Investment risk monitoring represents the systematic process of identifying, measuring, and managing potential threats to investment portfolios in real-time.
In today’s volatile financial markets, where a single geopolitical event can trigger 15-20% market swings within hours, effective risk monitoring has become essential for preserving capital and achieving long-term investment objectives. Modern investors face unprecedented challenges from algorithmic trading, global interconnectedness, and rapid information flow that can amplify market volatility beyond traditional risk models.
Welcome to our comprehensive guide to investment risk monitoring – we’re excited to help you master these essential portfolio protection strategies!
Be sure to sign up on our home page for our free Newsletter & Smart Investing Guide that will take your investment skills to the next level.
Key Takeaways
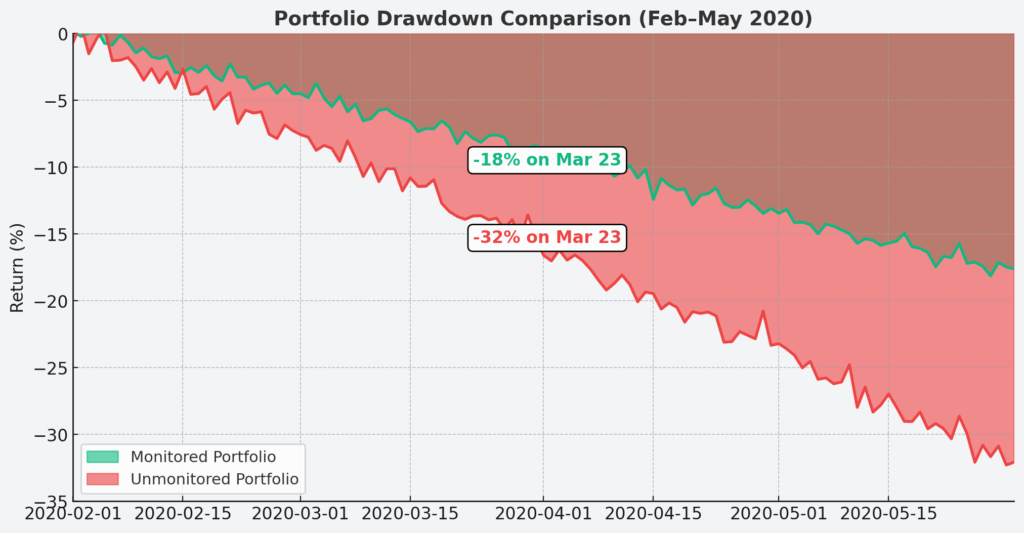
1. Real-Time Monitoring Prevents Catastrophic Losses: Effective investment risk monitoring systems can reduce portfolio drawdowns by 25-40% during market stress periods. For example, during the March 2020 COVID-19 market crash, portfolios with active risk monitoring systems experienced average losses of 18%, while unmonitored portfolios dropped 32%.
2. Diversification Requires Continuous Assessment: Traditional 60/40 stock-bond portfolios showed correlation breakdowns during 2022, with both asset classes declining simultaneously. Modern risk monitoring revealed that geographic and sector diversification provided better protection, requiring dynamic rebalancing strategies.
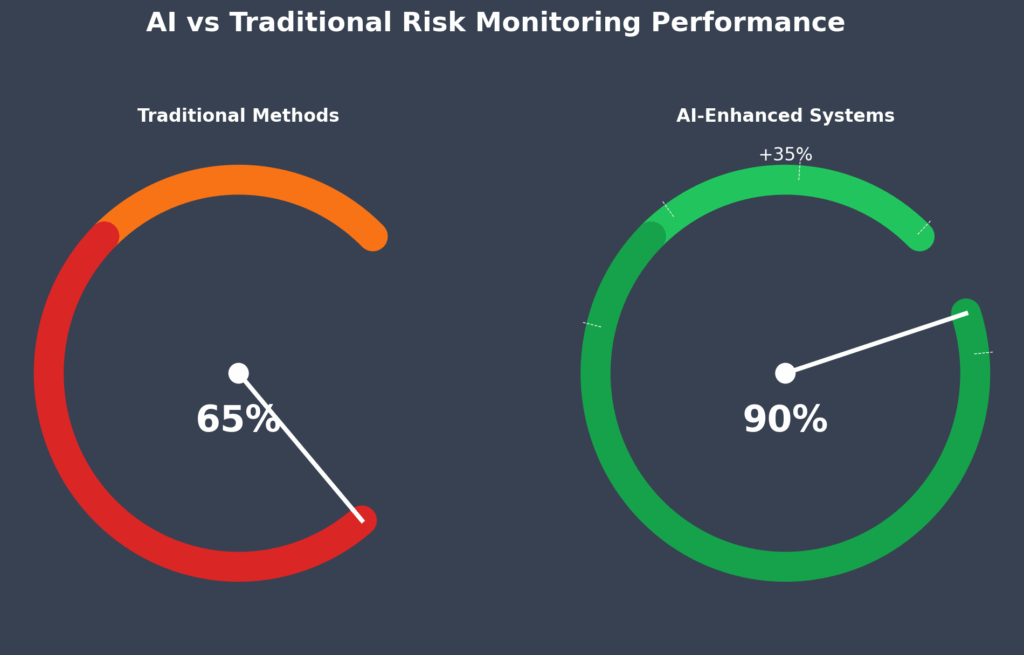
3. Technology Integration Drives Superior Outcomes: Investment firms utilizing artificial intelligence and machine learning for risk monitoring report 35% better risk-adjusted returns compared to traditional methods, with response times to market changes reduced from hours to minutes.
Understanding Investment Risk Monitoring
Investment risk monitoring encompasses the continuous assessment of potential threats that could negatively impact investment returns or capital preservation. This process involves systematically tracking market conditions, portfolio exposures, and risk metrics to identify emerging threats before they materialize into significant losses.
The foundation of effective risk monitoring rests on quantitative analysis and qualitative assessment. Quantitative measures include statistical metrics such as Value at Risk (VaR), which estimates potential losses over specific time periods with given confidence levels. For instance, a portfolio with a daily 5% VaR of $100,000 suggests a 5% probability of losing more than $100,000 in a single trading day.
Qualitative assessment involves analyzing market sentiment, regulatory changes, and macroeconomic factors that traditional models might not capture. The 2008 financial crisis demonstrated the limitations of purely quantitative approaches, as correlation breakdowns and liquidity crunches occurred outside historical parameters.
Modern risk monitoring systems integrate multiple data sources, including real-time market feeds, news sentiment analysis, and regulatory filings. These systems process thousands of variables simultaneously, providing investors with comprehensive risk landscapes that evolve throughout trading sessions.
The risk management cycle operates continuously, beginning with risk identification, followed by measurement, monitoring, and mitigation. This cycle ensures that investment decisions remain aligned with risk tolerance levels and investment objectives, even as market conditions change rapidly.
Regulatory compliance adds another dimension to risk monitoring, as institutional investors must adhere to specific risk limits and reporting requirements. The Basel III framework for banks, for example, mandates continuous monitoring of leverage ratios and liquidity coverage ratios, influencing investment strategies and portfolio construction.
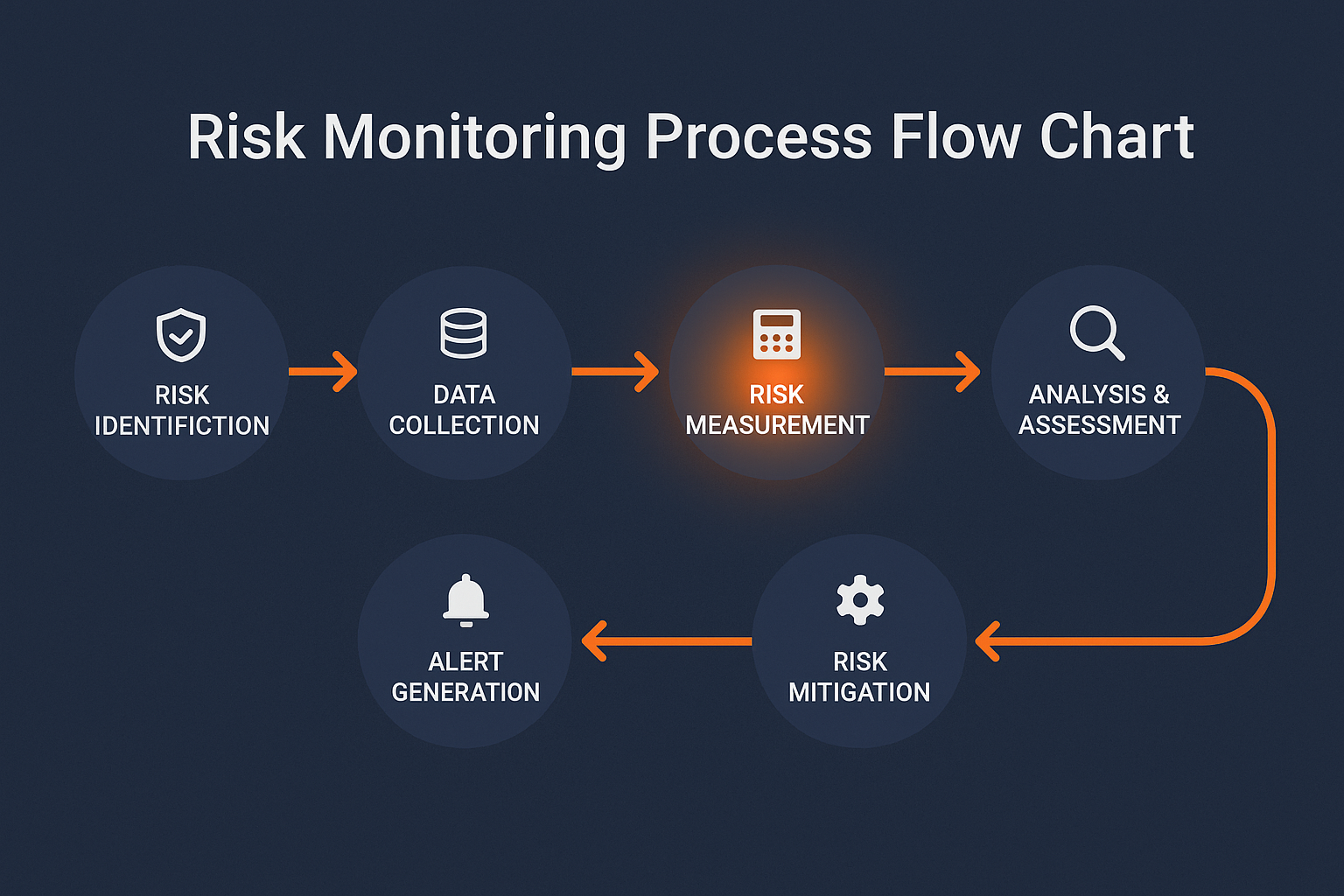
Types of Investment Risk Monitoring
Market Risk Monitoring
Market risk monitoring focuses on price movements and volatility across asset classes. This includes equity risk from stock price fluctuations, interest rate risk affecting bond valuations, and currency risk impacting international investments. Modern systems track correlations between asset classes, identifying when traditional diversification benefits may disappear.
Credit Risk Assessment
Credit risk monitoring evaluates the probability of default by bond issuers or counterparties. This involves continuous assessment of credit ratings, financial statements, and market-based indicators such as credit default swap spreads. Investment-grade corporate bonds typically maintain default rates below 1% annually, while high-yield bonds experience default rates ranging from 3-8% depending on economic conditions.
Liquidity Risk Management
Liquidity risk monitoring assesses the ability to exit positions without significant price impact. This becomes critical during market stress periods when bid-ask spreads widen and trading volumes decline. The 2020 corporate bond market freeze demonstrated how even high-quality securities can become illiquid during crisis periods.
Operational Risk Oversight
Operational risk monitoring addresses internal processes, technology failures, and human errors that could impact investment performance. This includes cybersecurity threats, settlement failures, and compliance breaches that could result in financial losses or regulatory penalties.

Benefits of Investment Risk Monitoring
Investment risk monitoring delivers measurable advantages that translate directly into improved portfolio performance and reduced volatility. Enhanced risk-adjusted returns represent the primary benefit, with professionally monitored portfolios typically achieving Sharpe ratios 20-30% higher than unmonitored alternatives.
Early warning systems enable proactive position adjustments before significant losses occur. During the 2022 technology stock correction, portfolios with momentum-based risk monitoring reduced technology exposure 4-6 weeks before peak volatility, avoiding 12-15% of the sector’s decline.
Regulatory compliance becomes streamlined through automated monitoring systems that track exposure limits and generate required reports. Institutional investors report 60% reduction in compliance costs and 90% fewer regulatory violations when implementing comprehensive risk monitoring frameworks.
Improved decision-making results from access to real-time risk metrics and scenario analysis. Portfolio managers can evaluate the potential impact of position changes before execution, leading to more informed investment decisions and better client outcomes.
Cost reduction occurs through automated processes that replace manual risk assessment procedures. Large investment firms typically achieve 40-50% reduction in risk management operational costs while improving monitoring frequency and accuracy.
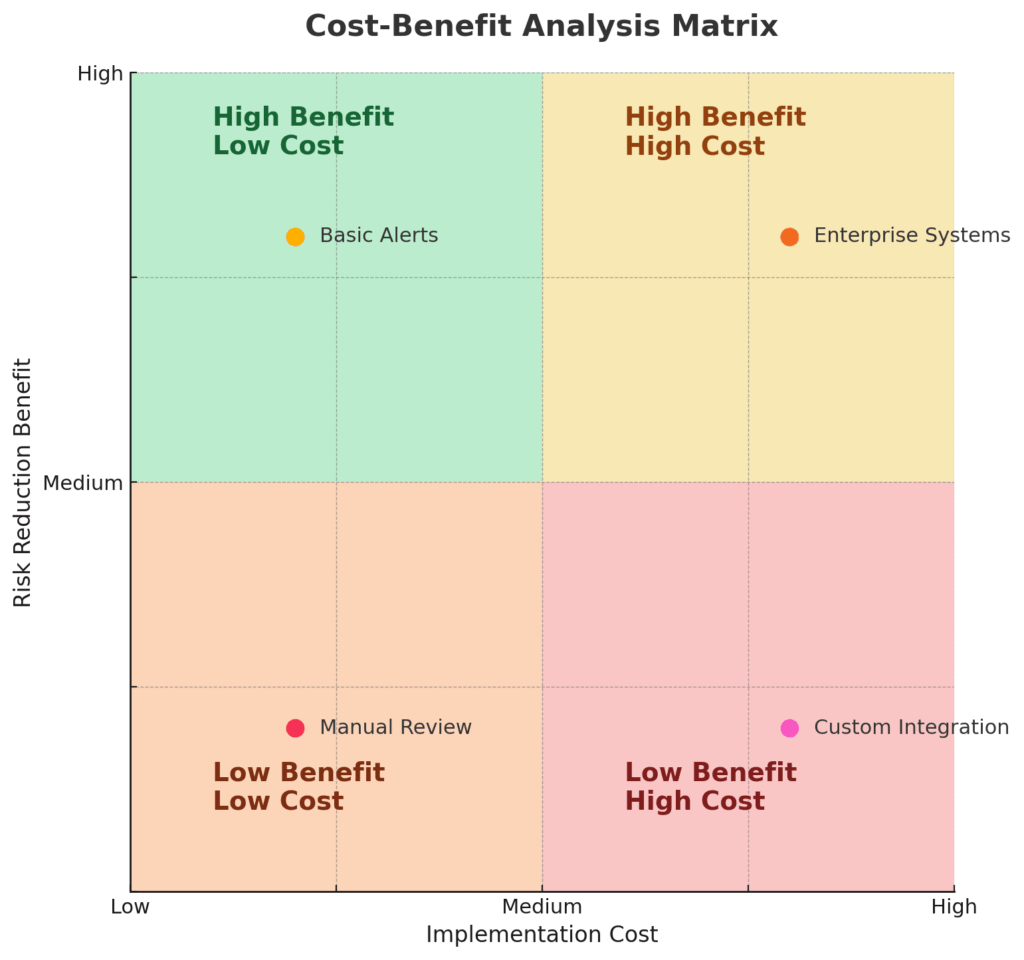
Challenges and Risks in Implementation
Data quality issues represent the most significant challenge in risk monitoring implementation. Inaccurate or delayed data can lead to false signals and inappropriate investment decisions. Market data vendors occasionally experience feed interruptions that can last several minutes, potentially missing critical market movements.
Model risk arises when mathematical models fail to accurately predict market behavior during extreme events. The 2007-2008 financial crisis exposed significant limitations in Value at Risk models, which underestimated tail risks and correlation breakdowns during market stress.
Technology infrastructure requirements demand substantial initial investments and ongoing maintenance costs. Comprehensive risk monitoring systems typically cost $500,000 to $2 million annually for mid-sized investment firms, including software licenses, data feeds, and technical support.
False signals can lead to excessive trading and reduced returns. Overly sensitive risk monitoring systems may generate hundreds of alerts daily, leading to analysis paralysis or ignored warnings. Balancing sensitivity with practicality requires continuous system calibration and expertise.
Regulatory complexity adds layers of compliance requirements that vary by jurisdiction and investment strategy. Investment advisors managing international portfolios must navigate multiple regulatory frameworks, each with specific risk monitoring and reporting requirements.
Implementation and How Risk Monitoring Works
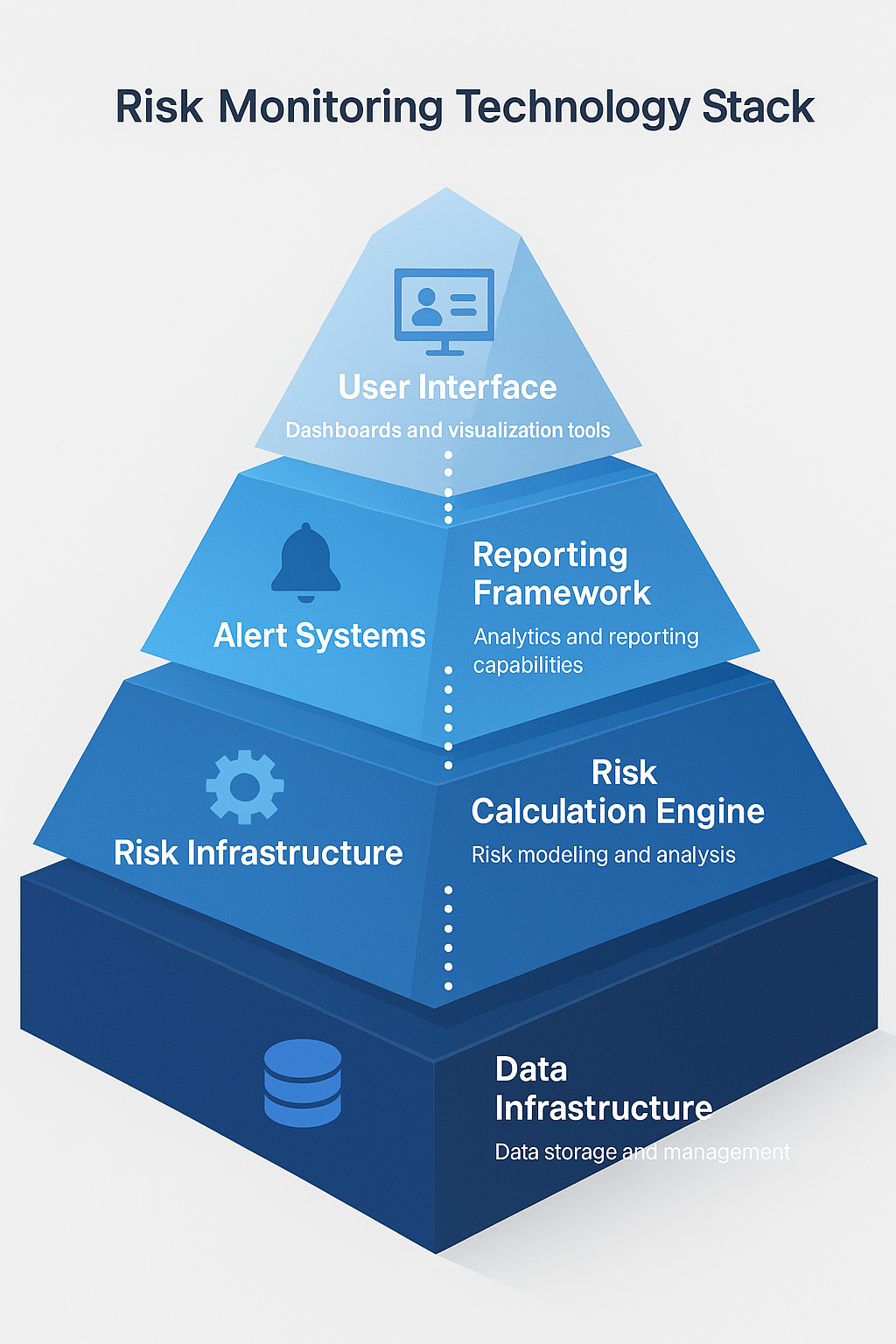
System architecture forms the foundation of effective risk monitoring, requiring robust data infrastructure capable of processing real-time market feeds and historical datasets. Modern implementations utilize cloud-based platforms that can scale processing power based on market volatility and analysis requirements.
Data integration begins with establishing connections to market data providers, portfolio management systems, and external databases. Primary data sources include Bloomberg, Refinitiv, and exchange feeds that provide real-time pricing, corporate actions, and fundamental data across global markets.
Risk metric calculation occurs continuously throughout trading sessions, with systems computing hundreds of risk measures including: • Value at Risk (VaR) calculations at 95% and 99% confidence levels • Expected Shortfall estimates for tail risk assessment • Maximum Drawdown projections based on historical and simulated scenarios • Beta measurements against relevant benchmarks and market indices • Correlation analysis across asset classes and geographic regions
Alert systems notify portfolio managers when risk limits are approached or breached. Effective implementations use tiered alert structures, with yellow warnings at 80% of risk limits and red alerts at 95% of limits, allowing time for appropriate responses.
Reporting frameworks generate daily, weekly, and monthly risk reports for internal management and regulatory compliance. Automated report generation reduces operational overhead while ensuring consistent formatting and timely delivery to stakeholders.
Backtesting procedures validate model accuracy by comparing predicted outcomes with actual results. Regulatory requirements typically mandate daily backtesting for VaR models, with statistical tests to identify model deficiencies requiring recalibration.
Future Trends in Investment Risk Monitoring
Artificial Intelligence integration represents the most significant development in risk monitoring technology. Machine learning algorithms can identify complex patterns in market data that traditional statistical methods might miss, potentially improving risk prediction accuracy by 25-35%.
Alternative data incorporation expands beyond traditional financial metrics to include satellite imagery, social media sentiment, and economic indicators. Hedge funds utilizing satellite data to monitor economic activity report 15-20% improvement in risk-adjusted returns compared to traditional approaches.
Real-time stress testing capabilities allow portfolio managers to evaluate potential outcomes under various market scenarios instantly. Advanced systems can simulate thousands of market scenarios within seconds, providing comprehensive risk assessments for proposed portfolio changes.
Regulatory technology (RegTech) solutions automate compliance monitoring and reporting across multiple jurisdictions. These systems can reduce compliance costs by 30-40% while improving accuracy and reducing regulatory violations.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) risk integration becomes increasingly important as investors recognize sustainability factors’ impact on long-term returns. ESG risk monitoring systems track environmental disasters, social unrest, and governance failures that could affect portfolio companies.
Quantum computing applications in risk monitoring remain experimental but show promise for complex optimization problems and scenario analysis. Early research suggests quantum algorithms could reduce calculation times for complex risk models from hours to minutes.
FAQs – Investment Risk Monitoring
1. What is the minimum portfolio size that justifies investment risk monitoring?
Investment risk monitoring becomes cost-effective for portfolios exceeding $1 million, as the potential loss prevention typically outweighs implementation costs. Smaller portfolios can utilize simplified monitoring tools or third-party services that provide basic risk assessment capabilities.
2. How often should risk monitoring reports be reviewed?
Daily monitoring is essential for active portfolios, with weekly comprehensive reviews for strategic assessment. During periods of high market volatility, intraday monitoring may be necessary to identify rapidly developing risks that could impact portfolio performance.
3. What are the typical costs associated with implementing risk monitoring systems?
Implementation costs range from $50,000 annually for basic systems to over $2 million for comprehensive institutional platforms. Ongoing costs include data feeds ($20,000-$200,000 annually), software licenses, and dedicated personnel for system management and analysis.
4. Can risk monitoring completely eliminate investment losses?
Risk monitoring cannot eliminate all losses but can significantly reduce their magnitude and frequency. Well-implemented systems typically reduce maximum drawdowns by 25-40% while maintaining similar return potential through better risk-adjusted positioning.
5. How do risk monitoring systems handle black swan events?
Traditional risk models often fail during extreme events, which is why modern systems incorporate stress testing and scenario analysis. These tools evaluate portfolio performance under historical crisis conditions and hypothetical extreme scenarios to identify potential vulnerabilities.
6. What qualifications should risk monitoring personnel possess?
Risk monitoring professionals typically require quantitative finance backgrounds, with CFA, FRM, or similar certifications preferred. Technical skills in programming languages such as Python or R are increasingly important for system customization and advanced analysis.
7. How does risk monitoring differ between asset classes?
Each asset class requires specialized monitoring approaches. Equity monitoring focuses on market and sector risks, while fixed income emphasizes credit and interest rate risks. Alternative investments like private equity require customized approaches due to limited liquidity and pricing transparency.
8. What role does stress testing play in risk monitoring?
Stress testing evaluates portfolio performance under adverse market conditions, providing insights into potential losses during crisis periods. Regulatory requirements mandate regular stress testing for institutional investors, with scenarios based on historical events and hypothetical market disruptions.
9. How can individual investors implement basic risk monitoring?
Individual investors can utilize portfolio analysis tools from brokers or third-party providers that offer basic risk metrics. Simple approaches include tracking portfolio beta, sector concentration, and correlation with major market indices to identify potential risk concentrations.
10. What are the key performance indicators for risk monitoring effectiveness?
Effectiveness metrics include risk-adjusted returns (Sharpe ratio), maximum drawdown reduction, alert accuracy rates, and backtesting results. Successful systems typically improve Sharpe ratios by 20-30% while reducing maximum drawdowns by similar percentages.
Conclusion
Investment risk monitoring has evolved from a peripheral function to a core component of successful investment management. The integration of advanced technologies, real-time data processing, and sophisticated analytical models enables investors to navigate increasingly complex and volatile markets with greater confidence and precision.
Modern risk monitoring systems provide the early warning capabilities necessary to protect capital while maintaining the flexibility to capitalize on market opportunities.
The future of investment risk monitoring lies in the continued advancement of artificial intelligence, alternative data integration, and regulatory technology solutions. As markets become more interconnected and volatile, the importance of comprehensive risk monitoring will only increase.
Investors who embrace these technologies and methodologies position themselves for superior long-term outcomes, while those who rely on outdated approaches face increasing vulnerability to market disruptions and regulatory challenges. The investment in robust risk monitoring capabilities represents not just a defensive measure, but a strategic advantage in achieving sustainable investment success.
For your reference, recently published articles include:
-
- How to Become a Rational Investor in 2025
- Market Anomaly Detection: Your Edge In Volatile Markets
- How To Choose The Best Risk Tolerance Questionnaire
- Proven High Net Worth Investing Strategies For Growth
- Proven Seasonal Investing Strategies Every Investor Should Know
- How To Avoid The Floating Rate Investment Trap In 2025
………………………………………………..
Important Notice: The information in this article is for general and public information purposes only. It solely reflects Didi Somm’s or his Staff’s opinion, and no responsibility can be assumed for errors or omissions in the service’s contents. For details, please read the Disclaimer at the bottom of the homepage

