
In today’s digital age, the democratization of investing has made trading more accessible than ever before. The emergence of zero-cost trading platforms has revolutionized how individual investors interact with financial markets, potentially saving thousands of dollars in trading fees annually.
This Trading Fee Comparison Guide explores explicitly the landscape of fee-free trading, its implications for investors, and how to maximize its benefits while understanding the underlying risks.
Key Takeaways
- While zero-cost trading eliminates traditional commission fees, brokers still generate revenue through alternative channels such as payment for order flow (PFOF), margin lending, and premium services. For example, a typical investor trading 100 shares of a $50 stock would save $4.95-$6.95 per trade compared to traditional commission structures, but might face slightly wider bid-ask spreads that could cost $0.01-$0.02 per share in hidden execution costs.
- The rise of zero-commission trading has fundamentally altered the competitive landscape of retail broking, forcing established players to adapt or risk obsolescence. Traditional brokers like Charles Schwab and E*TRADE have eliminated their base commission fees, leading to industry-wide consolidation and a greater focus on additional revenue streams such as advisory services and premium features.
- Zero-cost trading platforms have significantly lowered barriers to entry for retail investors, with the minimum investment often dropping from $500-$1,000 to as little as $1. This democratization has led to a 27% increase in retail trading participation since 2019, though it has also raised concerns about increased speculative trading and the need for enhanced financial literacy.
Table of Contents
Understanding Zero-Cost Trading
Zero-cost trading, also known as commission-free trading, refers to the practice of executing financial transactions without paying traditional broker commissions. This model emerged as a disruptive force in the financial services industry, challenging the conventional fee-based structure that had dominated for decades.
The concept gained mainstream attention in 2013 when Robinhood launched its mobile-first, commission-free trading platform. Since then, the model has become increasingly prevalent, with major brokers adopting similar approaches to remain competitive. The transformation has been particularly impactful in the equity and ETF markets, where transaction fees historically ranged from $4.95 to $9.95 per trade.
The elimination of trading commissions represents a fundamental shift in how brokerages generate revenue and how retail investors approach market participation. This change has coincided with broader technological advances in financial services, creating a more accessible and cost-effective trading environment.
Types of Zero-Cost Trading Platforms
Direct-to-Consumer Platforms
| Platform | Account Minimum | Available Assets | Premium Features Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Robinhood | $0 | Stocks, ETFs, Options, Crypto | $5/month |
| Webull | $0 | Stocks, ETFs, Options, Crypto | $2.99/month |
| Public | $0 | Stocks, ETFs, Crypto | No premium tier |
These platforms focus on providing a streamlined, mobile-first experience with basic trading functionality and educational resources. They typically generate revenue through payment for order flow, margin lending, and premium subscriptions.
Traditional Broker Platforms
| Platform | Account Minimum | Available Assets | Premium Features Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Charles Schwab | $0 | Stocks, ETFs, Options, Mutual Funds | $29.95/month |
| Fidelity | $0 | Stocks, ETFs, Options, Mutual Funds | $19.99/month |
| E*TRADE | $0 | Stocks, ETFs, Options, Mutual Funds | $24.99/month |
Traditional brokers offer more comprehensive services, including research tools, advisory services, and broader asset selection. Their zero-commission trading often comes with access to physical branches and more sophisticated trading platforms.
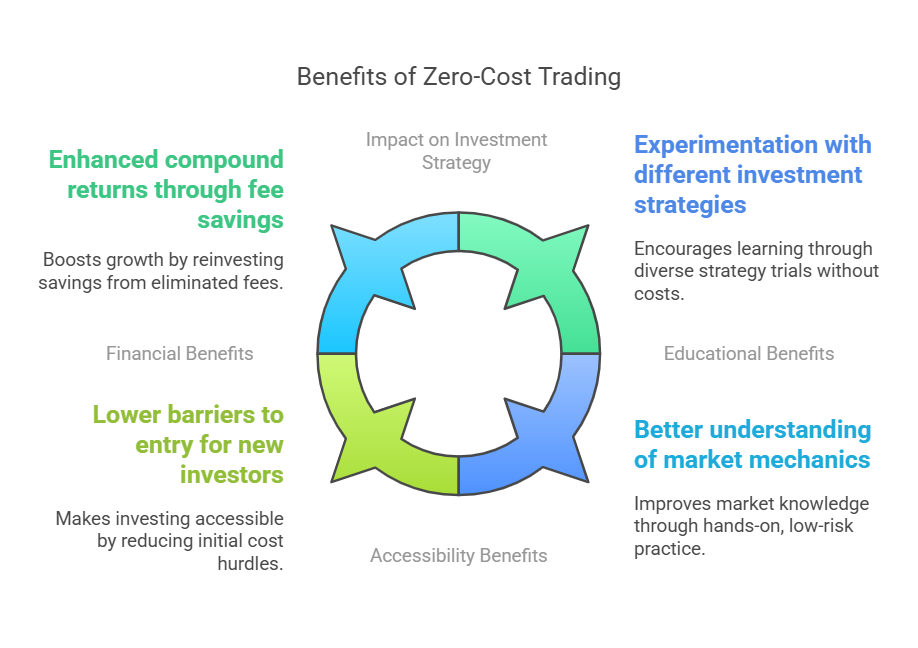
Benefits of Zero-Cost Trading
Financial Benefits
- Elimination of per-trade commission fees (typically $4.95-$9.95 savings per trade)
- Reduced minimum investment requirements
- More frequent portfolio rebalancing without cost penalties
- Enhanced compound returns through fee savings
Accessibility Benefits
- Lower barriers to entry for new investors
- Increased market participation opportunities
- Simplified investment process
- Greater flexibility in investment strategies
Educational Benefits
- Risk-free practice with smaller trade sizes
- Experimentation with different investment strategies
- Better understanding of market mechanics
- Enhanced focus on investment fundamentals rather than fee management
Challenges and Risks
Hidden Costs
The absence of direct trading commissions doesn’t eliminate all costs. Investors should be aware of:
- Payment for order flow execution quality impact
- Wider bid-ask spreads
- Foreign exchange fees
- Margin interest rates
- Premium feature costs
- Account maintenance fees
Behavioral Risks
The elimination of trading costs can lead to:
- Increased trading frequency without strategic justification
- Reduced due diligence before trades
- Greater susceptibility to market volatility
- Emotional decision-making
Platform Risks
Users of zero-cost trading platforms may face:
- Limited research tools
- Basic order types
- Platform downtime during high volatility
- Restricted access to certain investment products
- Limited customer service
How Zero-Cost Trading Works
Revenue Generation Methods
Zero-cost trading platforms generate revenue through various alternative channels:
- Payment for Order Flow (PFOF)
- Routing orders to market makers
- Average revenue of $0.00026 per share
- Represents 50-80% of revenue for major platforms
- Interest Income
- Margin lending (typically 2.5-8% annual interest)
- Cash sweep programs
- Securities lending
- Premium Services
- Advanced trading platforms
- Research tools
- Real-time data
- Professional analysis
Order Execution Process
- Order Placement
- User submits trade through platform
- Basic validation checks performed
- Routing
- Order sent to market makers
- Best execution price sought
- PFOF agreements applied
- Execution
- Trade completed at market price
- Confirmation sent to user
- Settlement process begins
Implementation Strategies
Platform Selection Criteria
- Trading volume requirements
- Asset class availability
- Research needs
- Technology preferences
- Customer service requirements
- Account protection levels
Account Optimization
- Utilizing available research tools
- Understanding order types
- Managing cash efficiently
- Maximizing platform features
- Monitoring execution quality
Risk Management
- Position sizing
- Diversification strategies
- Stop-loss implementation
- Regular portfolio review
- Performance tracking
Future Trends in Trading Fee Comparison
Technological Advancements
- Integration of artificial intelligence for trading suggestions
- Enhanced mobile trading capabilities
- Improved risk management tools
- Blockchain-based settlement systems
- Advanced analytics platforms
Market Evolution
- Increased competition among platforms
- Further industry consolidation
- New revenue model innovations
- Enhanced regulatory oversight
- Expanded asset class availability
User Experience Improvements
- Personalized trading interfaces
- Enhanced educational resources
- Improved social trading features
- Better integration with financial planning tools
- Advanced portfolio analysis capabilities
FAQs – Trading Fee Comparison
- What is zero-cost trading? Zero-cost trading refers to the ability to execute financial transactions without paying traditional broker commissions. While the direct trading fee is eliminated, other costs may still apply, such as spread costs or premium feature fees.
- How do zero-cost trading platforms make money? These platforms generate revenue through multiple channels, including payment for order flow, margin lending, premium subscriptions, cash sweep programs, and securities lending. They may also charge for additional services like research tools or advanced trading features.
- Are there any hidden costs in zero-cost trading? Yes, potential hidden costs include wider bid-ask spreads, payment for order flow execution quality impact, foreign exchange fees, margin interest rates, and premium feature costs. These costs may be less transparent than traditional commission fees.
- How does zero-cost trading affect market quality? The impact is mixed. While it has increased market participation and liquidity, some argue it has led to increased volatility and potentially poorer execution quality due to payment for order flow arrangements.
- What are the minimum requirements to start zero-cost trading? Most platforms require no minimum deposit to open an account, though some may require minimum balances for certain features. Users typically need to be 18 years or older and meet basic regulatory requirements.
- How does zero-cost trading compare to traditional brokerage services? Zero-cost platforms typically offer fewer research tools and customer service options but provide basic trading functionality without commissions. Traditional brokers often provide more comprehensive services but may charge for premium features.
- What types of assets can be traded commission-free? Common commission-free assets include stocks, ETFs, and some cryptocurrencies. Options trading may be commission-free but still incur per-contract fees. Some platforms also offer commission-free mutual funds.
- Is zero-cost trading suitable for all investors? While accessible to all, zero-cost trading may be more suitable for self-directed investors comfortable with digital platforms and basic research tools. Active traders and those requiring extensive research may prefer traditional platforms.
- How can investors maximize the benefits of zero-cost trading? Investors can maximize benefits by understanding platform features, utilizing available research tools, maintaining disciplined trading strategies, and being aware of potential hidden costs and risks.
- What regulatory considerations apply to zero-cost trading? Zero-cost trading platforms must comply with SEC regulations, FINRA rules, and other relevant financial regulations. They must maintain appropriate customer protections and meet best execution requirements.
Conclusion
The rise of zero-cost trading represents a fundamental shift in how retail investors access financial markets. While the elimination of commission fees has democratized investing and reduced barriers to entry, it has also created new challenges and considerations for investors. Understanding the actual costs, benefits, and risks of zero-cost trading platforms is essential for making informed investment decisions.
Looking ahead, the zero-cost trading landscape will likely continue to evolve with technological advances and changing regulatory requirements. As competition intensifies and platforms innovate, investors can expect improved services and features, though they must remain vigilant about understanding the actual costs and implications of their trading activities.
Success in this environment requires combining the benefits of commission-free trading with sound investment principles and risk management strategies.
For your reference, recently published articles include:
- Retire 10 Years Earlier: Revolutionary Financial Goal Planning Strategies
- The Perfect Portfolio: Secrets Of Best Asset Allocation Models Revealed
- Market Volatility Indicators Explained – Best Expert Guide
- How To Secure 8% Fixed Returns: The Ultimate Guide To Fixed Income Analytics
- ETF Performance Analysis – Best Advice For Successful Investing
………………………………………………..
Important Notice: The information in this article is for general and public information purposes only. It solely reflects Didi Somm’s or his Staff’s opinion, and no responsibility can be assumed for errors or omissions in the service’s contents. For details, please check the Disclaimer at the bottom of the homepage.

