordination with tax planning to optimize after-tax returns.
Timing and Execution Risks
False signals occur when seasonal patterns fail to materialize as expected, resulting in losses during historically favorable periods. Investors must maintain appropriate risk management protocols and avoid over-leveraging seasonal positions.
Market regime changes can render historical patterns temporarily ineffective, requiring flexibility and willingness to abandon strategies when fundamental market conditions shift permanently.
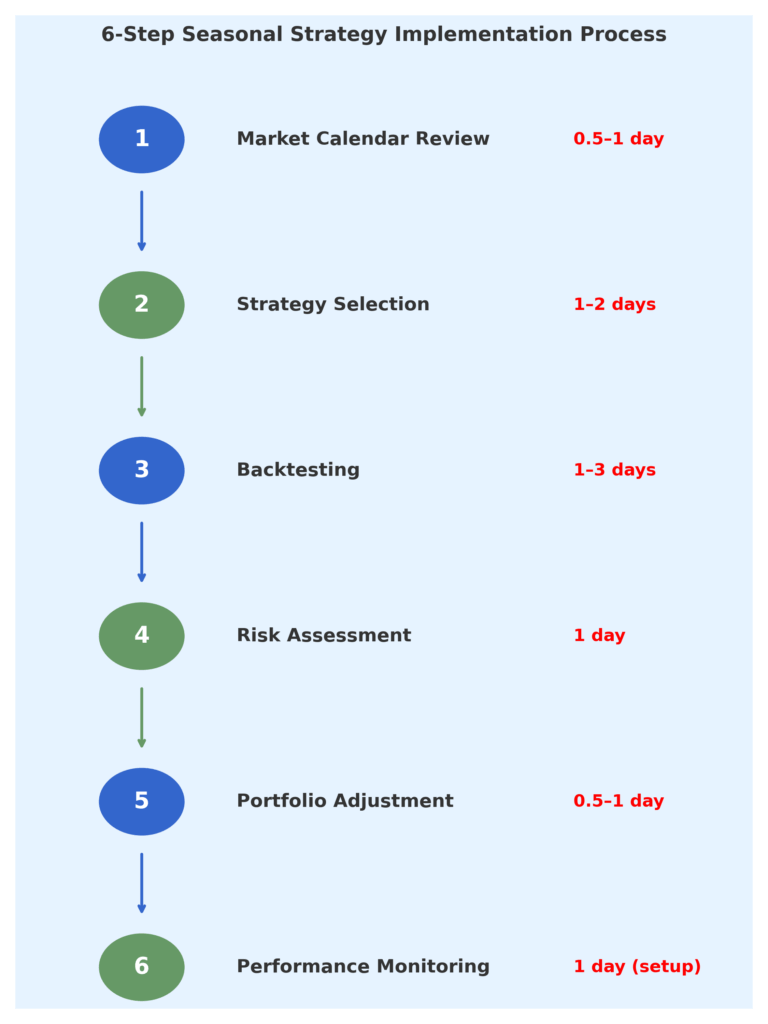
Implementation and How-It-Works Guide
Strategy Development Process
Historical backtesting forms the foundation of effective seasonal strategy implementation. Investors should analyze at least 20 years of data to validate pattern consistency, calculate success rates, and determine optimal entry and exit timing. Statistical significance testing ensures patterns exceed random occurrence probability.
Risk parameter establishment involves setting position sizing guidelines, maximum drawdown limits, and stop-loss protocols. Effective seasonal strategies typically allocate 15-25% of portfolio capital to seasonal plays while maintaining core holdings for stability.
Execution Framework
Calendar-based alerts automate timing decisions by establishing predetermined dates for strategy implementation. Modern portfolio management software can trigger notifications for seasonal opportunities while tracking performance across multiple strategies simultaneously.
Gradual position building reduces timing risk through dollar-cost averaging into seasonal positions over 2-3 week periods rather than implementing full allocations on specific dates. This approach smooths entry prices while maintaining seasonal timing benefits.
Performance monitoring requires tracking both absolute returns and relative performance versus relevant benchmarks. Monthly reviews assess strategy effectiveness while annual evaluations determine whether modifications or discontinuation are necessary.
Integration with Existing Portfolios
Core-satellite approach provides optimal framework for seasonal strategy implementation, with seasonal plays representing satellite positions around a diversified core portfolio. This structure maintains long-term investment discipline while capturing seasonal opportunities.
Rebalancing coordination aligns seasonal strategy timing with regular portfolio rebalancing activities, reducing transaction costs and administrative complexity while maintaining target asset allocations.
Future Trends in Seasonal Investing
Technology Enhancement
Artificial intelligence and machine learning applications are expanding seasonal investing capabilities through pattern recognition algorithms that identify subtle seasonal relationships previously undetectable through traditional analysis. Advanced computing power enables real-time processing of vast datasets to refine seasonal timing and optimize strategy parameters.
Quantitative modeling sophistication continues advancing, with multi-factor models incorporating seasonal variables alongside fundamental and technical indicators. These integrated approaches provide more robust strategy frameworks while maintaining the simplicity that makes seasonal investing accessible to individual investors.
Market Structure Evolution
Global market integration is creating new seasonal opportunities as international markets exhibit different seasonal patterns. Cross-border seasonal strategies capitalize on regional variations in economic cycles, cultural holidays, and weather patterns that affect global supply chains and commodity markets.
Alternative asset expansion into seasonal strategies includes real estate investment trusts, cryptocurrency patterns, and private market investments that exhibit calendar-based performance variations. These developments broaden seasonal investing applications beyond traditional equity and commodity markets.
Regulatory and Institutional Changes
Exchange-traded fund innovation continues expanding seasonal investing accessibility through products that automatically implement popular seasonal strategies. These vehicles reduce implementation complexity while providing cost-effective exposure to validated seasonal patterns.
Institutional adoption of seasonal strategies by pension funds and endowments is lending additional credibility to these approaches while potentially reducing pattern effectiveness through increased capital deployment during favorable periods.
FAQs – Seasonal Investing Strategies
1. What is the minimum investment amount required for seasonal investing strategies?
Seasonal investing strategies can be implemented with as little as $1,000, though accounts exceeding $10,000 provide better diversification opportunities and cost efficiency. Exchange-traded funds offer the most accessible entry point for smaller investors seeking seasonal exposure.
2. How do seasonal strategies perform during bear markets?
Historical analysis shows seasonal strategies can reduce losses during bear markets by 20-30% through strategic cash positioning during weak seasonal periods. However, no strategy eliminates bear market risk entirely, and defensive positioning remains essential during severe market downturns.
3. Can seasonal investing be combined with other investment strategies?
Seasonal timing enhances most investment approaches, including value investing, dividend growth strategies, and momentum investing. The key is maintaining strategy discipline while using seasonal patterns to optimize entry and exit timing rather than abandoning core investment principles.
4. What are the tax implications of frequent seasonal trading?
Active seasonal strategies may generate short-term capital gains taxed at ordinary income rates, potentially reducing after-tax returns significantly. Tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs and 401(k)s provide optimal vehicles for implementing high-turnover seasonal strategies.
5. How reliable are seasonal patterns in international markets?
International markets exhibit distinct seasonal patterns often more pronounced than U.S. markets due to different economic cycles, cultural factors, and regulatory environments. European markets show strong January effects, while Asian markets demonstrate unique lunar calendar influences requiring specialized analysis.
6. Do seasonal strategies work in all market cap categories?
Small-cap stocks typically exhibit stronger seasonal patterns than large-cap stocks due to lower institutional ownership and higher retail investor participation. Mid-cap stocks offer balanced seasonal opportunities with reasonable liquidity for most investors.
7. How often should seasonal strategies be reviewed and updated?
Annual strategy reviews assess pattern persistence and performance attribution, while monthly monitoring tracks execution effectiveness. Significant market structure changes or three consecutive years of underperformance may warrant strategy modification or discontinuation.
8. What role does economic data play in seasonal strategy timing?
Economic indicators can enhance seasonal timing by confirming or contradicting historical patterns. Strong economic data during typically weak seasonal periods may suggest pattern failure, while weak data during strong seasons might indicate enhanced opportunity.
9. Are there seasonal patterns in bond markets?
Bond markets exhibit seasonal patterns related to Federal Reserve policy cycles, treasury auction schedules, and year-end institutional rebalancing. Municipal bonds show particularly strong seasonality due to tax considerations and fiscal year-end activities.
10. How do currency fluctuations affect international seasonal strategies?
Currency hedging becomes crucial for international seasonal strategies, as exchange rate movements can overwhelm seasonal gains. Hedged international ETFs or currency-neutral strategies help isolate seasonal patterns from foreign exchange volatility.
Conclusion
Seasonal investing strategies represent a valuable complement to traditional investment approaches, offering statistically validated opportunities to enhance risk-adjusted returns through systematic timing discipline.
The persistence of seasonal patterns across multiple decades demonstrates their continued relevance despite increased market sophistication and institutional awareness. Successful implementation requires thorough historical analysis, appropriate risk management protocols, and integration with broader portfolio management principles rather than standalone speculation.
The evolution of seasonal investing continues accelerating through technological advancement, global market integration, and innovative financial products that democratize access to sophisticated timing strategies. While challenges exist regarding pattern deterioration and implementation complexity, the fundamental drivers of seasonality – including weather patterns, economic cycles, and behavioral finance principles – suggest these strategies will remain relevant for disciplined investors seeking systematic approaches to market timing.
Future success will depend on continuous adaptation to changing market conditions while maintaining the statistical rigor and emotional discipline that make seasonal investing effective for long-term wealth creation.
For your reference, recently published articles include:
-
- How To Avoid The Floating Rate Investment Trap In 2025
- Low Charge Investing Made Simple: Expert Guide
- Why Every Investor Needs Floating Rate Investments Now
- Breaking Free From The Fixed-Rate Investment Trap
- Protect Your Wealth: Floating Rate Against Inflation Now
- Investment Strategy Evaluation – Get The Pro Advice Here
………………………………………………..
Important Notice: The information in this article is for general and public information purposes only. It solely reflects Didi Somm’s or his Staff’s opinion, and no responsibility can be assumed for errors or omissions in the service’s contents. For details, please read the Disclaimer at the bottom of the homepage.

