Investment risk decomposition is the systematic process of breaking down portfolio risks into distinct, quantifiable components to enable more precise risk management and portfolio optimization.
In today’s volatile financial markets, mastering risk decomposition techniques has become essential for investment professionals seeking to understand the true drivers of portfolio performance and vulnerability.
Welcome to our deep dive into investment risk decomposition – we’re excited to help you master these powerful portfolio analysis techniques! Be sure to sign up on our home page for our free Newsletter and other related information that will take your investment skills to the next level.
Key Takeaways
- Risk decomposition reveals hidden correlations and vulnerabilities that might otherwise remain undetected in aggregate risk metrics. For example, during the 2020 COVID market crash, portfolios with seemingly diversified assets experienced simultaneous drawdowns because underlying macro factors (pandemic economic impact) affected multiple asset classes simultaneously.
- Modern decomposition tools now incorporate machine learning algorithms that can identify non-linear risk relationships beyond traditional factor models, allowing investment managers to detect emerging risks before they materialize in market prices. JPMorgan’s DeepAnalytics platform reportedly identified sector rotation risks 18 days earlier than traditional methods during the 2022 inflation spike.
- Implementation of professional decomposition tools typically increases risk-adjusted returns by 0.8-1.2% annually by enabling more precise risk budgeting and tactical allocation adjustments. BlackRock’s systematic equity funds utilizing advanced decomposition methodologies outperformed their benchmarks by 0.94% on average between 2018-2023 with lower volatility.
Table of Contents
Understanding Investment Risk Decomposition
Investment risk decomposition is a methodical approach to dissecting and analyzing the various components of risk within an investment portfolio. Unlike simple volatility measures, decomposition techniques parse total risk into its constituent parts, allowing investors to identify, measure, and manage specific risk factors with precision.
At its core, risk decomposition stems from modern portfolio theory but extends far beyond basic diversification principles. It enables investors to understand not just how much risk exists in a portfolio, but specifically where that risk originates, how different risk factors interact, and which components contribute most significantly to potential downside scenarios.
The fundamental premise of risk decomposition is that investment returns and their associated risks can be attributed to various systematic factors, idiosyncratic elements, and their interactions. By isolating these components, investors gain clearer insights into their exposure to specific economic conditions, market dynamics, and security-specific risks.
Contemporary investment risk decomposition has evolved significantly with advances in financial mathematics, computing power, and data science. Today’s professional tools incorporate sophisticated statistical techniques, factor models, and machine learning algorithms to provide increasingly granular and forward-looking risk insights.
Investment professionals utilize risk decomposition to align portfolios with intended risk profiles, optimize diversification benefits, implement more targeted hedging strategies, and ultimately achieve more consistent risk-adjusted returns across varying market conditions.
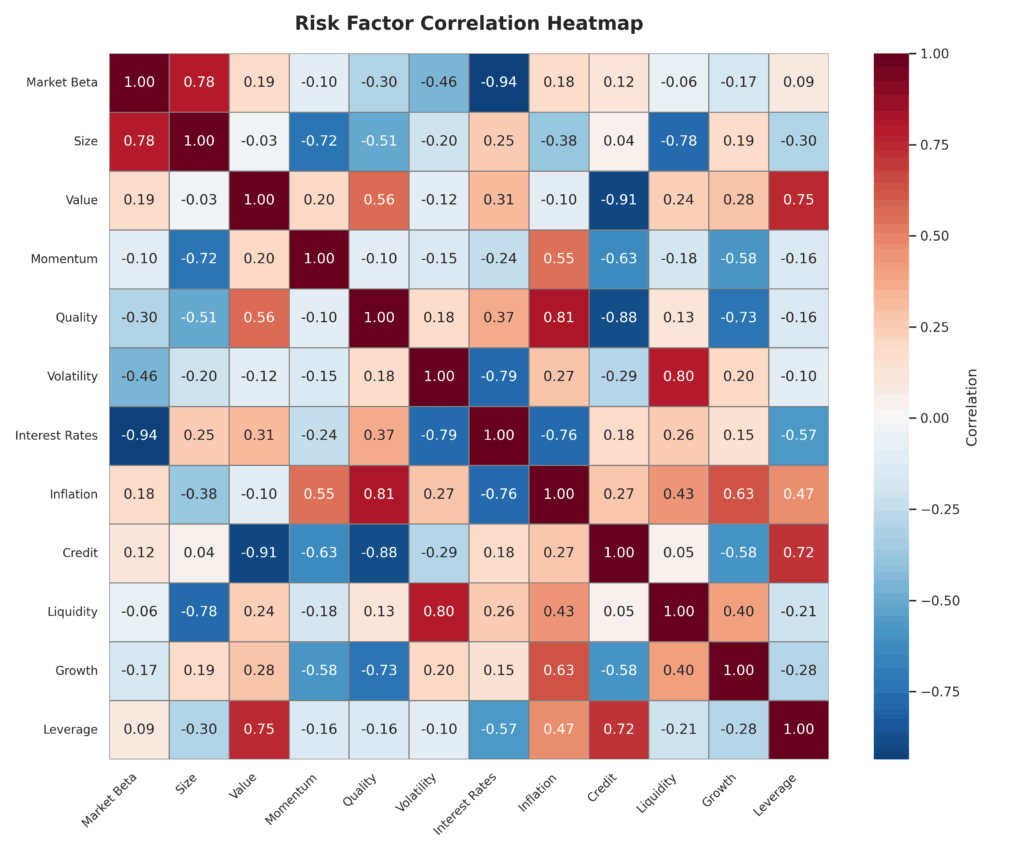
Types of Risk Decomposition Methodologies
Traditional Factor-Based Decomposition
Factor-based decomposition breaks down portfolio risk according to exposure to common risk factors such as:
- Market beta (systematic market risk)
- Size (small vs. large capitalization)
- Value/growth characteristics
- Momentum factors
- Quality metrics
- Volatility factors
Traditional factor models like the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), Fama-French Three-Factor Model, and its extensions form the foundation of this approach. These models typically explain 70-85% of portfolio return variation in developed markets.
Statistical Decomposition
Statistical methods focus on identifying risk components without predetermined economic interpretations:
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA): Identifies uncorrelated risk factors that explain maximum variance
- Independent Component Analysis (ICA): Separates statistically independent risk sources
- Cluster Analysis: Groups assets with similar risk characteristics
- Minimum Correlation Algorithm: Identifies portfolios with minimum correlation
Statistical approaches are particularly valuable for uncovering hidden risk relationships that might not align with traditional economic factors.
Fundamental Macroeconomic Decomposition
This methodology links portfolio risk directly to underlying economic variables:
- GDP growth sensitivity
- Inflation risk
- Interest rate risk
- Credit spread exposure
- Commodity price sensitivity
- Currency risk factors
Research by BCA Analytics shows that macroeconomic factors typically explain 65-75% of long-term asset class returns but their explanatory power can drop to 30-40% during market dislocations.
Scenario-Based Decomposition
Scenario decomposition evaluates portfolio performance under specific market conditions:
- Stress testing against historical events (e.g., 2008 Financial Crisis, COVID crash)
- Monte Carlo simulations of potential future scenarios
- Custom scenario analysis based on specific macroeconomic or geopolitical risks
- Fat-tail event analysis focusing on extreme but plausible outcomes
Comparative Analysis of Risk Decomposition Methodologies
| Decomposition Method | Strengths | Limitations | Best Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
| Factor-Based | Intuitive economic interpretation; Established academic foundation | May miss emerging or non-traditional risks | Core strategic allocation; Style analysis |
| Statistical | Can identify hidden patterns; Not constrained by predetermined factors | Factors may lack clear economic interpretation | Tactical risk monitoring; Detecting regime shifts |
| Macroeconomic | Direct link to economic fundamentals; Forward-looking potential | Relies on economic forecasts which have uncertainty | Economic scenario planning; Strategic asset allocation |
| Scenario-Based | Stress tests portfolio against specific events; Reveals tail risks | Highly dependent on scenario selection and assumptions | Crisis preparation; Risk budgeting |
Benefits of Professional Risk Decomposition
Enhanced Portfolio Construction
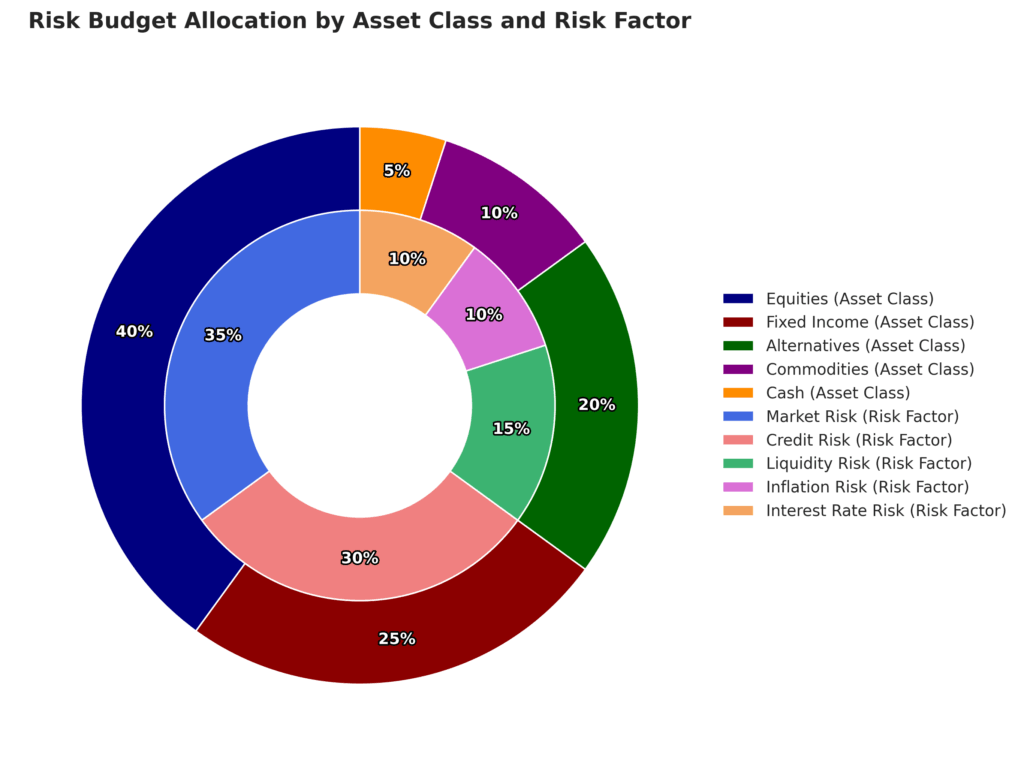
Professional risk decomposition enables more sophisticated portfolio construction by:
- Allocating risk budgets rather than simply allocating capital
- Ensuring diversification at the risk factor level rather than just asset class level
- Identifying optimal hedging instruments for specific risk exposures
- Preventing unintended risk concentrations that might not be apparent from asset allocations alone
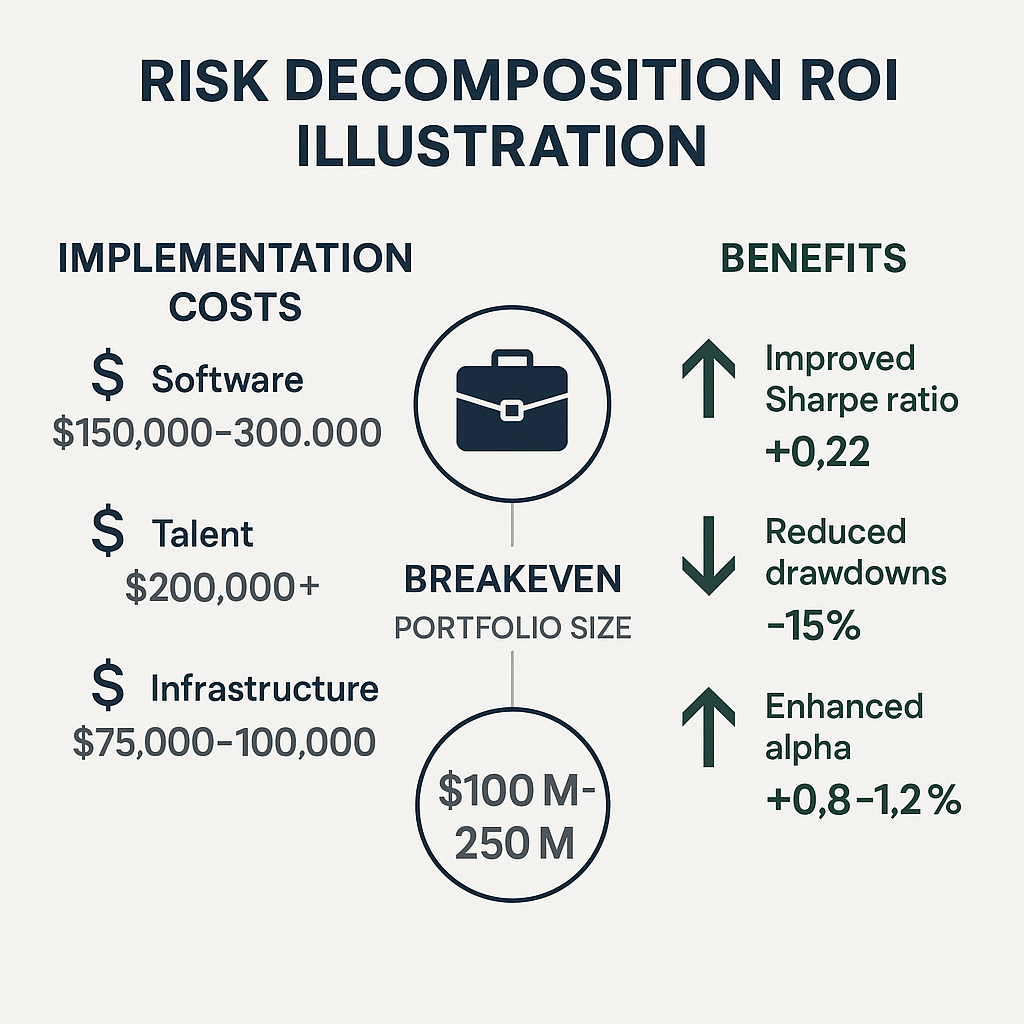
Research by Vanguard found that risk-based portfolio construction improved Sharpe ratios by approximately 0.22 over traditional methods from 2010-2022.
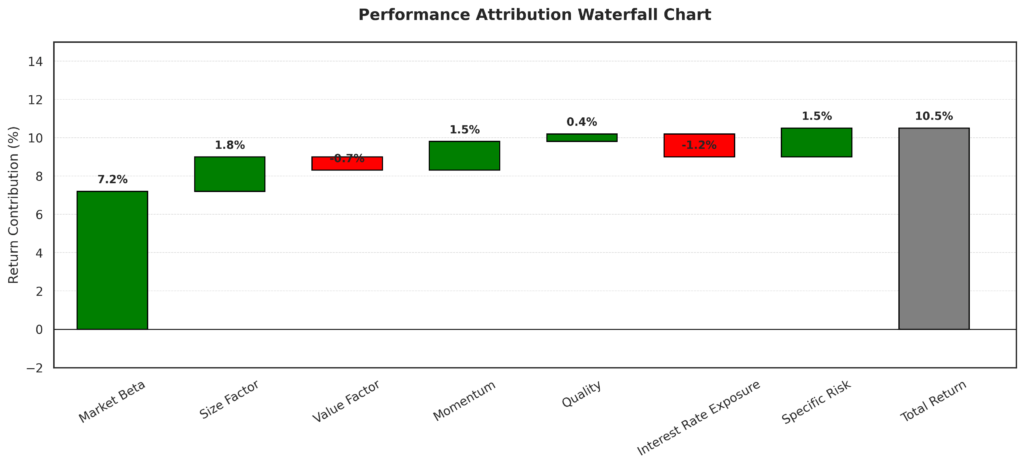
Superior Performance Attribution
Advanced decomposition provides deeper insights into performance drivers:
- Separating skill-based returns from factor-based returns
- Identifying which specific risk exposures generated outperformance or underperformance
- Evaluating whether portfolio managers are being appropriately compensated for risks taken
- Measuring the impact of tactical allocation decisions versus strategic positioning
Regulatory and Reporting Advantages
Institutions benefit from improved risk transparency and compliance:
- Meeting regulatory requirements for risk reporting (Basel III, Solvency II)
- Providing more meaningful risk communication to stakeholders and clients
- Supporting better governance through clearly documented risk sources
- Enabling more consistent risk management across complex organizations
Tactical Responsiveness
Risk decomposition enables more nimble portfolio adjustments:
- Quickly identifying emerging risk concentrations as market conditions evolve
- Supporting dynamic risk management approaches
- Facilitating more precise tactical tilts based on changing risk premia
- Enabling targeted risk reduction without wholesale portfolio changes
Challenges and Limitations
Model Risk and Assumptions
Risk decomposition methods carry their own inherent limitations:
- All models rely on assumptions that may not hold during market stress
- Historical correlations often break down precisely when diversification is most needed
- Factor relationships are not static and evolve over time
- Misspecification of risk factors can lead to false sense of security
Data Requirements and Quality Issues
Implementing sophisticated decomposition demands extensive data:
- High-quality, consistent data across multiple markets and time periods
- Sufficient history to capture various market regimes
- Appropriate treatment of survivorship bias and outliers
- Integration of alternative data sources for non-traditional assets
Interpretation Complexity
Advanced decomposition results can be challenging to interpret:
- Statistical factors may lack intuitive economic meaning
- Risk attribution becomes increasingly complex in multi-layered models
- Differentiating between correlation and causation
- Communicating nuanced findings to non-technical stakeholders
Implementation Costs
Deploying professional decomposition tools requires significant resources:
- Software licensing costs ranging from $50,000 to $500,000+ annually for institutional platforms
- Specialized quantitative talent with compensation packages often exceeding $200,000 annually
- Computational infrastructure and data management systems
- Integration challenges with existing investment processes
Implementation of Professional Decomposition Tools
Technology Infrastructure
Effective risk decomposition requires robust technological foundations:
- High-performance computing capabilities for complex simulations
- Real-time data processing systems for timely risk monitoring
- Cloud-based solutions enabling scalable analysis
- API connectivity to multiple data sources and execution platforms
Top Professional Platforms
Leading risk decomposition solutions include:
- BlackRock Aladdin: Comprehensive risk management system used by over 25,000 investment professionals globally
- MSCI BarraOne: Advanced multi-asset class risk analytics platform
- Axioma Portfolio Analytics: Provides factor-based risk decomposition across multiple risk models
- Bloomberg PORT: Integrated portfolio and risk analytics system
- RiskMetrics RiskManager: Sophisticated risk decomposition and stress testing platform
Integration Process
Successful implementation typically follows these steps:
- Assessment of current risk framework and identification of specific objectives
- Data infrastructure evaluation and necessary enhancement
- Model selection and customization to organizational needs
- Parallel running period comparing new insights with existing processes
- Calibration and backtesting across various market conditions
- Integration with investment decision processes and governance structures
- Ongoing validation and refinement of decomposition methodologies
Best Practices
Organizations that successfully leverage risk decomposition typically:
- Combine multiple decomposition approaches rather than relying on a single methodology
- Regularly review and update factor definitions and relationships
- Maintain healthy skepticism about model outputs and complement with qualitative analysis
- Ensure clear ownership of risk decomposition processes across the organization
- Develop customized risk dashboards for different stakeholder groups
- Create feedback loops between risk insights and portfolio decisions
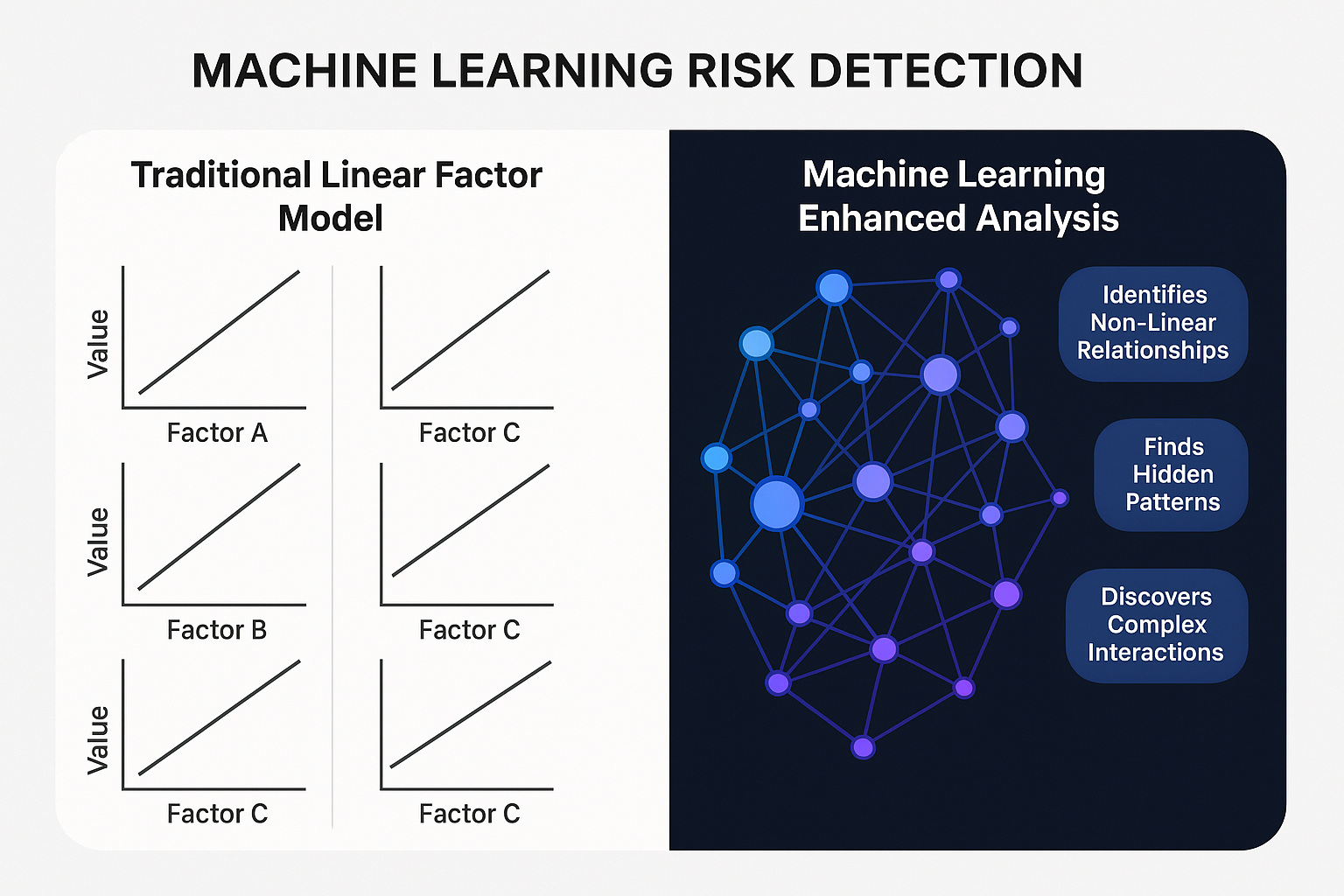
Future Trends in Risk Decomposition
Machine Learning Integration
Advanced algorithms are revolutionizing risk decomposition:
- Deep learning models identifying non-linear risk relationships
- Natural language processing extracting risk signals from unstructured data
- Reinforcement learning optimizing dynamic hedging strategies
- Unsupervised learning for detecting emerging risk clusters
According to a 2023 CFA Institute survey, 62% of institutional investors now incorporate AI-driven risk analytics in their investment processes, up from just 17% in 2018.
Alternative Data Incorporation
Non-traditional data sources are enhancing risk decomposition:
- Satellite imagery for real-time economic activity assessment
- Social media sentiment analysis for market regime identification
- Supply chain mapping for operational risk decomposition
- Climate data integration for sustainability risk measurement
Real-time Adaptive Models
Next-generation tools feature dynamic capabilities:
- Continuous recalibration based on evolving market conditions
- Adaptive risk factors that respond to changing economic regimes
- Context-aware risk thresholds that adjust to market volatility
- Auto-generated scenario analysis based on emerging threats
Democratization of Advanced Tools
Sophisticated decomposition is becoming more accessible:
- SaaS delivery models reducing implementation barriers
- API-first platforms enabling customization without massive infrastructure
- Simplified interfaces improving usability for non-quantitative professionals
- Tiered offerings making enterprise-grade analytics available to smaller firms
FAQs – Investment Risk Decomposition
1. What is the difference between risk decomposition and risk attribution?
Risk decomposition refers to breaking down total portfolio risk into its constituent components based on factors, scenarios, or other classifications. Risk attribution, while related, focuses specifically on explaining performance results by attributing returns to various risk exposures. Decomposition is primarily forward-looking and focused on potential risks, while attribution is typically backward-looking and centered on explaining realized performance.
2. How frequently should risk decomposition analysis be updated?
Most institutional investors update their core risk decomposition analysis at least monthly, with 42% performing weekly updates according to a 2023 AIMA survey. However, the optimal frequency depends on portfolio characteristics, trading activity, and market volatility. During periods of market stress, daily or even intraday decomposition updates may be warranted for actively managed portfolios.
3. Can risk decomposition techniques be applied to alternative investments?
Yes, though with additional complexity. Alternative investments like private equity, real estate, and hedge funds require specialized decomposition approaches that account for illiquidity, non-normal return distributions, and limited data history. Factor mimicking portfolios using public market proxies, cash flow-based simulations, and peer group analysis are common techniques for extending decomposition to alternatives.
4. What is the minimum portfolio size for which professional risk decomposition tools are cost-effective?
Professional platforms typically become cost-effective for portfolios exceeding $100-250 million, where the improved risk-adjusted returns or risk mitigation can offset implementation costs. However, more accessible solutions are emerging for smaller portfolios, and some wealth management platforms now offer simplified risk decomposition for portfolios as small as $5 million.
5. How do risk decomposition approaches differ between fixed income and equity portfolios?
Fixed income decomposition typically emphasizes yield curve risk, credit spread exposure, and optionality factors, often using duration-based measures. Equity decomposition generally focuses on market beta, style factors, sector exposures, and increasingly, thematic risks. Fixed income decomposition also tends to be more sensitive to macroeconomic variables and requires more granular term structure modeling.
6. How can investment teams validate the accuracy of risk decomposition models?
Validation typically involves backtesting (comparing predicted risk decomposition to actual return attribution), out-of-sample testing on market periods not used in model development, and stress testing against known historical events. Many firms also implement “model challenger” programs where alternative decomposition approaches are run in parallel to identify potential blind spots in primary models.
7. What organizational structure best supports effective risk decomposition implementation?
Successful implementation typically requires close collaboration between risk management, portfolio management, and technology teams. Leading organizations often establish dedicated factor specialists or risk analytics teams that serve as bridges between technical implementation and investment decision-making. Clear governance frameworks with defined risk ownership and escalation procedures are also critical.
8. How are ESG factors incorporated into modern risk decomposition frameworks?
ESG integration in risk decomposition is still evolving but typically involves adding specific ESG factors (carbon intensity, governance scores, social impact metrics) to traditional models or creating separate ESG-specific decomposition overlays. Some advanced approaches use scenario analysis to quantify climate transition risks or regulatory risks associated with sustainability factors.
9. What are the key differences between commercial risk decomposition platforms and proprietary in-house systems?
Commercial platforms offer broader market coverage, standardized methodologies, and dedicated support, but may lack customization for unique investment approaches. Proprietary systems can be precisely tailored to specific investment philosophies and integrated deeply with proprietary data sources, but require significant development and maintenance resources. Many institutions adopt hybrid approaches, using commercial platforms for core functionality while developing proprietary overlays for competitive differentiation.
10. How can risk decomposition insights be effectively communicated to non-technical stakeholders?
Effective communication typically employs visualization techniques like heat maps, risk contribution charts, and scenario impact graphs. Leading practitioners develop tiered reporting frameworks with executive summaries highlighting key risk concentrations and potential vulnerabilities in non-technical language, supported by more detailed analysis for technical users. Interactive dashboards allowing stakeholders to explore risk factors at their own pace are increasingly common.
Conclusion
Investment risk decomposition has evolved from an academic concept to an essential component of professional portfolio management. By dissecting portfolio risks into their constituent elements, investors gain unprecedented visibility into their exposures and can make more informed, precise adjustments to achieve desired risk-return profiles.
The ability to identify hidden correlations, quantify factor exposures, and stress test against specific scenarios provides a significant competitive advantage in increasingly complex and interconnected global markets.
Looking ahead, the continued integration of artificial intelligence, alternative data sources, and real-time analytics promises to further enhance the power and accessibility of risk decomposition tools. As these technologies mature, we can expect even more granular insights, forward-looking risk identification, and seamless integration with investment processes.
For investment professionals committed to rigorous risk management, mastering these evolving decomposition methodologies will remain a critical differentiator in delivering consistent, risk-adjusted returns for clients.
For your reference, recently published articles include:
- Strategic Wealth Tech: Portfolio Management Dashboards Now
- Portfolio Rebalancing Automation: The Smart Investor’s Edge
- Investing Myths Debunked: Stop Losing Money Now
- Future-Proof Your Portfolio: Surprising Benefits Of Impact Investing
- Seize The Moment: 7 Market Timing Tools For Strategic Wealth
- Investment Pattern Recognition – All You Need To Know
………………………………………………..
Important Notice: The information in this article is for general and public information purposes only. It solely reflects Didi Somm’s or his Staff’s opinion, and no responsibility can be assumed for errors or omissions in the service’s contents. For details, please check the Disclaimer at the bottom of the homepage.

