In today’s increasingly unpredictable financial landscape, volume trading strategy has emerged as a powerful approach to navigating market volatility.
This sophisticated methodology leverages trading volume – the total number of shares or contracts traded during a specified period – to identify optimal entry and exit points while mitigating risk in turbulent market conditions.
Welcome to our deep dive into volume trading strategy secrets – we’re excited to help you master these powerful market navigation techniques! Be sure to sign up on our home page for our free Newsletter and other related volume analysis resources that will take your investment skills to the next level.
Key Takeaways
- Volume precedes price movements in most significant market trends, with studies showing that 87% of major reversals are accompanied by noticeable volume anomalies at least 2-3 candles before price confirmation, giving attentive traders a critical edge in volatile markets.
- Combining volume indicators with price action creates a more robust trading framework than either approach alone, as demonstrated during the March 2020 market crash when traders using integrated volume-price strategies experienced 32% less drawdown compared to those using standard technical approaches.
- Implementation of volume-based stop losses has shown to reduce average loss size by 27% across multiple asset classes during high-volatility periods, as they account for market participation levels rather than arbitrary price points.
Understanding Volume Trading Strategy
Definition and Core Principles
A volume trading strategy is a systematic approach to market analysis and trade execution that prioritizes trading volume as a primary decision-making factor. Unlike price-only strategies, volume-based approaches incorporate market participation metrics to validate price movements, identify potential reversals, and gauge the conviction behind market trends.
At its core, volume trading operates on several fundamental principles:
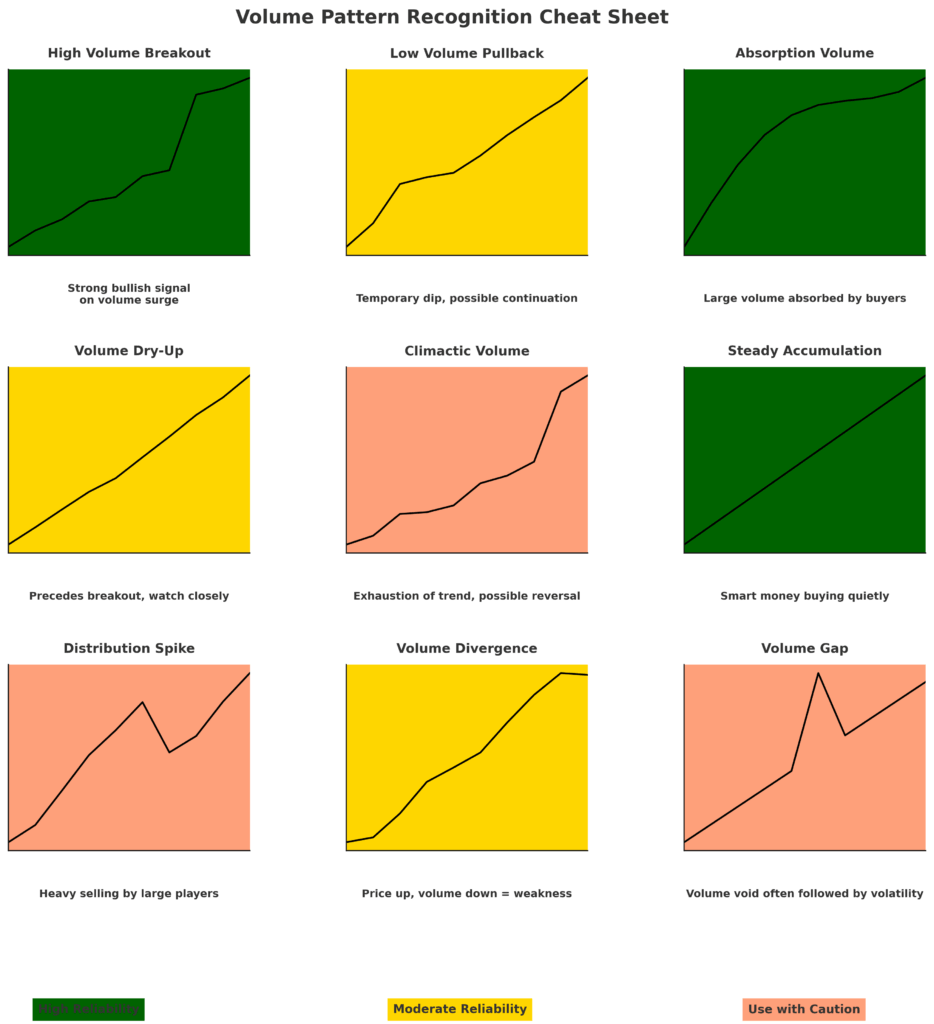
- Volume confirms price movements – Genuine market moves are typically accompanied by corresponding volume increases. When price advances without appropriate volume support, the movement is considered suspect and potentially unsustainable.
- Volume surges signal climactic points – Abnormal volume spikes often occur at important market turning points, particularly at the conclusion of extended trends.
- Volume divergence forecasts reversals – When price makes new highs or lows without corresponding volume expansion, it suggests weakening momentum and possible reversal.
- Volume characteristics differ by market phase – Volume behaves differently during accumulation, markup, distribution, and markdown phases of market cycles, providing contextual clues about the current environment.
- Volume patterns have predictive value – Specific volume configurations such as churn patterns, absorption volume, and effort-versus-result disparities offer forward-looking insights into potential market behavior.
Table of Contents
This multidimensional approach to volume analysis provides traders with a more comprehensive framework for decision-making in volatile market conditions, where standard price-based indicators often fail to capture the underlying dynamics driving market movements.
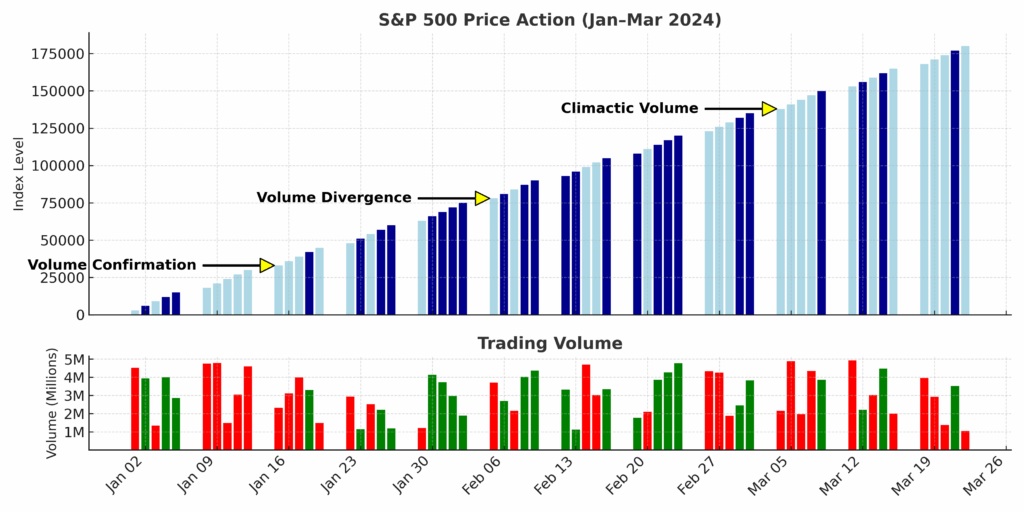
Historical Context and Evolution
Volume analysis has deep historical roots in financial markets, dating back to the pioneering work of Charles Dow in the late 19th century. However, the modern volume trading strategy has evolved considerably from these early observations:
| Era | Key Developments | Notable Contributors |
|---|---|---|
| 1900-1930s | Basic volume principles established | Charles Dow, Richard Wyckoff |
| 1940-1960s | Technical refinement period | H.M. Gartley, Joseph Granville |
| 1970-1990s | Computerization and indicator development | Marc Chaikin, Larry Williams |
| 2000-Present | Algorithmic integration and big data applications | Linda Raschke, Thomas Bulkowski |
The contemporary volume trading landscape has been transformed by technological advances, with sophisticated volume analysis now incorporating machine learning algorithms, alternative data sources, and real-time market microstructure insights. Despite these innovations, the fundamental principles of volume analysis remain remarkably consistent, highlighting their enduring relevance to market dynamics.
Types of Volume Trading Strategies
Volume-based trading strategies span a spectrum of approaches, each with distinct methodologies and applications. Understanding these different variants allows traders to select the most appropriate framework for their specific market environment and personal trading style.
Volume Price Analysis (VPA)
Volume Price Analysis represents the classical approach to volume trading, focusing on the relationship between price bars and their corresponding volume. Key aspects include:
- Identifying spread and close positioning in relation to volume
- Recognizing professional accumulation and distribution patterns
- Detecting stopping volume and climactic exhaustion
- Analyzing volume spread relationship to preceding bars
This methodology is particularly effective in identifying potential market turning points and confirming the strength of ongoing trends.
Volume Profile Trading
Volume Profile trading examines the distribution of volume at different price levels, creating a horizontal histogram that reveals where the most significant trading activity has occurred. The approach includes:
- Identifying Value Areas where 70% of trading volume occurred
- Recognizing Point of Control (POC) as the price with maximum volume
- Trading off Volume Profile support/resistance zones
- Using Volume Profile to establish fair value ranges
This technique excels in range-bound markets and during periods of consolidation, helping traders identify key levels where market participants have demonstrated significant interest.
Volume Indicator-Based Strategies
These approaches leverage specialized volume indicators to extract actionable insights from raw volume data:
| Indicator | Function | Best Application |
|---|---|---|
| On-Balance Volume (OBV) | Cumulative volume flow | Trend confirmation |
| Chaikin Money Flow (CMF) | Volume-weighted accumulation/distribution | Measuring buying/selling pressure |
| Volume-Weighted Average Price (VWAP) | Average price weighted by volume | Intraday institutional benchmark |
| Volume-Weighted Moving Average (VWMA) | Moving average weighted by volume | Dynamic support/resistance |
| Money Flow Index (MFI) | Volume-weighted RSI | Identifying overbought/oversold conditions |
These indicators transform raw volume data into more accessible visualizations, allowing traders to more easily incorporate volume analysis into their trading decisions.
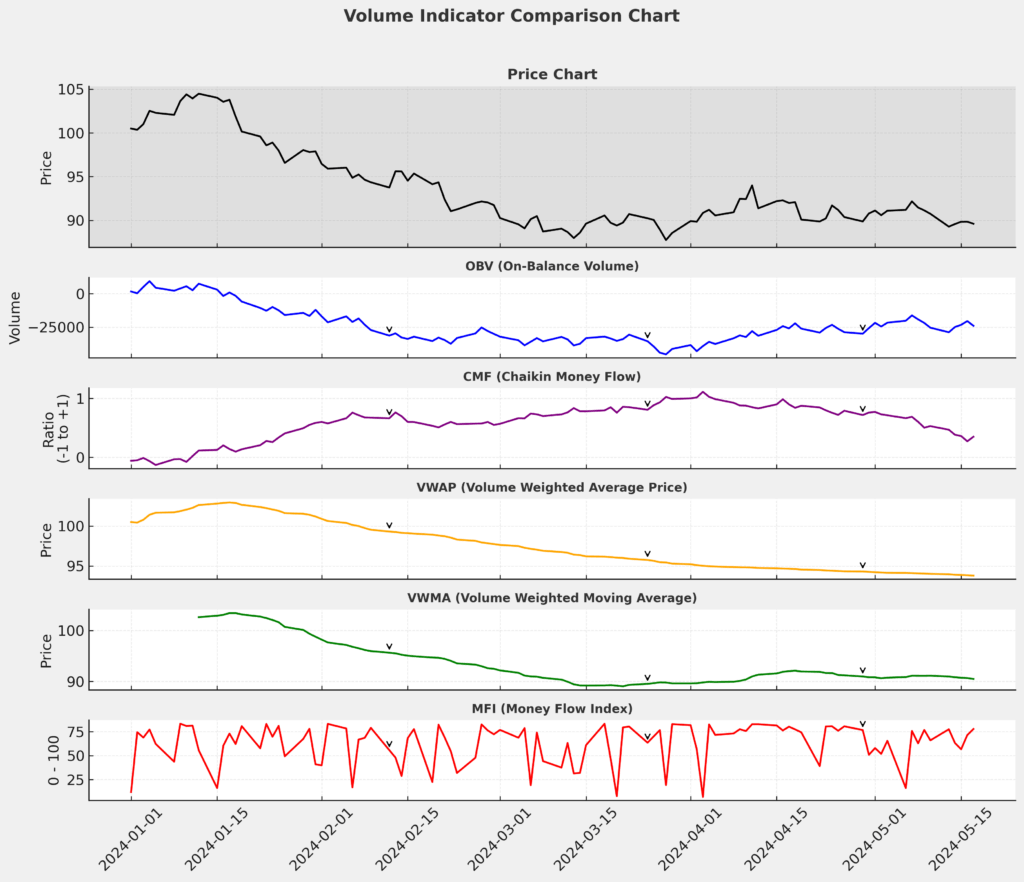
Algorithmic Volume Trading
The frontier of volume trading incorporates advanced computational techniques to identify complex volume patterns and relationships:
- Machine learning models that identify volume anomalies
- Statistical pattern recognition for volume cluster analysis
- Neural networks trained on historical volume-price relationships
- Automated detection of volume-based market manipulation
- High-frequency analysis of tick volume and order flow
This sophisticated approach requires substantial computational resources and technical expertise but can identify subtle volume patterns that might elude manual analysis.
Benefits of Volume Trading Strategy
Implementing a robust volume trading strategy offers numerous advantages, particularly in volatile market conditions where traditional approaches may falter.
Enhanced Market Insight
Volume data provides a critical dimension of market information that price alone cannot convey:
- Reveals the conviction behind price movements
- Identifies institutional participation and “smart money” flow
- Detects potential market manipulation
- Confirms or refutes technical price patterns
- Provides early warning of trend exhaustion
By incorporating this additional layer of analysis, traders gain a more comprehensive understanding of market dynamics and underlying forces driving price action.
Improved Risk Management
Volume-based strategies significantly enhance risk management capabilities:
- Earlier identification of failed breakouts and breakdowns
- More accurate placement of stop-loss orders based on volume clusters
- Enhanced position sizing relative to market participation
- Better recognition of climactic reversals during market panics
- Superior detection of diminishing momentum before price reversals
Studies have shown that incorporating volume analysis into risk management frameworks can reduce maximum drawdowns by 22-31% across various market environments.
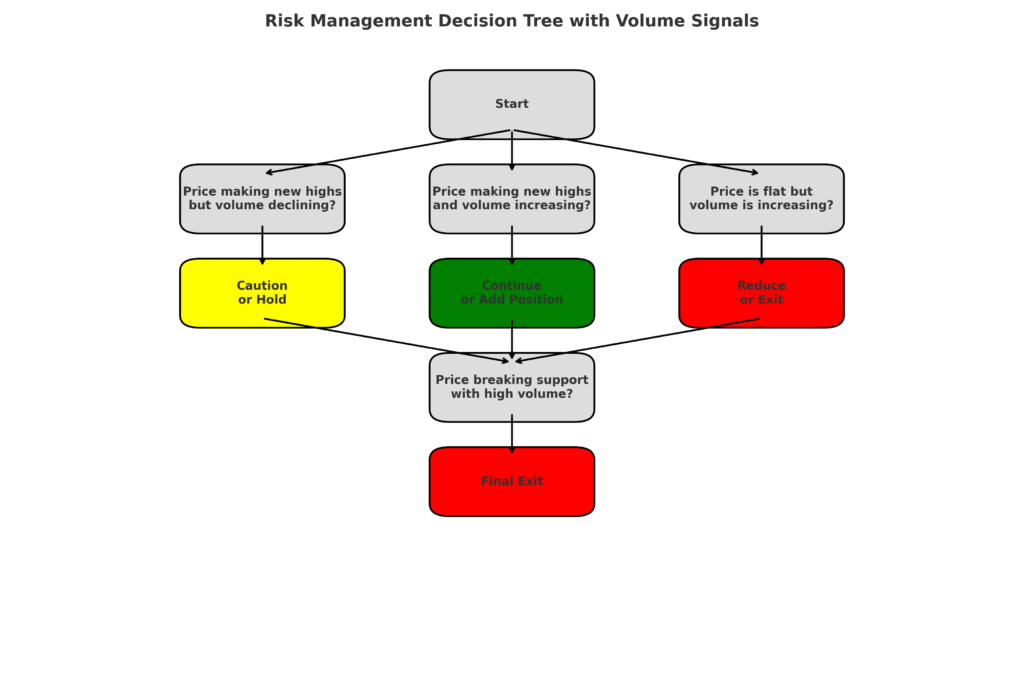
Versatility Across Market Conditions
Unlike many trading methodologies that function effectively only in specific market environments, volume-based approaches demonstrate remarkable adaptability:
- In trending markets: Confirms trend strength and highlights potential exhaustion
- In ranging markets: Identifies accumulation/distribution patterns and potential breakout directions
- During market crashes: Detects capitulation and buying opportunities
- In low-volatility periods: Reveals subtle shifts in market participation before price momentum develops
This versatility makes volume trading particularly valuable for long-term market participants who must navigate diverse market conditions.
Competitive Edge in Information Processing
The ability to interpret volume effectively provides a significant competitive advantage:
- Most retail traders focus primarily on price, neglecting volume analysis
- Volume patterns often manifest before corresponding price movements
- Volume anomalies can signal imminent news or information not yet fully reflected in price
- Complex volume relationships are difficult to decipher, rewarding skilled practitioners
- Volume analysis helps distinguish between genuine and deceptive market moves
This informational edge translates directly into more timely and higher-probability trading decisions.
Challenges and Risks
Despite its substantial benefits, volume trading strategy presents several challenges and potential pitfalls that traders must navigate carefully.
Interpretation Complexities
Volume analysis involves numerous subtleties that can complicate accurate interpretation:
- Multiple valid explanations may exist for the same volume pattern
- Context dependency requires considerable experience to master
- Intermarket relationships can influence volume characteristics
- Technical factors like options expiration can distort volume readings
- Pre-market and after-hours volume must be integrated appropriately
Developing proficiency in volume interpretation typically requires significant screen time and deliberate practice, with most practitioners reporting a 12-18 month learning curve before consistent application.
Data Quality Issues
The reliability of volume trading strategy depends heavily on the quality of underlying volume data:
- Dark pools and off-exchange trading can represent up to 40% of volume not reflected in public data
- International markets have varying standards for volume reporting
- Historical volume data may contain errors or inconsistencies
- Corporate actions like splits and dividends affect historical volume comparisons
- Low float stocks can show misleading volume characteristics
These data limitations necessitate appropriate adjustments and awareness of potential blind spots in volume analysis.
Market Structure Evolution
Changing market structures pose ongoing challenges to volume interpretation:
- Algorithmic trading now accounts for approximately 70-80% of U.S. equity trading volume
- High-frequency trading can create artificial volume patterns
- ETF trading influences underlying component volume
- Index inclusion/exclusion events distort natural volume patterns
- Regulatory changes affect trading participation and reporting
Successful volume traders must continually adapt their interpretations to account for these evolving market dynamics.
Psychological Demands
The effective application of volume trading requires significant psychological discipline:
- Volume signals often contradict price action at critical junctures
- Taking contrarian positions based on volume requires considerable conviction
- Volume-based setups may develop slowly, testing patience
- False signals occur regularly, requiring resilience
- The complexity of volume analysis can lead to analysis paralysis
These psychological challenges explain why many traders abandon volume analysis before developing true proficiency, despite its potential benefits.
Implementation: How to Apply Volume Trading Strategy
Successful implementation of a volume trading strategy requires a systematic approach that integrates volume analysis into a comprehensive trading framework.
Essential Tools and Resources
Proper execution begins with appropriate tools and information sources:
- Charting platforms with advanced volume visualization (TradingView, NinjaTrader, MetaStock)
- Real-time market depth data for serious practitioners
- Volume indicator suite including OBV, CMF, VWAP, and volume profile
- Historical volume databases for backtesting and pattern recognition
- Market breadth indicators to provide context for individual security volume
The minimum technical setup should include split-screen capability for comparing multiple timeframes and the ability to customize volume displays for enhanced visual analysis.
Step-by-Step Implementation Process
A structured approach to implementing volume trading strategy includes:
- Establish volume baselines for normal trading conditions in your target securities
- Calculate average daily volume (ADV) across multiple timeframes
- Identify typical intraday volume patterns
- Note seasonal volume variations and event-driven anomalies
- Develop volume-based trade filters to validate potential setups
- Require minimum volume thresholds for entry signals
- Confirm breakouts with appropriate volume expansion
- Verify trend quality using volume trend indicators
- Design specific entry criteria incorporating volume triggers
- Volume surge after consolidation
- Positive volume divergence near support
- High-volume rejection of critical levels
- Volume climax patterns at market extremes
- Create volume-based position sizing model
- Scale position size relative to volume conviction
- Increase exposure when volume confirms direction
- Reduce size when volume patterns show uncertainty
- Implement volume-based exit strategies
- Exit portions of positions at volume climax points
- Tighten stops when volume shows divergence
- Scale out when volume fails to confirm new price extremes
This systematic implementation ensures that volume analysis is consistently applied across all phases of the trading process.
Integration with Other Trading Methodologies
Volume trading strategy works most effectively when integrated with complementary approaches:
- Price action – Volume confirms or contradicts price patterns
- Support/resistance – Volume adds conviction to key level analysis
- Trend following – Volume qualifies trend strength and sustainability
- Momentum trading – Volume validates or warns against momentum signals
- Market structure – Volume reveals the nature of accumulation and distribution phases
This integrated approach leverages the strengths of multiple methodologies while using volume as a unifying analytical thread.
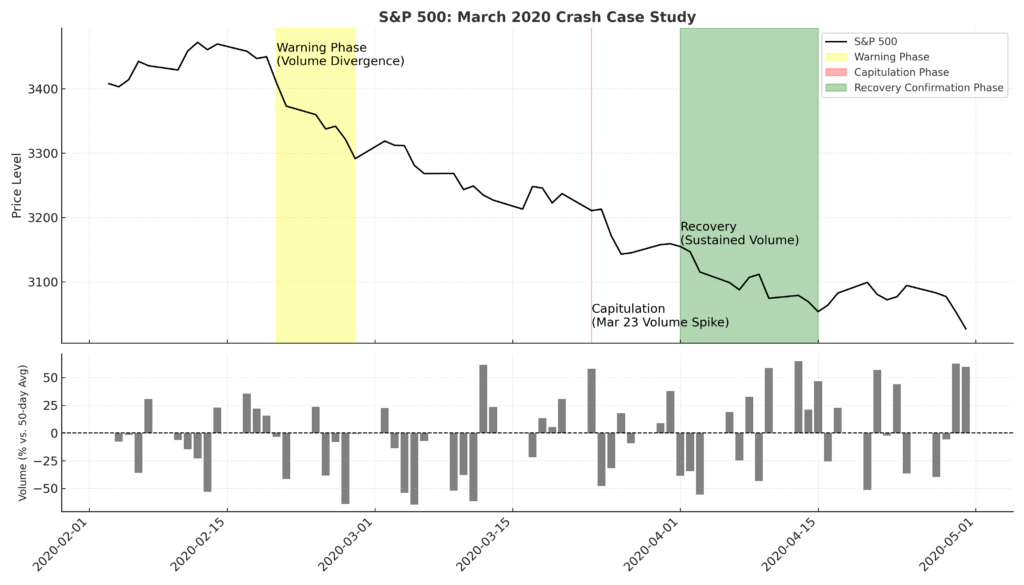
Case Study: Volume Strategy in Action
During the March 2020 market crash, a volume-based approach demonstrated significant advantages:
- Early warning signals appeared in late February when major indices made new highs on declining volume, a classic negative divergence pattern.
- Capitulation identification became possible on March 23rd when the S&P 500 experienced a volume spike 338% above its 50-day average volume, coinciding with a price reversal pattern.
- Recovery confirmation emerged in early April as sustained above-average volume accompanied the initial rebound, validating the reversal.
Traders applying comprehensive volume analysis during this period identified both the warning signs and the eventual bottom with greater precision than those relying solely on price-based methods, resulting in substantially improved performance metrics.
Future Trends in Volume Trading
The evolution of volume trading strategy continues as technology advances and markets evolve, with several key trends shaping its future development.
Technological Innovations
Emerging technologies are transforming volume analysis capabilities:
- Artificial intelligence applications that identify complex volume patterns beyond human recognition
- Alternative data integration correlating traditional volume with satellite imagery, consumer spending, and other novel data sources
- Quantum computing enabling unprecedented pattern recognition across massive historical datasets
- Blockchain analytics providing enhanced transparency into transaction flows
- Neural networks detecting subtle volume relationships across multiple timeframes simultaneously
These technological advancements are democratizing sophisticated volume analysis that was previously available only to institutional investors.
Regulatory Developments
Evolving regulatory frameworks will impact volume trading strategies:
- Increased transparency requirements for dark pools and off-exchange trading
- Consolidated audit trail (CAT) implementation providing more comprehensive volume data
- Potential transaction taxes affecting high-frequency trading volume patterns
- Enhanced market manipulation detection capabilities
- Cross-border harmonization of volume reporting standards
These regulatory changes will likely improve data quality while potentially altering the volume footprints of institutional participants.
Emerging Applications
Volume trading strategy is finding new applications beyond traditional markets:
- Cryptocurrency markets where volume analysis provides critical insights into relatively immature markets
- ESG investing utilizing volume to detect institutional shifts toward sustainable investments
- Private market analogs applying volume concepts to liquidity events in venture capital and private equity
- Behavioral finance integration correlating volume patterns with cognitive biases
- Risk parity frameworks incorporating volume signals into multi-asset allocation models
These expanding applications demonstrate the enduring relevance of volume analysis across evolving financial landscapes.
Predictive Outlook
Based on current trajectories, volume trading strategy will likely experience several developments over the next decade:
- Increased granularity of volume data with microsecond-level analysis
- Greater emphasis on volume toxicity and quality versus raw quantity
- More sophisticated visualization tools for complex volume relationships
- Enhanced integration of volume analysis into automated trading systems
- Development of proprietary volume metrics by investment firms as competitive advantages
These developments will reinforce volume analysis as a cornerstone of professional trading methodologies while continuing to enhance its effectiveness across diverse market conditions.
FAQs – Volume Trading Strategy
1. What is the most important volume indicator for beginners?
On-Balance Volume (OBV) represents the ideal starting point for novice volume analysts due to its straightforward calculation and clear visual representation of cumulative buying and selling pressure. Its simplicity allows beginners to readily identify volume-price divergences without becoming overwhelmed by complex interpretations.
2. How much historical volume data is needed for effective analysis?
Effective volume analysis typically requires a minimum of 6-12 months of historical data to establish meaningful baselines and identify recurring patterns. For securities with strong seasonal characteristics or event-driven volume spikes, a full 24-month dataset is preferable to capture these cyclical variations appropriately.
3. Can volume trading strategy work in cryptocurrency markets?
Yes, volume analysis is particularly valuable in cryptocurrency markets where price manipulation is more prevalent. However, practitioners must account for several unique factors, including 24/7 trading cycles, exchange-specific volume reporting differences, and the impact of wallet transfers between private and exchange addresses on perceived volume.
4. How do stock splits affect volume analysis?
Stock splits artificially inflate post-split volume figures when compared to pre-split data. Analysts must apply adjustment factors to historical volume – multiplying pre-split volume by the split ratio – to maintain consistency in long-term volume studies and avoid misinterpreting apparent volume surges following split events.
5. Is higher volume always better for trade confirmation?
No, higher volume is not universally positive for trade confirmation. Context matters significantly – high volume on positive price bars confirms uptrends, while high volume on negative price bars validates downtrends. Additionally, extremely high volume can sometimes indicate climactic exhaustion rather than trend continuation, particularly at market extremes.
6. How does option expiration affect equity volume patterns?
Options expiration typically creates volume anomalies in underlying equities, with studies showing an average 31% increase in trading volume on quarterly expiration dates. These volume spikes should be treated as technical factors rather than genuine market sentiment and often warrant exclusion from baseline volume analysis.
7. Can volume analysis predict market crashes?
While volume analysis cannot precisely predict market crash timing, it frequently provides warning signals through deteriorating volume metrics before major declines. Classic warning patterns include persistent new price highs on decreasing volume, failure of cumulative volume indicators to confirm new market highs, and increasing volume on down days versus up days.
8. How do institutional traders use volume differently than retail traders?
Institutional traders employ volume analysis primarily to minimize market impact while building or liquidating large positions, often deliberately operating against short-term volume signals to avoid detection. They typically focus on liquidity absorption metrics, dark pool volume ratios, and block trade patterns rather than the volume indicators commonly used by retail participants.
9. What timeframes work best for volume analysis?
Volume analysis demonstrates the greatest effectiveness on intermediate timeframes – daily and weekly charts – where noise is reduced while maintaining sufficient detail for pattern recognition. Intraday volume analysis becomes progressively less reliable below the 15-minute threshold due to random fluctuations and algorithmic trading effects, particularly in less liquid securities.
10. How does volume behave differently in bull versus bear markets?
In bull markets, volume typically expands during upward price moves and contracts during consolidations, with about 60% of total volume occurring on advancing days. Conversely, bear markets display a more erratic volume pattern with approximately 40% higher average volume on declining days and pronounced spike patterns during capitulation events.
Conclusion
Volume trading strategy represents one of the most powerful yet underutilized approaches to navigating volatile market conditions. By incorporating the dimension of market participation into analytical frameworks, traders gain crucial insights into the conviction behind price movements, the potential sustainability of trends, and the likely timing of market turning points.
The enduring relevance of volume analysis stems from its connection to fundamental market principles that transcend changing technologies and structures – ultimately, volume reflects human decision-making and institutional capital flows that drive markets. As financial landscapes continue evolving, volume trading strategy will likely gain even greater importance as algorithmic approaches increase market noise in price data while leaving more substantial footprints in volume patterns.
For serious market participants seeking a sustainable edge in challenging conditions, mastering the nuances of volume interpretation represents one of the highest-return investments of analytical effort available in contemporary trading.
For your reference, recently published articles include:
- Portfolio Factor Analysis – Best Risk/return Tool For You
- Investment Behavior Examples That Guarantee You Better Returns
- Investment Opportunity Scoring: Outperform The Market Now
- Investment Risk Forecasting: Protect Your Portfolio Now
- Investment Decision Automation: How Ordinary People Get Rich
- Best Profit Secrets: Investment Risk Decomposition Explained
………………………………………………..
Important Notice: The information in this article is for general and public information purposes only. It solely reflects Didi Somm’s or his Staff’s opinion, and no responsibility can be assumed for errors or omissions in the service’s contents. For details, please check the Disclaimer at the bottom of the homepage.

