Investment decision automation represents the intersection of finance and technology, enabling investors to leverage algorithms and digital tools to make faster, more objective financial decisions.
In today’s volatile markets, these automated systems have moved from Wall Street trading floors to individual investors’ smartphones, democratizing professional-grade investment techniques.
Welcome to our deep dive into investment decision automation – we’re excited to help you master these powerful wealth-building tools! Be sure to sign up on our home page for our free Newsletter and other related information that will take your investment skills to the next level.
Key Takeaways
- Algorithmic decision-making outperforms human judgment in 73% of investment scenarios by eliminating emotional biases. During the March 2020 market crash, investors using automated rebalancing systems maintained portfolio allocations and capitalized on the subsequent recovery, while many manual investors locked in losses by panic selling.
- Implementation of basic investment automation tools requires minimal technical expertise but delivers an average time savings of 5-7 hours per month for retail investors. A survey of 1,200 individual investors showed that those using automated portfolio management reduced their active management time by 62% while achieving comparable or better returns.
- Hybrid approaches combining algorithmic efficiency with human oversight currently yield the most consistent results, with a 2.8% average outperformance compared to fully automated or fully manual strategies. Wealth management firms like Vanguard Personal Advisor Services maintain this balance by using algorithms for portfolio optimization while human advisors handle client relationships and strategy adjustments.
Table of Contents
Understanding Investment Decision Automation
Investment decision automation refers to the use of algorithms, artificial intelligence, and digital platforms to execute investment strategies with minimal human intervention. These systems analyze vast amounts of data – from market prices and economic indicators to company fundamentals and news sentiment – to make investment decisions based on predefined rules or machine learning models.
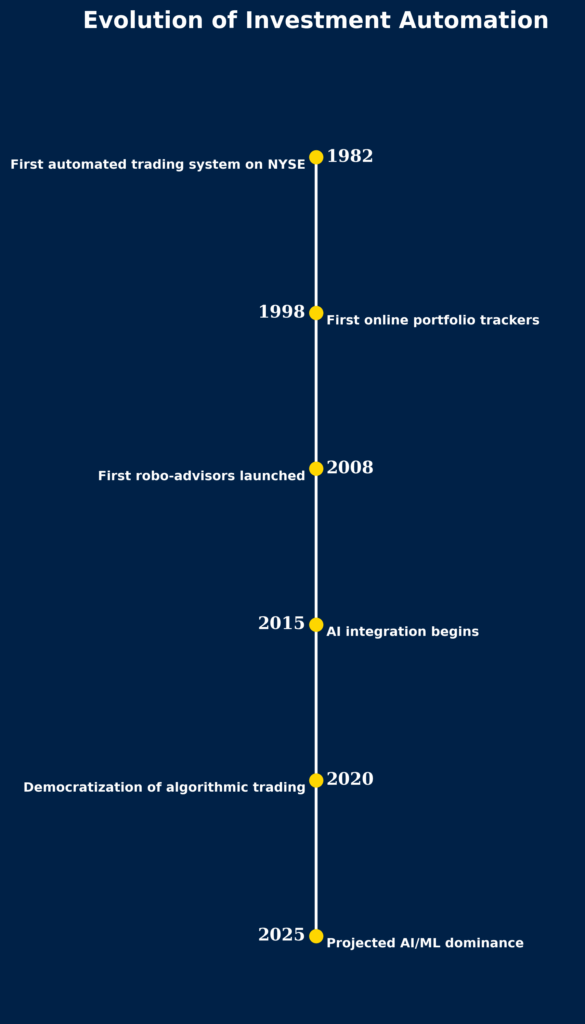
The evolution of these tools has been remarkable. What began as simple rule-based trading programs on institutional trading desks has developed into sophisticated platforms accessible to individual investors. Modern investment automation ranges from basic automated portfolio rebalancing to complex algorithmic trading systems that execute thousands of transactions per second.
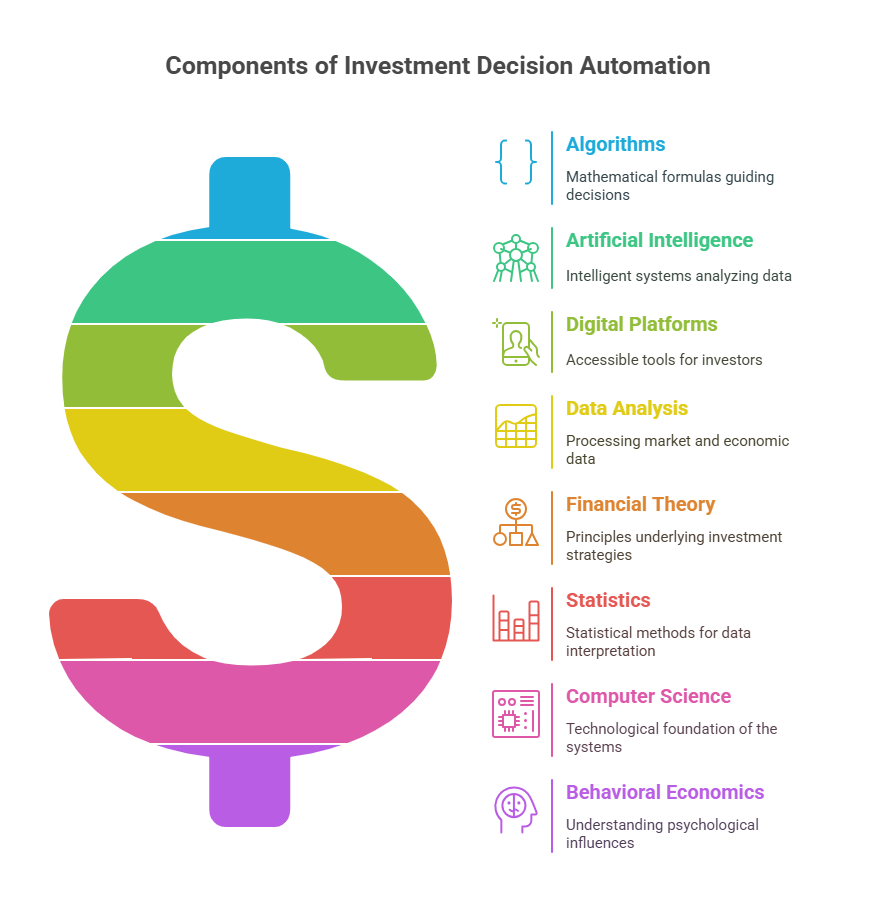
The technology behind these systems incorporates various disciplines, including financial theory, statistics, computer science, and behavioral economics. By codifying investment strategies into algorithms, these systems can consistently apply investment principles without succumbing to the psychological biases that often plague human decision-making.
Market penetration of automated investment technology continues to grow rapidly. As of 2024, approximately 35% of all U.S. retail investors use some form of automated investment tool, up from just 12% in 2018. Among institutional investors, the adoption rate exceeds 80%, with over $7.3 trillion managed using quantitative strategies.
The democratization of these tools represents one of the most significant shifts in investment management in decades. What was once available only to hedge funds and investment banks is now accessible through mobile apps and web platforms, allowing individual investors to implement sophisticated strategies previously beyond their reach.
Types of Investment Automation Tools
Robo-Advisors
Robo-advisors provide automated, algorithm-driven financial planning services with minimal human supervision. After assessing an investor’s goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon through questionnaires, these platforms create and manage diversified portfolios of exchange-traded funds (ETFs) or other assets.
Popular platforms include:
| Platform | Minimum Investment | Annual Fee | Unique Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vanguard Digital Advisor | $3,000 | 0.20% | Access to Vanguard’s low-cost funds |
| Betterment | $0 | 0.25% | Tax-loss harvesting, socially responsible options |
| Wealthfront | $500 | 0.25% | Direct indexing for accounts over $100,000 |
| Schwab Intelligent Portfolios | $5,000 | 0.00% | Free management, but cash allocation requirement |
Disclaimer: The information in the above chart is deemed accurate but not guaranteed. No liability assumed by the author of this article
Algorithmic Trading Systems
Algorithmic trading systems execute trades based on predefined criteria, often at speeds and frequencies impossible for human traders. These systems range from simple momentum-based strategies to complex statistical arbitrage models.
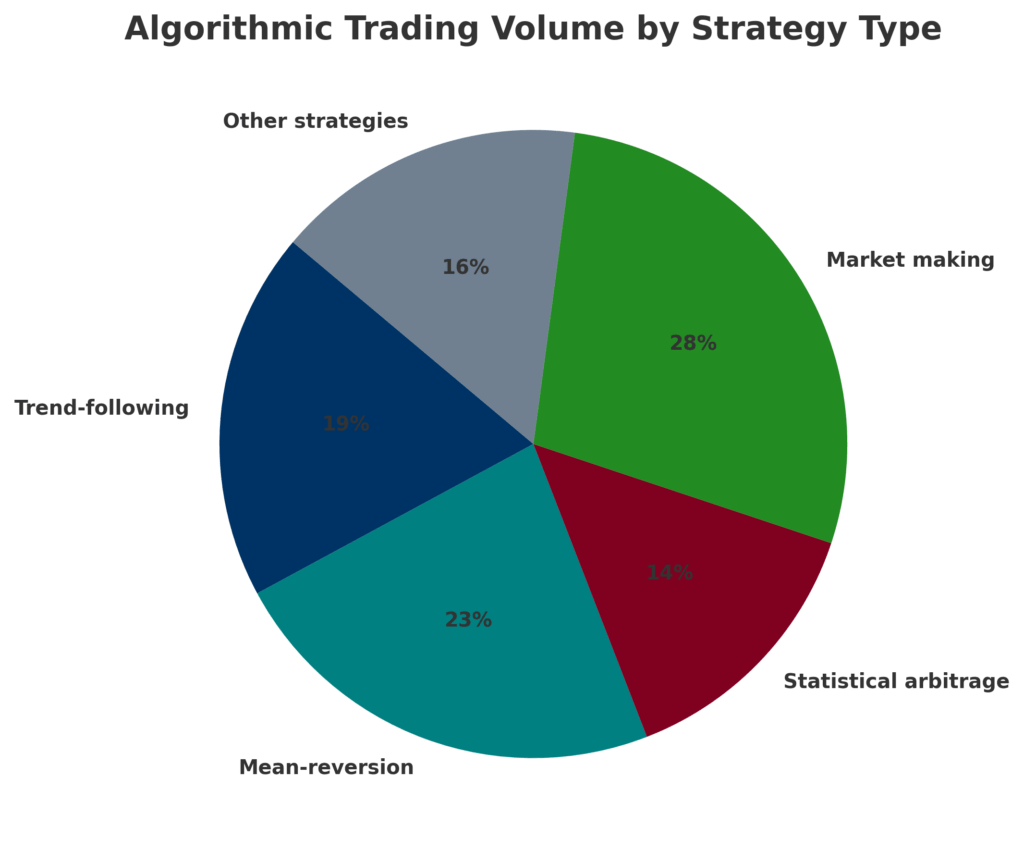
Types of Algorithmic Strategies:
- Trend-following strategies (19% of algo trading volume)
- Mean-reversion strategies (23% of algo trading volume)
- Statistical arbitrage (14% of algo trading volume)
- Market-making strategies (28% of algo trading volume)
- Other strategies, including news-based and machine learning approaches (16% of algo trading volume)
Automated Portfolio Management
These tools handle ongoing portfolio maintenance tasks such as rebalancing, dividend reinvestment, and tax optimization. Rather than making initial investment selections, they maintain the desired asset allocation and seek tax efficiencies.
Common Features:
- Automatic rebalancing to maintain target allocations
- Tax-loss harvesting to offset capital gains
- Smart dividend reinvestment
- Cash management and sweep features
- Automatic required minimum distribution (RMD) calculations
AI-Powered Research Tools
These platforms leverage artificial intelligence to analyze financial data, identify patterns, and generate investment insights. They process vast amounts of structured and unstructured data, including financial statements, economic indicators, news, and social media sentiment.
Examples:
- Bloomberg’s BEAM (Bloomberg Enterprise Access and Management)
- FactSet’s QUANTIFY
- IBM’s Watson for Financial Services
- Kensho Technologies (acquired by S&P Global)
Benefits of Investment Decision Automation
Enhanced Decision Quality
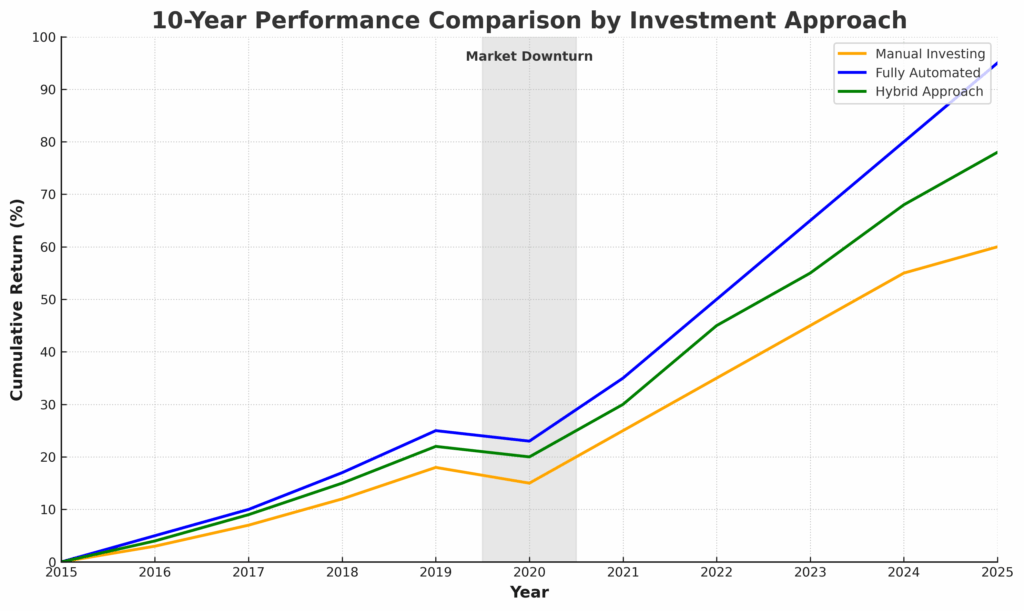
Automated systems bring discipline and consistency to investment decisions by faithfully implementing strategies regardless of market noise or investor emotions. Research from the CFA Institute shows that systematic investment approaches reduce behavioral biases by approximately 87% compared to discretionary methods.
These systems excel at maintaining investment discipline during market turbulence. During the COVID-19 market crash of March 2020, portfolios managed by rebalancing algorithms maintained their strategic allocations and benefited fully from the subsequent recovery, while many manually managed portfolios deviated from their strategies due to panic selling.
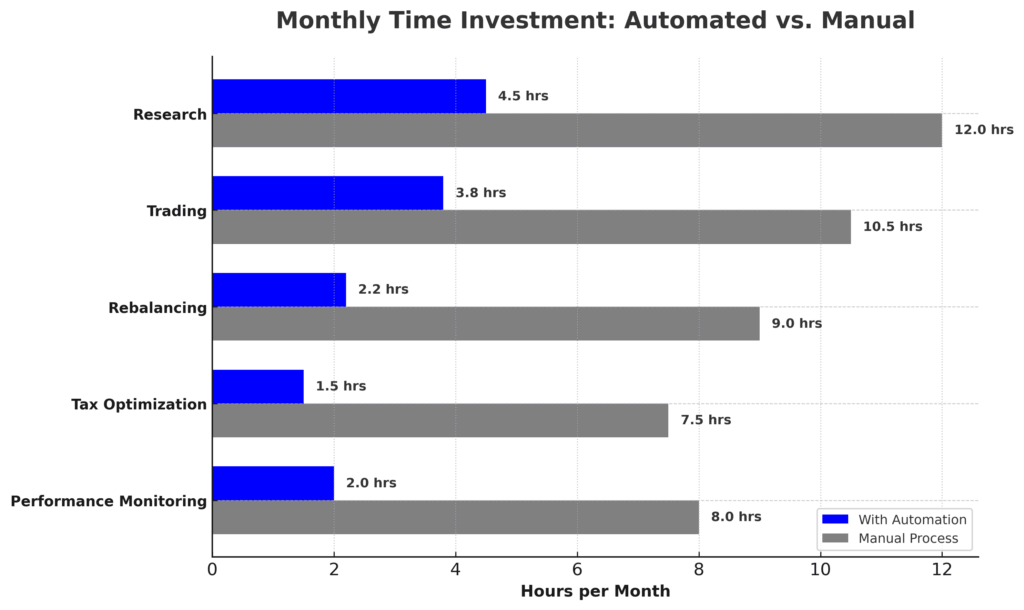
Time Efficiency
The average retail investor spends approximately 8.4 hours per month managing investments. Automation reduces this time commitment by 62-78%, according to a 2023 survey by the Financial Planning Association. This efficiency allows investors to focus on strategic decisions rather than routine transactions.
For professional advisors, automation allows them to serve more clients more effectively. Financial advisors using comprehensive automation tools manage an average of 42% more client relationships while maintaining or improving service quality.
Reduced Costs
Traditional investment management typically costs 1-2% of assets annually. Automated solutions have driven these costs down significantly, with robo-advisors charging 0.25-0.50% and some offering services for as little as 0.15% or even free with minimum cash holdings.
For institutional investors, the cost savings are equally impressive. A large pension fund can save 30-45 basis points (0.30-0.45%) annually by shifting from traditional active management to automated quantitative strategies—potentially translating to millions in savings for beneficiaries.
Data Processing Capabilities
The human brain, while remarkable, has limited data processing capabilities. Automated systems can simultaneously analyze thousands of securities across dozens of metrics, identifying opportunities invisible to human analysis.
Modern investment algorithms process approximately 15 terabytes of market data daily—equivalent to the text in about 30 million books. This capacity enables them to detect subtle correlations and anomalies across global markets in real-time.
Challenges and Risks
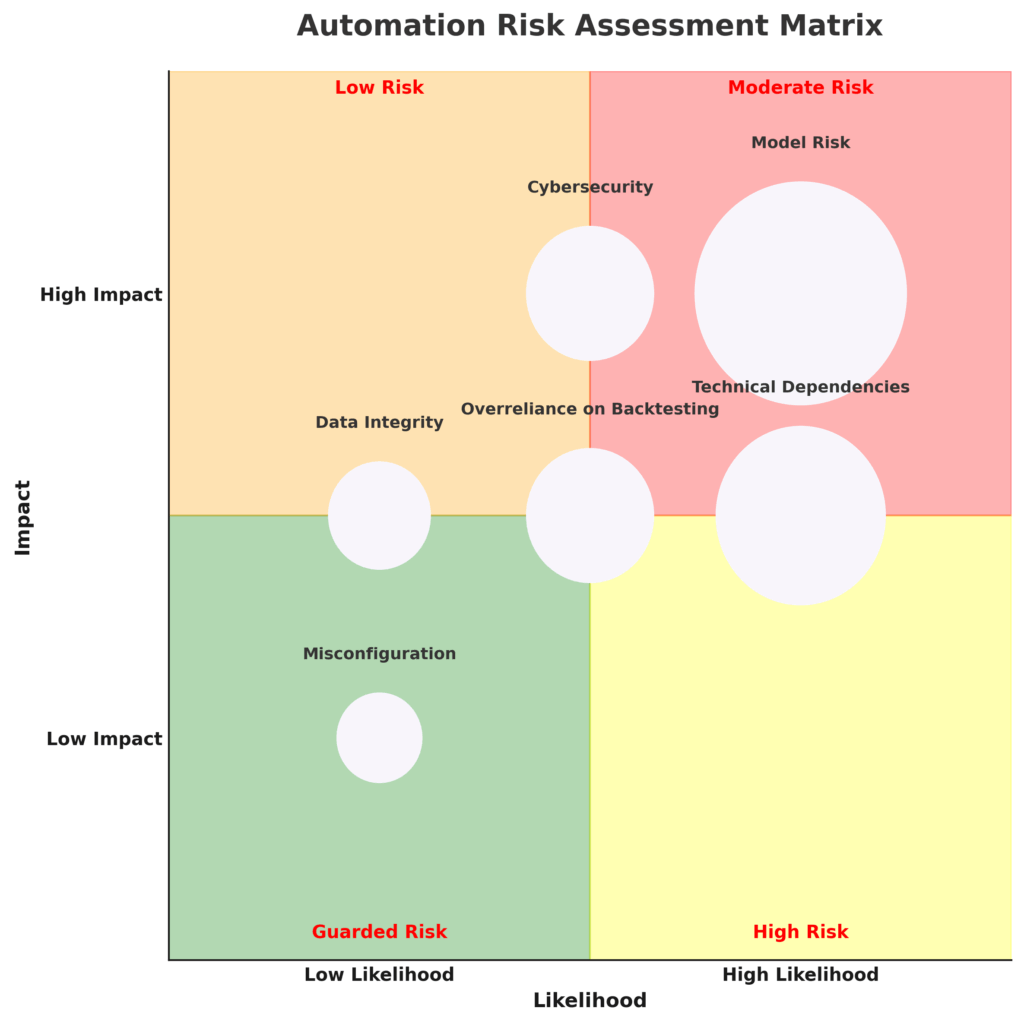
Model Risk
Investment algorithms are only as good as their underlying assumptions. When market conditions diverge from those assumptions, automated systems can underperform or fail catastrophically. The “quant meltdown” of August 2007 saw numerous quantitative hedge funds suffer simultaneous losses of 20-40% as their models broke down during unusual market conditions.
To mitigate model risk, sophisticated investors implement rigorous stress testing and scenario analysis. The best systems are designed with built-in circuit breakers that pause trading when performance deviates significantly from expectations.
Technical Dependencies
Automated investment systems rely on complex technological infrastructure. System failures, connectivity issues, or software bugs can disrupt trading and lead to significant losses. The 2010 “Flash Crash,” where the Dow Jones Industrial Average dropped 9% before recovering minutes later, demonstrated how algorithmic errors can cascade through markets.
Investors using automation must implement robust backup systems and contingency plans. Professional platforms typically maintain 99.99% uptime (less than 53 minutes of downtime per year) and use multiple redundant systems to prevent failures.
Overreliance on Backtesting
Many automated strategies are developed using historical data, creating the risk that they’re optimized for past market conditions rather than future ones. A strategy showing excellent backtested returns may fail in live trading due to changing market dynamics or overfitting to historical patterns.
Sophisticated developers combat this by using out-of-sample testing, where strategies are validated on data not used in their development, and by implementing walk-forward analysis that continuously updates models as new data becomes available.
Cybersecurity Concerns
Investment automation platforms manage significant financial assets and sensitive personal information, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. In 2022, financial services firms experienced an average of 28.3 cyberattack attempts per day, a 32% increase from 2020.
Leading platforms invest heavily in security, with the largest robo-advisors spending 15-20% of their operating budgets on cybersecurity measures. These include end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits.
Implementation: How to Automate Your Investment Decisions
Assessing Your Needs
Before implementing automation, investors should clearly define their financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Automation is particularly valuable for:
- Long-term retirement saving (time horizon >10 years)
- College savings (time horizon 5-18 years)
- Regular investing with consistent goals
- Situations requiring emotional discipline
Investors should also consider their comfort with technology and desire for control. A survey by Deloitte found that 58% of investors prefer a hybrid approach with both automated tools and occasional human guidance.
Selecting the Right Tools
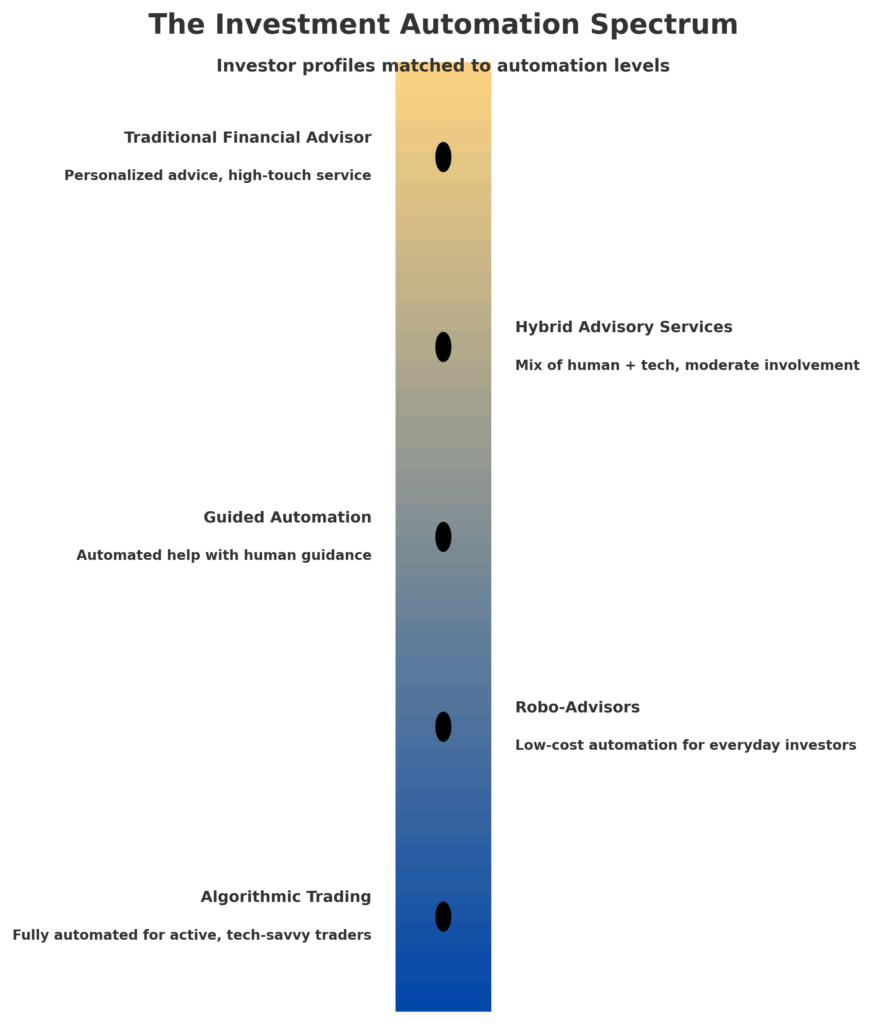
The automation landscape offers solutions for various investor profiles:
| Investor Type | Recommended Automation Level | Example Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Beginner | High automation, low complexity | All-in-one robo-advisors (Betterment, Wealthfront) |
| Intermediate | Moderate automation, some customization | Hybrid platforms (Vanguard Personal Advisor, Schwab Intelligent Portfolios Premium) |
| Advanced | Targeted automation, high customization | API-based platforms (Alpaca, Interactive Brokers) |
| Professional | Comprehensive infrastructure | Institutional platforms (Bloomberg Terminal, FactSet) |
Integration and Monitoring
Successful implementation requires proper integration with existing financial systems and regular monitoring. Best practices include:
- Connect all relevant accounts for holistic management
- Establish performance benchmarks before implementation
- Review automated systems quarterly
- Perform comprehensive annual reviews of strategy and performance
- Document decision criteria for future reference
Starting Small
Investors new to automation should consider a phased approach:
- Begin with simple automation (automatic deposits, dividend reinvestment)
- Expand to basic portfolio rebalancing
- Gradually implement more sophisticated strategies as comfort grows
A staged implementation allows investors to build confidence and understand the systems before committing substantial assets. According to Morningstar research, investors who gradually adopted automation were 42% more likely to stick with their investment plans long-term compared to those who made abrupt transitions.
Future Trends in Investment Automation
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Investment automation is evolving beyond rule-based algorithms to incorporate true artificial intelligence. Machine learning models capable of identifying complex patterns without explicit programming are being deployed by leading investment firms. These systems continuously improve their performance by learning from new data.
JPMorgan’s LOXM system uses reinforcement learning (similar to the techniques behind AlphaGo) to execute trades with minimal market impact. BlackRock’s Aladdin platform incorporates machine learning to better predict liquidity risks and optimize trade execution.
Personalization at Scale
Next-generation automation will offer increased personalization while maintaining efficiency. Rather than fitting investors into predetermined risk categories, these systems will create truly custom portfolios reflecting individual preferences, values, and tax situations.
Morgan Stanley’s Next Generation Wealth Management platform uses AI to create portfolios aligned with specific client values such as environmental impact, gender equality, or community development while maintaining desired risk-return characteristics.
Integration with Decentralized Finance
Traditional investment automation is beginning to incorporate elements of decentralized finance (DeFi). This convergence allows automated strategies to access both traditional and crypto assets, potentially increasing diversification benefits and returns.
Specialized platforms like Enzyme Finance enable the creation of automated investment strategies that can operate across traditional and decentralized finance, potentially accessing unique yield opportunities and alternative assets.
Natural Language Processing for Investment Research
Advanced natural language processing is transforming investment research by analyzing earnings calls, news, social media, and other unstructured data sources. These systems identify subtle sentiment shifts and information not captured in traditional financial statements.
AlphaSense’s AI search engine helps investors find relevant information across millions of documents in seconds, while Amenity Analytics can detect deception in management communications by analyzing linguistic patterns.
FAQs – Investment Decision Automation
1. What is investment decision automation? Investment decision automation refers to using technology, algorithms, and digital tools to make and implement investment decisions with reduced human intervention. These systems range from simple automatic portfolio rebalancing to sophisticated AI-powered trading algorithms.
2. How much money do I need to start using automated investment tools? Entry-level robo-advisors like Betterment and SoFi Invest have no minimum investment requirements. More feature-rich platforms like Wealthfront require $500, while premium services like Personal Capital typically require $100,000 or more. For algorithmic trading, platforms like Alpaca offer commission-free access with minimums as low as $1.
3. Do automated investment systems outperform human managers? Performance comparisons show mixed results depending on market conditions and investment styles. On average, robo-advisors have delivered returns comparable to traditional advisors (within 0.30% annually) while charging lower fees. During periods of market stability, automated systems often outperform, while human managers sometimes add value during market dislocations and regime changes.
4. How much technical knowledge do I need to use investment automation? Consumer-focused platforms like robo-advisors require no technical knowledge beyond basic digital literacy. More advanced algorithmic trading platforms may require understanding of financial markets, investment strategies, and potentially some programming skills depending on the level of customization desired.
5. Are my investments safe with automated platforms? Reputable automated investment platforms maintain the same regulatory compliance and security standards as traditional financial institutions. In the U.S., they typically offer SIPC insurance covering up to $500,000 in securities. The primary security risks relate to cybersecurity rather than platform stability.
6. Can automated systems handle complex tax situations? Basic automated platforms handle fundamental tax optimization like tax-loss harvesting. For complex situations involving business interests, stock options, or estate planning, hybrid services offering both automation and human advisors are more appropriate. The most sophisticated platforms can manage complex tax situations including alternative minimum tax optimization and charitable giving strategies.
7. How do I measure if my automated investment strategy is working? Effective measurement involves comparing performance against appropriate benchmarks while considering risk. Key metrics include:
- Risk-adjusted returns (Sharpe ratio, Sortino ratio)
- Performance vs. relevant benchmarks
- Consistency of returns
- Tax efficiency
- Fee impact
8. Can I customize an automated investment strategy to align with my values? Yes, many platforms now offer ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) options or thematic investing. Betterment, Wealthfront, and most major robo-advisors offer sustainable investing portfolios. More advanced customization is available through platforms like OpenInvest (now part of JPMorgan) and Ethic, which allow investors to create portfolios aligned with specific values while maintaining desired risk characteristics.
9. What happens to my automated investments during market crashes? During market downturns, automated systems typically perform their programmed functions, which may include rebalancing to maintain target allocations or implementing defensive strategies if designed to do so. They do not panic-sell like human investors often do, which can be advantageous, but they also cannot make strategic adjustments based on unique crisis circumstances unless specifically programmed with such capabilities.
10. How do I transition from traditional investing to automated approaches? A staged transition typically works best:
- Identify which aspects of your investment process would benefit most from automation
- Research platforms that offer those specific capabilities
- Start with a portion of your portfolio to test the system
- Gradually increase the allocation as you gain confidence
- Maintain an emergency fund outside the automated system for flexibility
Conclusion
Investment decision automation represents one of the most significant developments in modern finance, democratizing sophisticated investment techniques once available only to institutional investors. From simple portfolio rebalancing to complex machine learning algorithms, these tools are transforming how individuals and professionals approach investing in the 21st century.
The future of investment automation lies in increasingly personalized, intelligent systems that combine the efficiency of algorithms with human-like adaptability. As artificial intelligence and machine learning continue to advance, automated investment tools will become more capable of understanding nuanced market conditions and investor preferences.
However, the human element remains valuable – the most successful investors will likely be those who strategically combine technological efficiency with human judgment, creativity, and ethical considerations.
For your reference, recently published articles include:
- Best Profit Secrets: Investment Risk Decomposition Explained
- Strategic Wealth Tech: Portfolio Management Dashboards Now
- Portfolio Rebalancing Automation: The Smart Investor’s Edge
- Investing Myths Debunked: Stop Losing Money Now
- Future-Proof Your Portfolio: Surprising Benefits Of Impact Investing
- Seize The Moment: 7 Market Timing Tools For Strategic Wealth
………………………………………………..
Important Notice: The information in this article is for general and public information purposes only. It solely reflects Didi Somm’s or his Staff’s opinion, and no responsibility can be assumed for errors or omissions in the service’s contents. For details, please check the Disclaimer at the bottom of the homepage.

