In today’s volatile economic climate, establishing reliable passive income streams has become an essential financial strategy for achieving long-term wealth and security.
The “Generate $10,000 Monthly: Ultimate Passive Income Blueprint” outlines a comprehensive framework for building and scaling multiple passive revenue channels that can collectively yield substantial monthly returns with minimal ongoing effort.
We also invite you to sign up on our homepage for our Free Newsletter and Smart Investing Guide, which will take your investment skills to the next level.
Welcome to “Finance & Investments” by Didi Somm!
Important Notice: The information in this article is for general and public information purposes only. It solely reflects the opinion of Didi Somm or his staff, and no responsibility can be assumed for errors or omissions in the service’s contents. For details, please read the Disclaimer at the bottom of the homepage.
Key Takeaways
1. Diversification across multiple passive income streams is essential for achieving the $10,000 monthly target. The most successful passive income portfolios incorporate 5-7 distinct revenue channels rather than relying on a single source.
For example, Jason, a former marketing executive, reached his $10,000 monthly goal by combining dividend stocks ($2,800), rental properties ($3,200), affiliate marketing ($1,500), digital products ($1,700), and royalties ($800). This diversification not only increases total income but also provides crucial protection against market fluctuations in any single sector.
2. Initial time and capital investment requirements vary significantly across passive income strategies. While dividend investing might require $350,000-$500,000 capital at 4% yield to generate meaningful returns, content creation strategies like YouTube channels demand 300-500 hours of upfront work before monetization becomes viable.
Sarah, a teacher, started with just $10,000 in capital but invested 25 hours weekly for 18 months developing digital courses, which now generate $7,500 monthly with only 5 hours of maintenance work. Understanding these input-to-return ratios is critical for selecting strategies aligned with your resources.
3. Technological leverage and automation are transforming traditional passive income models. Modern passive income strategies increasingly incorporate AI tools, API integrations, and automated systems that significantly reduce ongoing maintenance requirements.
Michael, a software developer, built an automated SaaS application that handles customer onboarding, billing, and basic support without human intervention, scaling to $12,000 monthly with only 8 hours of weekly oversight. This technological leverage represents a fundamental shift from older passive income models that required substantial ongoing management.
Table of Contents
What Is Passive Income?
Passive income refers to earnings derived from ventures in which an individual is not actively involved on a day-to-day basis. Unlike active income, which requires direct, ongoing effort (such as a traditional job), passive income continues to flow after the initial investment of time, money, or both. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) formally categorizes passive income as earnings from rental activities or business activities in which the earner does not materially participate.
However, in contemporary financial planning, the concept has evolved beyond this strict definition to encompass any revenue stream that requires minimal ongoing maintenance once established. The critical distinction of true passive income lies in its ability to scale without a proportional increase in time investment – creating the powerful income-to-effort asymmetry that makes these strategies so appealing.
It’s important to note that most passive income streams are not truly “set and forget.” They typically require significant upfront investment (either capital, time, or specialized knowledge) and periodic maintenance. The “passive” aspect refers to the disproportionate relationship between ongoing effort and continued returns, not the complete absence of work.
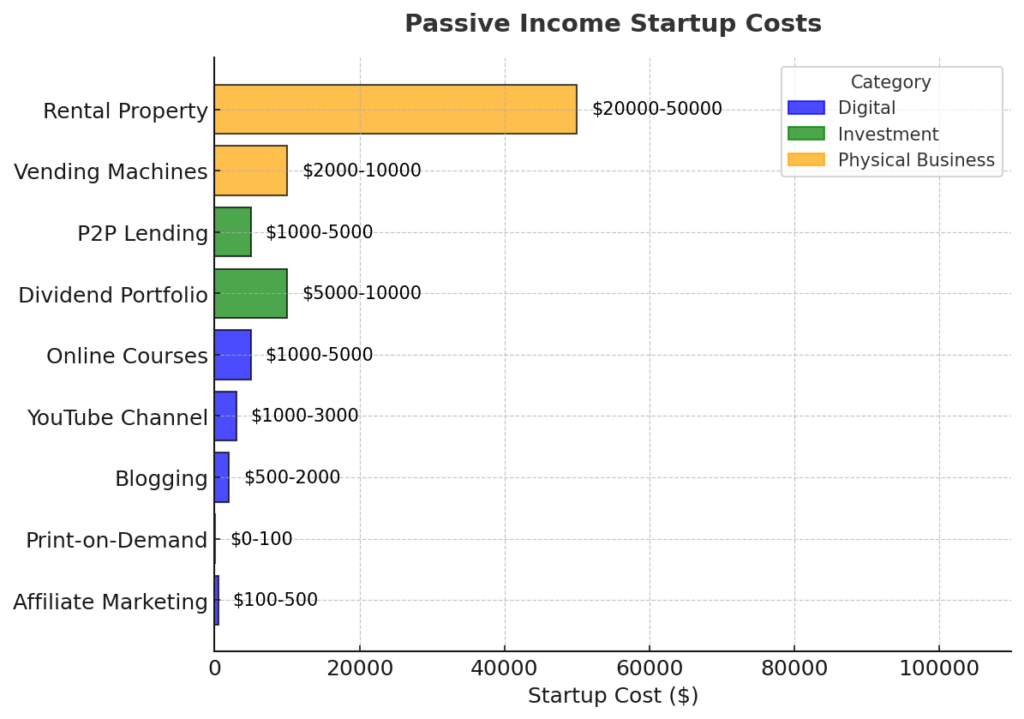
Types of Passive Income Strategies
Investment-Based Income Streams
Investment-based passive income leverages financial capital to generate returns without active involvement in the underlying business operations. These passive income strategies typically require significant initial capital but minimal time investment.
Dividend Stocks and ETFs
Dividend-paying stocks and Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) represent ownership in companies that distribute a portion of their profits to shareholders on a regular basis, typically quarterly.
Key characteristics:
- Average dividend yield ranges: 2-6% annually
- Minimum effective investment: $20,000-$50,000 for meaningful monthly income
- Risk level: Moderate (dependent on specific securities selected)
- Liquidity: High (can be sold during market hours)
Implementation steps:
- Research dividend aristocrats (companies with 25+ years of consecutive dividend increases)
- Build a diversified portfolio across multiple sectors
- Consider dividend ETFs like SCHD, VYM, or HDV for instant diversification
- Implement dividend reinvestment plans (DRIPs) to compound returns
- Monitor quarterly for dividend sustainability and growth potential
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
REITs are companies that own, operate, or finance income-producing real estate across various sectors, distributing 90% of taxable income to shareholders as dividends.
Key characteristics:
- Average dividend yield: 3-8% annually
- Minimum effective investment: $10,000-$25,000
- Risk level: Moderate to high (sector-dependent)
- Liquidity: High (publicly traded REITs)
Popular REIT sectors:
- Residential
- Commercial
- Healthcare
- Data centers
- Self-storage
- Mortgage REITs
Bonds and Fixed-Income Securities
Bonds represent loans to governments, municipalities, or corporations that pay fixed interest over a predetermined period.
Types of bonds and typical yields:
| Bond Type | Typical Yield Range (2025) | Risk Level | Minimum Investment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Treasury | 3.8-4.5% | Very Low | $100 |
| Municipal | 3.5-5.0% | Low | $5,000 |
| Corporate (Investment Grade) | 4.5-6.0% | Moderate | $1,000 |
| Corporate (High Yield) | 6.0-9.0% | High | $1,000 |
| International | 4.0-10.0% | Moderate to High | $1,000 |
Bond implementation strategies:
- Bond laddering (staggering maturities)
- Focus on investment-grade securities for lower risk
- Consider bond ETFs for diversification with lower capital requirements
- Balance duration risk with interest rate environment
Peer-to-Peer Lending
Peer-to-peer lending platforms connect investors directly with borrowers, allowing individuals to act as lenders and earn interest on loans.
Leading platforms and characteristics:
| Platform | Average Returns | Minimum Investment | Loan Types |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prosper | 5.5-9.0% | $25 | Personal |
| Funding Circle | 4.5-6.5% | $500 | Small Business |
| PeerStreet | 6.0-9.0% | $1,000 | Real Estate |
| Upstart | 7.0-15.0% | $100 | Personal |
Risk management in P2P lending:
- Diversify across 100+ loans to mitigate default risk
- Focus on higher credit grade borrowers initially
- Start with smaller investment amounts to learn the platform
- Reinvest returns to compound growth
- Consider secondary markets for liquidity needs
Real Estate-Based Income Streams
Real estate remains one of the most established and reliable forms of passive income, offering multiple avenues for generating returns.
Rental Properties
Residential and commercial rental properties provide ongoing income through tenant payments while potentially appreciating in value over time.
Return metrics:
- Average cap rate (nationwide): 4-10% (location dependent)
- Cash-on-cash return: 6-12% with conventional financing
- Total ROI including appreciation: 10-20% annually in growing markets
Property types comparison:
| Property Type | Average Cap Rate | Typical Down Payment | Management Complexity | Tenant Turnover |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Family | 4-6% | 20-25% | Moderate | Low-Moderate |
| Multi-Family (2-4 units) | 5-8% | 25-30% | Moderate-High | Moderate |
| Apartment Building | 5-10% | 25-35% | High | High |
| Commercial | 6-12% | 30-40% | High | Low |
| Vacation Rental | 8-15% | 25-30% | Very High | Very High |
Implementation strategies:
- House hacking (owner-occupy multi-unit property)
- BRRRR method (Buy, Rehab, Rent, Refinance, Repeat)
- Turnkey property investment
- Value-add opportunities
Management options:
- Self-management (highest returns, most time-intensive)
- Professional property management (7-10% of gross rent)
- Hybrid approaches (self-manage with maintenance contracts)
Real Estate Crowdfunding
Real estate crowdfunding platforms pool capital from multiple investors to finance real estate projects, providing access to commercial-scale opportunities with lower minimum investments.
Platform comparison:
| Platform | Minimum Investment | Average Returns | Accreditation Required | Investment Types |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fundrise | $10 | 8-12% | No | eREITs, eFunds |
| RealtyMogul | $5,000 | 7-15% | Yes (some offerings) | Commercial, Multi-family |
| CrowdStreet | $25,000 | 10-18% | Yes | Commercial, Development |
| Groundfloor | $10 | 7-14% | No | Fix-and-flip loans |
| Arrived Homes | $100 | 5-10% | No | Single-Family Rentals |
Risk considerations:
- Lack of liquidity (typical hold periods 3-7 years)
- Uneven project quality across platforms
- Limited investor control
- Regulatory uncertainties in newer platforms
Short-Term Rentals
Platforms like Airbnb and VRBO have transformed property monetization, allowing owners to generate premium returns compared to traditional long-term rentals.
Revenue potential comparison:
| Market Type | Short-Term Rental Premium vs. Long-Term | Occupancy Rates | Seasonality Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Core | 30-80% | 65-85% | Low |
| Vacation Destination | 50-150% | 45-90% | Very High |
| Suburban | 10-40% | 55-75% | Low |
| Rural/Destination | 40-100% | 40-70% | High |
Operational considerations:
- Higher operational demands than long-term rentals
- Significant pricing optimization opportunities
- Regulatory environment varies dramatically by location
- Automation tools can reduce management burden
Digital and Content-Based Income
The digital economy has created unprecedented opportunities for creating passive income through intellectual property and digital assets.
Blogging and Content Websites
Content websites generate revenue through advertising, affiliate marketing, and product sales by attracting targeted traffic.
Revenue metrics:
- Average RPM (Revenue Per Mille/1000 pageviews): $15-$30
- Traffic requirements for $1,000/month: ~33,000-67,000 monthly pageviews
- Content requirements: 50-100 high-quality articles (1,500+ words each)
- Time to profitability: 12-24 months for most niches
Monetization methods comparison:
| Method | Typical Revenue Range | Traffic Requirements | Implementation Difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Display Ads | $5-$30 RPM | High | Low |
| Affiliate Marketing | 3-50% commission | Moderate | Moderate |
| Digital Products | $10-$500 per product | Low-Moderate | High |
| Sponsored Content | $50-$2,000 per piece | Moderate | Moderate |
| Membership/Subscription | $5-$50 per member monthly | Low | High |
Implementation steps:
- Niche selection and validation
- Content strategy development
- SEO optimization
- Traffic building (18-24 months)
- Monetization implementation
- Scaling content production
- Systems development for maintenance
Digital Products and Online Courses
Digital products provide among the highest profit margins in passive income, with negligible per-unit costs after creation.
Product types and metrics:
| Product Type | Average Price Point | Creation Time | Platform Fees | Update Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| eBooks | $9-$29 | 40-100 hours | 30-70% | Low |
| Online Courses | $97-$2,000 | 100-300 hours | 0-50% | Moderate |
| Templates/Printables | $5-$50 | 10-40 hours | 0-35% | Low |
| Software/Apps | $5-$100/month | 200-1000+ hours | 0-30% | High |
| Photography/Graphics | $5-$200 | Variable | 30-50% | Low |
Sales funnel requirements:
- Lead magnets (freebies for email capture)
- Email nurture sequences (5-10 emails)
- Sales pages and marketing materials
- Payment processing infrastructure
- Delivery mechanisms
- Basic customer support systems
YouTube Channels and Podcast Monetization
Video and audio content platforms provide multiple revenue streams once audience thresholds are reached.
YouTube metrics:
- Monetization threshold: 1,000 subscribers and 4,000 watch hours
- Average RPM: $2-$10 per 1,000 views (niche dependent)
- Content requirements: 50-100 videos for sustainable traffic
- Additional revenue: Sponsorships, affiliate marketing, product sales
Podcast metrics:
- Advertising rates: $15-$30 CPM (cost per 1,000 listeners)
- Monetization threshold: ~5,000-10,000 downloads per episode
- Sponsorship opportunities: Begin at ~1,000 consistent listeners
- Content requirements: 30-50 episodes for audience building
Implementation considerations:
- High production value requirements
- Significant upfront content creation demands
- Competitive landscape analysis
- Distribution and promotion strategies
- Monetization diversification
Print-On-Demand and E-commerce
On-demand product platforms handle production, shipping, and customer service, allowing creators to focus purely on design and marketing.
Platform comparison:
| Platform | Product Types | Profit Margins | Upfront Costs | Fulfillment Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Printful | Apparel, Home Goods | 20-40% | $0 | High |
| Merch by Amazon | T-shirts, Hoodies | 10-30% | $0 | High |
| Redbubble | Wide Range | 10-30% | $0 | Moderate |
| Etsy + POD | Varied | 15-40% | Minimal | Varies |
| Shopify + POD | Custom Shop | 20-50% | $29/month | Varies |
Success requirements:
- Niche audience identification
- Design quality and uniqueness
- Marketing and traffic generation
- Product-market fit validation
- Pricing strategy optimization
Business and System-Based Income
These strategies involve creating or investing in business systems that can operate without the owner’s daily involvement.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS businesses provide software solutions on a subscription basis, offering highly scalable recurring revenue with low marginal costs.
Development approaches:
- Custom development: $10,000-$100,000+ initial investment
- White-label solutions: $3,000-$25,000 setup costs
- No-code/low-code platforms: $50-$500/month ongoing costs
Key metrics:
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): $200-$500 for small business SaaS
- Lifetime Value (LTV): $1,000-$5,000 for typical B2B solutions
- Churn rate benchmarks: 5-7% monthly (acceptable), 2-3% (excellent)
- Average Revenue Per User (ARPU): $50-$200/month for B2B
Operational requirements:
- Customer support systems
- Development and maintenance resources
- Payment processing infrastructure
- Marketing and sales funnels
- Onboarding and retention systems
Vending Machines and Automated Retail
Physical automated retail provides localized passive income opportunities with tangible assets.
Investment and return metrics:
| Machine Type | Initial Cost | Location Fees | Restocking Frequency | Potential Monthly Net |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bulk Candy | $200-$500 | $0-$50 | Monthly | $20-$50 |
| Snack/Beverage | $3,000-$5,000 | $50-$200 | Weekly | $300-$600 |
| Specialized (CBD, etc.) | $5,000-$10,000 | $100-$500 | Bi-weekly | $500-$1,200 |
| Laundromat | $50,000-$300,000 | Lease | Weekly maintenance | $1,000-$5,000 |
| ATM | $2,000-$8,000 | Revenue share | Cash replenishment | $200-$1,000 |
Location types and performance:
- High-traffic retail: Highest revenue, highest fees
- Office buildings: Moderate revenue, lower competition
- Apartment complexes: Steady income, captive audience
- Industrial areas: Lower traffic, lower location costs
Management options:
- Self-service (highest margins, time-intensive)
- Route operators (share 25-40% of revenue)
- Remote monitoring systems
Licensing and Intellectual Property
Creating and licensing intellectual property allows creators to earn royalties from assets used by others.
IP types and royalty structures:
| IP Type | Typical Royalty Rates | Creation Requirements | Protection Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Music | 8-12% streaming, 15-50% sync licensing | Production quality, distribution | Copyright |
| Photography | $0.10-$100+ per use | Portfolio development | Licensing, watermarks |
| Patents | 3-10% of revenue | Innovation, legal filing | Patent application |
| Trademarks | $5,000-$100,000+ licensing | Brand development | Trademark registration |
| Software | 10-50% revenue share | Development expertise | Copyright, patents |
Implementation considerations:
- Legal protection requirements
- Distribution channel development
- Licensing agreement structures
- Enforcement mechanisms
- Portfolio development strategies
Silent Business Partnerships
Investing capital in existing businesses as a silent partner provides ownership income without operational responsibilities.
Partnership structures:
| Structure | Typical Investment | Return Mechanism | Control Level | Risk Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angel Investment | $25,000-$500,000 | Exit/Acquisition | Advisory | Very High |
| Revenue Share | $10,000-$100,000 | % of Revenue | Minimal | High |
| Equity Partnership | Varies | Profit Distribution | Board Seat (possible) | High |
| Debt with Equity | $50,000-$250,000 | Interest + Equity | Covenants | Moderate-High |
Due diligence requirements:
- Financial statement analysis (3-5 years)
- Market and competitive assessment
- Management team evaluation
- Legal structure review
- Growth strategy validation
- Exit opportunity assessment
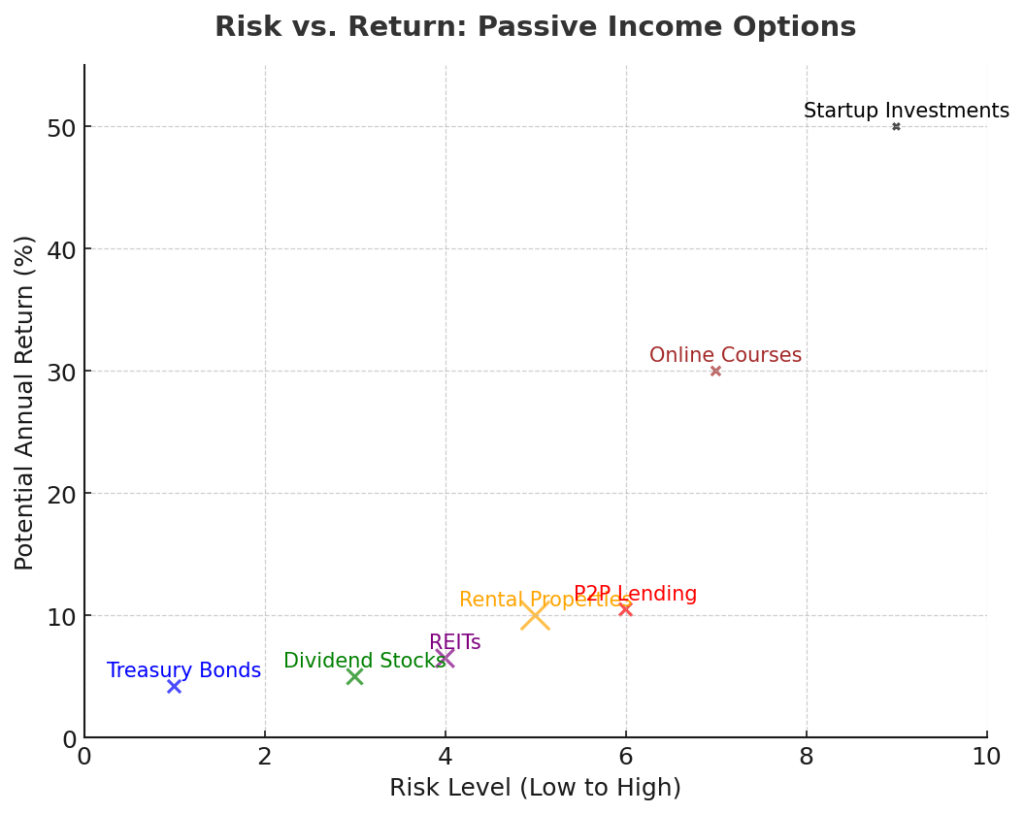
Benefits of Passive Income
Financial Independence and Security
Passive income provides a critical foundation for financial independence by decoupling earnings from active time investment. With sufficient passive income streams, individuals can achieve “FI” (Financial Independence) status, wherein basic living expenses are covered without traditional employment.
Tangible benefits include:
- Reduced dependency on single income source
- Protection against job loss or disability
- Ability to make career decisions based on interest rather than necessity
- Psychological security during economic downturns
- Accelerated retirement timelines
According to a 2024 survey by Financial Independence Network, individuals with passive income sources covering at least 50% of expenses reported 74% higher financial confidence scores compared to those relying exclusively on employment income.
Time Freedom and Lifestyle Design
Perhaps the most compelling advantage of passive income is the liberation of time—humanity’s most precious and non-renewable resource.
Time freedom enables:
- Geographical independence (location flexibility)
- Pursuit of passion projects without economic pressure
- Family and relationship prioritization
- Health and wellness focus
- Extended travel or sabbaticals
- Customized work schedules aligned with personal productivity patterns
Research by the Passive Income Institute found that entrepreneurs with structured passive income systems worked an average of 24.3 hours per week versus 52.7 hours for traditional business owners, while maintaining comparable income levels.
Portfolio Diversification and Risk Mitigation
Implementing multiple passive income streams creates natural portfolio diversification, protecting overall financial health from sector-specific disruptions.
Diversification advantages:
- Protection against industry-specific recessions
- Hedging against inflation through various asset classes
- Geographic risk distribution
- Balance between growth and cash flow
- Multiple economic cycle positioning
- Technological disruption protection
Financial advisors typically recommend 5-7 distinct income streams across different sectors and asset classes to maximize resilience against economic shocks.
Wealth Accumulation and Compound Growth
The mathematical advantage of passive income systems lies in their ability to reinvest earnings without proportional time expansion.
Wealth accumulation mechanisms:
- Reinvestment of passive earnings into additional assets
- Compounding returns across multiple asset classes
- Time leverage through systems and automation
- Tax advantages specific to investment income
- Reduced lifestyle inflation due to income stability
- Capital appreciation alongside cash flow
According to Vanguard research, investors who maintained diversified passive income portfolios demonstrated 23% higher total returns over 10-year periods compared to single-strategy investors with equivalent initial capital.
Challenges and Risks
Initial Time and Capital Requirements
The “passive” nature of these income streams frequently masks substantial upfront investments of time, capital, or both—creating a significant barrier to entry.
Typical requirements by strategy:
| Strategy | Initial Capital Needed | Time Investment | Path to Profitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dividend Investing | $100,000+ | 20-40 hours | Immediate |
| Rental Real Estate | $20,000-$150,000 | 40-100 hours | 1-3 months |
| Content Website | $1,000-$5,000 | 300-500 hours | 12-24 months |
| Online Course | $2,000-$10,000 | 200-400 hours | 3-9 months |
| SaaS Business | $5,000-$100,000 | 500-2,000 hours | 6-18 months |
| Vending Machines | $2,000-$10,000 per unit | 20-50 hours | 1-6 months |
Mitigation strategies:
- Start with lower-capital strategies
- Bootstrap using active income
- Leverage partnerships to share resource requirements
- Implement stepped approach beginning with highest ROI opportunities
- Use nights/weekends during transition from active income
- Reinvest initial passive income to accelerate growth
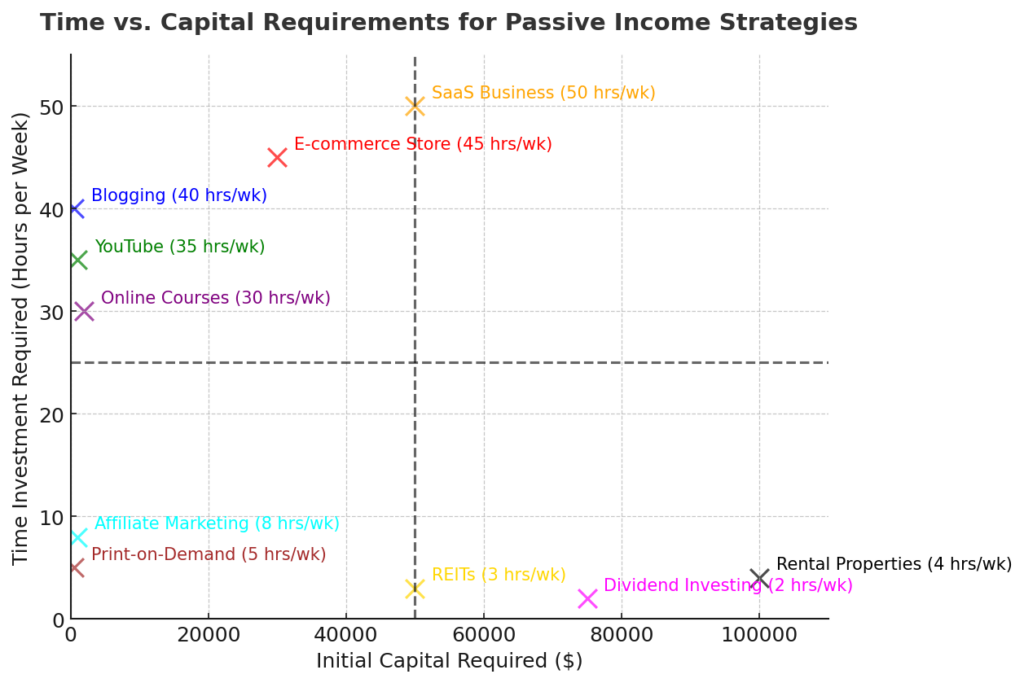
Ongoing Maintenance and System Management
Even the most “passive” income streams require some level of oversight, optimization, and management to maintain and grow.
Maintenance requirements:
| Income Stream | Weekly Time Requirement | Technical Skill Level | Delegation Potential |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dividend Portfolio | 1-2 hours | Moderate | High |
| Rental Property | 2-5 hours | Low-Moderate | Very High |
| Content Website | 5-20 hours | Moderate-High | Moderate |
| Digital Products | 3-10 hours | Moderate | Moderate |
| YouTube Channel | 10-30 hours | Moderate-High | Moderate |
| Vending Routes | 5-20 hours | Low | High |
Optimization techniques:
- Standard operating procedures (SOPs) documentation
- Automation through technology
- Outsourcing to specialized service providers
- Virtual assistant utilization
- Batch processing for routine tasks
- Regular systems audits and refinement
Market Volatility and Economic Cycles
All passive income strategies remain subject to broader market conditions, economic cycles, and sector-specific disruptions.
Vulnerability assessment:
| Income Type | Recession Impact | Inflation Impact | Interest Rate Sensitivity | Regulation Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dividend Stocks | High | Moderate | High | Low-Moderate |
| Real Estate | Moderate | Low (hedge) | Very High | Moderate |
| Bonds | Moderate | High (negative) | Very High | Low |
| Online Business | Moderate | Low | Low | Increasing |
| Intellectual Property | Low-Moderate | Low | Low | Moderate |
| P2P Lending | Very High | Moderate | Moderate | High |
Risk management approaches:
- Counter-cyclical asset allocation
- Geographic diversification
- Regular stress-testing of portfolios
- Cash reserves maintenance
- Strategic debt management
- Insurance and legal protection
Tax Implications and Regulatory Considerations
Passive income streams face varying tax treatment and regulatory frameworks that significantly impact net returns.
Tax considerations by income type:
| Income Source | Tax Classification | Typical Tax Rate | Available Deductions | Reporting Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dividends | Qualified Dividends | 0-20% | Investment expenses | 1099-DIV |
| Rental Income | Passive Activity | Ordinary Income + SE Tax | Depreciation, expenses | Schedule E |
| Digital Products | Self-Employment | Ordinary + 15.3% SE Tax | Business expenses | Schedule C |
| Royalties | Royalty Income | Ordinary Income | Cost of creation | Schedule E |
| Capital Gains | Investment Income | 0-20% (long-term) | Losses, expenses | Schedule D |
Regulatory factors:
- Securities regulations for investment offerings
- Real estate licensing requirements in certain activities
- Tax jurisdiction variations for digital businesses
- International income reporting requirements
- Business entity structure optimization
- Specific industry regulations (finance, health, etc.)
Implementation Strategies
Starting with Limited Capital (Under $10,000)
Building passive income with minimal starting capital requires leveraging personal skills, time investment, and scalable digital assets.
Optimal strategies for limited capital:
- Content-based assets
- Niche website development ($500-$1,000 startup)
- YouTube channel creation ($1,000-$2,000 for basic equipment)
- Self-published books ($500-$1,500 for editing/design)
- Digital product development
- Online courses ($1,000-$3,000 production cost)
- Templates and printables ($200-$500 software costs)
- Mobile applications ($2,000-$5,000 development)
- Micro-investments
- Fractional real estate through platforms like Fundrise ($500 minimum)
- Dividend ETFs with low minimums ($500-$1,000)
- P2P lending with diversified $25-50 loans
- Service arbitrage businesses
- Agency model with outsourced fulfillment
- Dropshipping with minimal inventory
- Print-on-demand merchandise
Implementation roadmap:
- Skill inventory and marketability assessment
- Digital asset platform selection
- MVP (Minimum Viable Product) creation
- Initial marketing through free/organic channels
- Reinvestment of early returns
- Systematic scaling through process documentation
Medium Capital Deployment ($10,000-$50,000)
With moderate capital, investors can access higher-yield opportunities with stronger cash flow potential.
Optimal strategies for medium capital:
- Real estate options
- House hacking (owner-occupied multi-unit, $15,000-$25,000 down payment)
- Turnkey rental property in lower-cost markets ($20,000-$30,000 down payment)
- Short-term rental conversion of existing property
- Higher-yield investments
- Dividend portfolio construction ($20,000-$40,000)
- Private lending secured by real estate ($10,000-$25,000)
- Small business minority stakes
- Semi-automated business models
- E-commerce with 3PL fulfillment
- White-label product development
- Software business acquisition (small apps)
- Mixed approach portfolio
- 40% dividend investments
- 30% real estate participation
- 20% digital asset development
- 10% high-risk/high-reward opportunities
Implementation timeline:
- Months 1-3: Market research and opportunity analysis
- Months 3-6: Initial capital deployment in primary vehicles
- Months 6-9: Systems development and optimization
- Months 9-12: Secondary opportunity development
- Year 2: Reinvestment and portfolio expansion
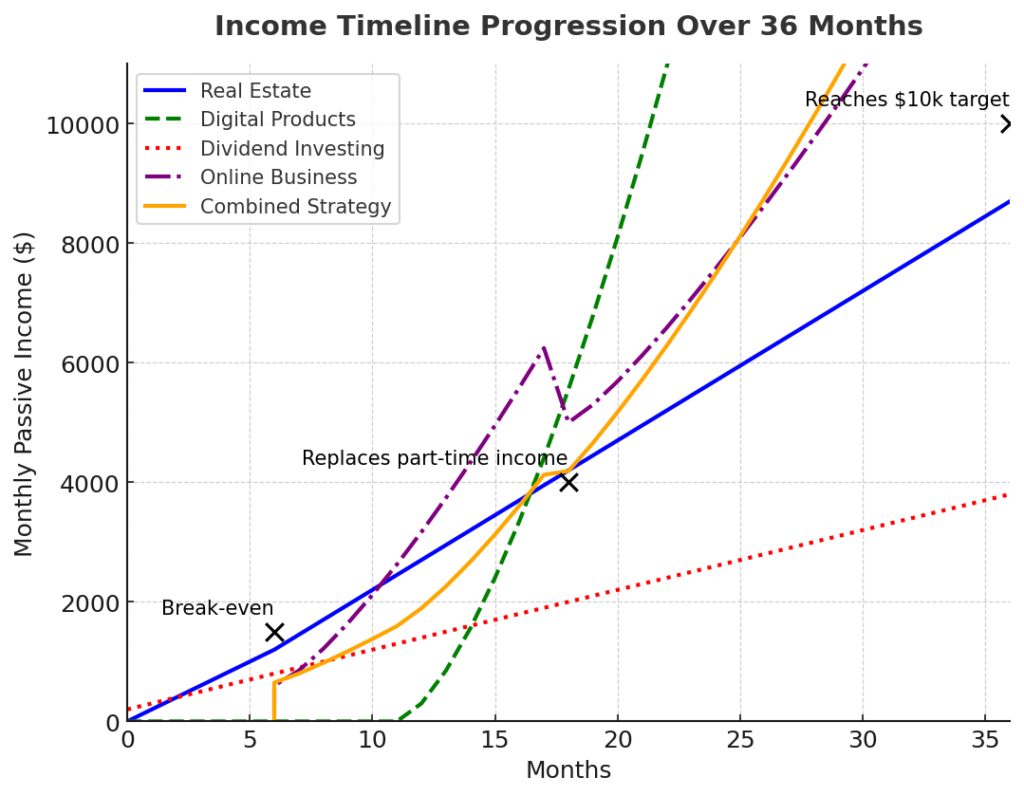
Scaling to $10,000 Monthly ($50,000-$250,000 Capital)
Achieving the $10,000 monthly passive income target typically requires substantial capital base, strategic allocation, and systems leverage.
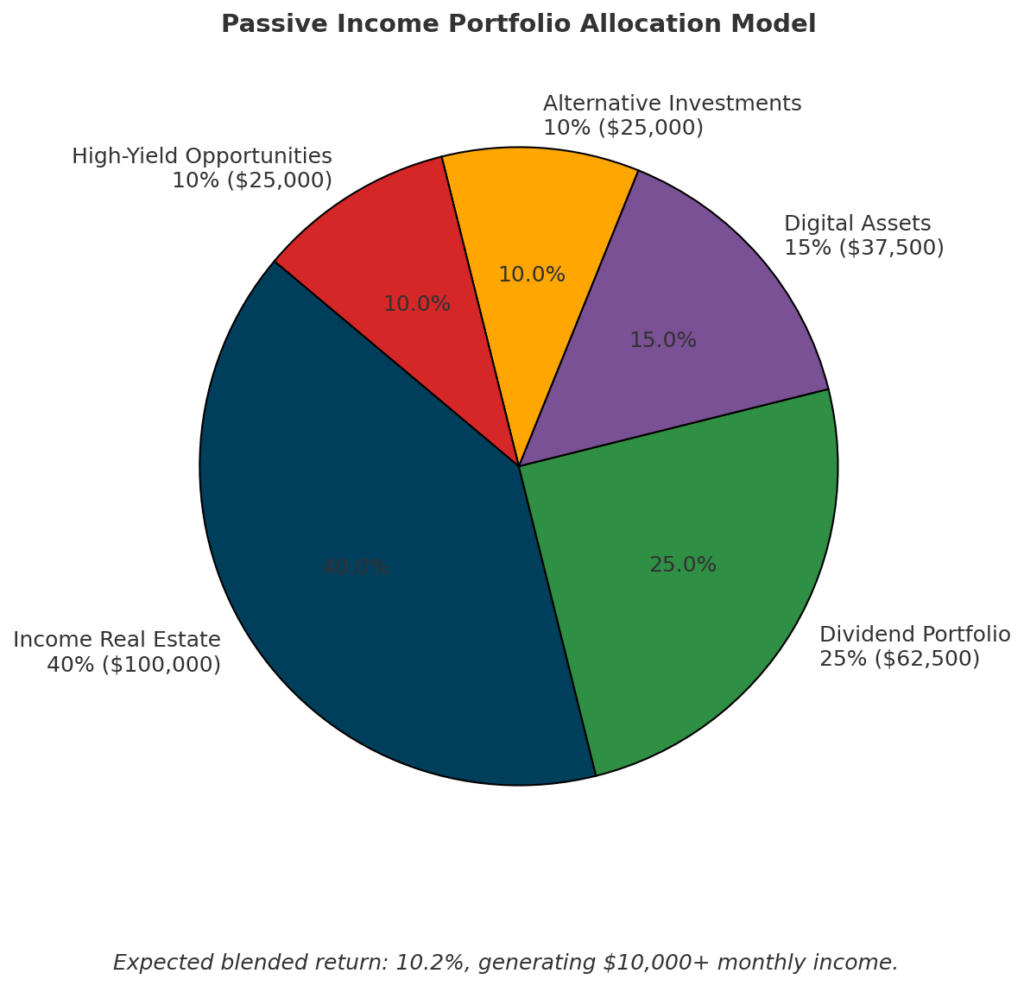
Capital allocation model:
| Asset Class | Allocation | Expected Return | Monthly Income | Time Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Income Real Estate | 40% ($100,000) | 8-12% CoC | $2,500-$3,000 | 5-10 hrs/month |
| Dividend Portfolio | 25% ($62,500) | 4-5% Yield | $1,000-$1,250 | 2-3 hrs/month |
| Digital Assets | 15% ($37,500) | 15-30% ROI | $1,500-$2,500 | 10-20 hrs/month |
| Alternative Investments | 10% ($25,000) | 8-15% Return | $800-$1,250 | 3-5 hrs/month |
| High-Yield Opportunities | 10% ($25,000) | 12-20% Return | $1,000-$1,500 | 5-10 hrs/month |
| TOTAL | $250,000 | 10.2% Blended | $10,000+ | 25-48 hrs/month |
Implementation process:
- Core income foundation establishment (real estate, dividends)
- Operational systems development for each asset class
- Outsourcing and automation implementation
- Performance tracking infrastructure
- Tax optimization strategy
- Reinvestment system for compounding
Timeline to full implementation:
- 90-120 days for initial investment deployment
- 6-12 months for system optimization
- 12-24 months to reach $10,000 monthly target
- 24-36 months to achieve full passivity (under 25 hours monthly)
Advanced Strategies for Experienced Investors ($250,000+)
Investors with substantial capital can implement sophisticated strategies that maximize returns while minimizing time investment.
Advanced implementation options:
- Real estate portfolio development
- Commercial property acquisition
- Development projects with promote structures
- Real estate fund creation
- Business acquisition and systematization
- Existing cash-flowing business purchase
- Operator installation with equity incentives
- Systems and process optimization
- Advanced investment vehicles
- Options income strategies (covered calls, etc.)
- Private equity participation
- Structured settlement investment
- Qualified business income optimization
- Tax strategy integration
- Multiple entity structures
- Geographic tax optimization
- Opportunity zone investments
- Charitable remainder trusts
Wealth preservation components:
- Insurance wrapping strategies
- Estate planning integration
- International diversification
- Inflation hedging allocations
Technology and Tools for Passive Income Management
Automation Platforms and Services
The technological revolution has created unprecedented opportunities for automating passive income management, dramatically reducing ongoing time requirements.
Key automation categories:
| Category | Example Tools | Functions | Monthly Cost | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Property Management | Buildium, AppFolio | Rent collection, maintenance, leasing | $40-$200 | 10-20 hrs/month |
| Investment Management | M1 Finance, Personal Capital | Rebalancing, dividend reinvestment | $0-$100 | 5-10 hrs/month |
| Content Management | WordPress, Zapier, Buffer | Publishing, distribution, updates | $20-$200 | 8-15 hrs/month |
| Customer Service | Intercom, Zendesk | Support ticketing, FAQs, onboarding | $50-$300 | 10-30 hrs/month |
| Financial Tracking | Quickbooks, Xero | Accounting, tax preparation, invoicing | $25-$150 | 5-15 hrs/month |
Implementation best practices:
- Start with core business processes
- Implement measurement before automation
- Focus on integration between systems
- Document processes before automating
- Calculate ROI based on time value
- Layer automation incrementally
Analytics and Reporting Tools
Effective passive income management requires robust tracking systems to monitor performance, identify optimization opportunities, and ensure tax compliance.
Essential analytics components:
| Function | Recommended Tools | Key Metrics | Implementation Difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance Tracking | Tableau, Google Data Studio | ROI, cash flow, capital appreciation | Moderate |
| Market Analysis | Ahrefs, Zillow Research | Competitive positioning, market trends | Moderate-High |
| Financial Forecasting | Excel, Causal | Projected returns, capital requirements | Moderate |
| Tax Optimization | TaxBit, Cointracker | Tax liability, depreciation tracking | Moderate-High |
| Portfolio Management | Sharesight, Stessa | Asset allocation, diversification metrics | Low-Moderate |
Data integration strategies:
- API connections between platforms
- Centralized data warehouse approach
- Regular automated reporting schedules
- Dashboard creation for at-a-glance monitoring
- Exception-based alerting for issues
- Quarterly performance review protocols
Outsourcing and Virtual Team Management
As passive income streams scale, strategic outsourcing becomes essential for maintaining passivity while enabling growth.
Key outsourcing areas:
| Function | Provider Types | Typical Cost | Management Overhead | ROI Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content Creation | Freelancers, Agencies | $15-$150/hour | Moderate | 3-6 months |
| Property Management | Management Companies | 8-12% of revenue | Low | Immediate |
| Technical Maintenance | Developers, Specialists | $25-$150/hour | Moderate | 1-3 months |
| Customer Support | VAs, Support Companies | $5-$25/hour | Moderate-High | 1-2 months |
| Financial Administration | Bookkeepers, CPAs | $25-$200/hour | Low | Immediate |
Team building progression:
- Task-based contractors for specific needs
- Part-time specialized roles for regular requirements
- Full-time virtual assistants for core operations
- Team leaders/managers as operations scale
- Standard operating procedures (SOPs) for all positions
- Performance-based compensation structures
Security and Risk Management Tools
Protecting passive income assets requires robust security measures and risk management systems.
Essential security components:
| Security Need | Solution Options | Implementation Cost | Maintenance Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Asset Protection | Two-factor authentication, password managers | $5-$20/month | Low |
| Business Entity Protection | LLC formation, umbrella insurance | $500-$2,000 initial | Low-Moderate |
| Investment Security | Diversification tools, alerts, fraud monitoring | $10-$100/month | Low |
| Intellectual Property | Trademark/copyright monitoring, DMCA services | $20-$300/month | Moderate |
| Physical Asset Protection | Property insurance, security systems | Varies by asset | Low |
Risk mitigation automations:
- Automated backup systems
- Fraud alert monitoring
- Cash flow warning systems
- Compliance deadline calendars
- Insurance coverage reviews
- Security audit scheduling
Future Trends in Passive Income Strategies
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming passive income ecosystems, creating both opportunities and challenges for investors.
Emerging AI applications:
- Algorithmic content creation reducing production costs
- Predictive analytics for investment timing and selection
- Customer service automation through conversational AI
- Market trend identification using natural language processing
- Personalization engines increasing conversion rates
- Smart contract automation reducing transaction friction
According to McKinsey’s 2024 AI in Business report, passive income businesses implementing AI solutions reported 23% higher efficiency ratios and 18% faster scaling capabilities compared to non-AI counterparts.
Implementation timeline:
- Current: Basic automation and template systems
- 1-2 years: Mainstream conversational AI for customer interaction
- 2-3 years: Predictive analytics for investment optimization
- 3-5 years: Autonomous system management with human oversight
- 5+ years: Fully autonomous business operations possible
Changing Financial and Regulatory Landscape
The passive income environment continues to evolve in response to regulatory changes, tax policies, and financial innovation.
Regulatory trend monitoring:
- Cryptocurrency and digital asset regulation
- Short-term rental restrictions in major markets
- Tax code changes affecting investment properties
- Securities law evolution for crowdfunding platforms
- Cross-border commerce and taxation requirements
- Content monetization platform policy changes
Strategic adaptation approaches:
- Jurisdictional diversification
- Entity structure flexibility
- Regulatory expertise development
- Proactive compliance systems
- Industry association participation
- Policy change monitoring automation
Emerging Passive Income Opportunities
New technologies and market shifts are creating novel passive income categories with substantial growth potential.
High-potential emerging categories:
| Category | Current Stage | Capital Requirements | Growth Potential | Time Horizon |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NFT Royalties | Early Adoption | $5,000-$50,000 | Very High | 3-7 years |
| Tokenized Real Estate | Early Development | $1,000-$100,000 | High | 2-5 years |
| Data Monetization | Early Mainstream | $10,000-$100,000 | Very High | 1-3 years |
| Automated DeFi | Experimental | $5,000-$50,000 | Extremely High | 3-10 years |
| Carbon Credit Markets | Emerging | $25,000-$250,000 | High | 2-7 years |
| Virtual Real Estate | Speculative | $1,000-$100,000 | Unknown | 5-15 years |
Evaluation criteria for emerging opportunities:
- Regulatory clarity and trajectory
- Technical barrier to entry assessment
- Market adoption indicators
- Institutional participation levels
- Infrastructure development status
- Talent migration patterns
Sustainability and Ethical Considerations
The future of passive income increasingly incorporates sustainability and ethical dimensions as both consumer preferences and regulatory environments evolve.
Key sustainability factors:
- Environmental impact of physical assets
- Social contribution of business models
- Governance structures and transparency
- Ethical sourcing and production considerations
- Community impact assessment
- Long-term resource utilization
According to Sustainable Investment Institute data, passive income assets with strong ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) ratings outperformed conventional counterparts by an average of 4.3% annually over the past five years, with particularly strong performance during market downturns.
Implementation strategies:
- ESG screening for investment portfolios
- Sustainability certification for physical assets
- Ethical supply chain verification
- Community benefit programs
- Impact measurement frameworks
- Transparent reporting systems
FAQs – Passive Income Strategies
1. How much capital is realistically needed to generate $10,000 monthly in passive income?
The capital requirements vary significantly based on strategy selection, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Using a blended approach:
- Low-risk approach (primarily dividend stocks, bonds, REITs): $2,000,000 – $3,000,000 (assuming 4-6% annual yields)
- Moderate-risk approach (balanced portfolio including real estate): $1,000,000 – $1,500,000 (assuming 8-12% blended returns)
- Higher-risk approach (business assets, digital properties): $250,000 – $500,000 (assuming 24-48% blended returns)
Most successful passive income portfolios reaching $10,000 monthly implement a staged approach, beginning with smaller targets ($1,000-$3,000 monthly) and reinvesting returns to scale over 3-7 years.
2. How truly “passive” are these income streams? What ongoing time commitments should I expect?
True passivity exists on a spectrum rather than as a binary state. Initial setup typically requires significant active involvement before transitioning to maintenance mode:
- Investment assets (stocks, bonds): 1-3 hours monthly for portfolio review and rebalancing
- Rental properties: 2-5 hours monthly with property management, 5-15 hours without
- Content websites: 5-20 hours monthly for content updates and optimization
- Digital products: 3-10 hours monthly for customer support and updates
- Automated businesses: 5-15 hours monthly for system oversight
The key is implementing robust systems, strategic outsourcing, and appropriate technology to minimize personal time requirements as income scales.
3. What are the tax implications of different passive income strategies?
Tax treatment varies significantly by income type and jurisdiction:
- Dividend income: Generally taxed at preferential qualified dividend rates (0-20% based on income bracket)
- Rental income: Subject to ordinary income tax but offset by depreciation and expense deductions
- Digital product/online business income: Typically subject to ordinary income tax plus self-employment tax (though entity structures can optimize)
- Capital gains: Preferential long-term rates (0-20%) for assets held over one year
- Royalty income: Ordinary income rates but may qualify for QBI deduction under certain circumstances
Consult with a tax professional to implement strategic entity structures, timing strategies, and deduction optimization based on your specific income mix.
4. Which passive income strategies have the lowest barrier to entry for beginners?
For those starting with limited capital and experience:
- Digital content creation (blogs, YouTube): $500-$2,000 startup cost
- Print-on-demand merchandise: $0-$100 to launch first products
- Self-published books: $500-$2,000 for professional editing and design
- Affiliate marketing: $100-$500 for website and basic tools
- Micro-investments through fractional platforms: Starting at $10-$100
The key success factor is selecting an area aligned with existing knowledge, skills, or interests to minimize the learning curve and accelerate implementation.
5. How do I protect my passive income streams during economic downturns?
Recession-proofing strategies include:
- Diversification across uncorrelated asset classes
- Maintaining 6-12 months of operating expenses in liquid reserves
- Focus on necessity-based business models (essential products/services)
- Implementing conservative debt structures (fixed-rate, long-term)
- Developing countercyclical income streams that perform better during downturns
- Geographic diversification to reduce regional economic exposure
- Stress-testing all investments assuming 30-50% revenue reduction
The most resilient passive income portfolios typically maintain 25-30% of assets in countercyclical or non-correlated positions.
6. What are the most common mistakes people make when building passive income?
Frequent pitfalls include:
- Underestimating initial time requirements (“passive” doesn’t mean “no work”)
- Insufficient diversification (over-concentration in a single asset or strategy)
- Inadequate systems development for scaling and maintenance
- Premature scaling before proving concept viability
- Neglecting tax planning and entity structuring
- Failing to account for market cycles in projections
- Underestimating ongoing capital requirements for maintenance and growth
- Insufficient documentation of processes and procedures
Successful implementation requires realistic expectations, thorough planning, and systematic execution with regular reassessment of performance and strategy.
7. How long does it typically take to build meaningful passive income?
Timeline expectations should be calibrated based on strategy and capital availability:
- Investment-based approaches (dividends, bonds): Immediate income proportional to capital deployed
- Real estate: 1-3 months to acquire and stabilize properties
- Content websites: 12-24 months to reach significant traffic and monetization
- Digital products: 3-9 months for creation, launch, and initial sales scaling
- Automated businesses: 6-18 months for development and customer acquisition
Most successful passive income portfolios take 3-5 years of consistent effort and reinvestment to reach substantial income levels ($5,000+ monthly).
8. How do I determine which passive income strategies best match my skills and resources?
Strategic selection should consider:
- Available starting capital (financial resources)
- Time availability for implementation
- Technical skills and learning capacity
- Risk tolerance and income stability needs
- Personal interests and knowledge areas
- Network and relationship assets
- Geographic advantages/limitations
Complete a personal asset inventory across these categories, then match to opportunity requirements using a weighted decision matrix to identify optimal starting strategies aligned with your specific situation.
9. What metrics should I track to evaluate passive income performance?
Key performance indicators include:
- Cash-on-cash return (annual cash flow / total investment)
- Total ROI (including appreciation/equity growth)
- Time efficiency ratio (income / hours required)
- Scalability potential (maximum income capacity)
- Risk-adjusted return (compared to market benchmarks)
- Income stability/volatility metrics
- Tax efficiency (after-tax return rate)
- System resilience (performance during disruptions)
Implement quarterly review protocols evaluating these metrics across all income streams with reallocation of resources toward highest-performing assets.
10. How do I create passive income with no money?
While true passive income typically requires either capital or time investment, zero-capital starting points include:
- Skill leveraging through content creation (using existing equipment)
- Knowledge monetization through affiliate marketing
- Sweat equity partnerships with capital providers
- House hacking using FHA loans (3.5% down payment)
- Service-to-product transformation of existing skills
- Fractional investments using microinvesting platforms ($5-$10)
- Revenue share arrangements with established businesses
The key approach is converting time, knowledge, or skills into assets that can generate ongoing returns without proportional ongoing time investment.
Conclusion – Passive Income Strategies
The journey to $10,000 monthly in passive income represents a transformative financial and lifestyle opportunity that extends far beyond simple monetary benefits.
By systematically building a diversified portfolio of income-generating assets, individuals can achieve unprecedented levels of financial freedom, time autonomy, and long-term security that traditional employment rarely provides.
The most successful passive income strategies share common elements: Systematic implementation, diversification across multiple asset classes, strategic leverage of technology and outsourcing, and continuous optimization of existing income streams.
While the specific combination of income sources should be tailored to individual circumstances, capital availability, and skill sets, the fundamental principles of asymmetric returns – where ongoing income disproportionately exceeds ongoing effort – remain consistent across approaches.
Looking forward, the passive income landscape continues to evolve with technological innovations like AI, machine learning, and blockchain creating unprecedented opportunities alongside traditional stalwarts like real estate and dividend investing.
Those who develop expertise in evaluating, implementing, and optimizing diverse income streams position themselves not just for current prosperity but for adaptability to emerging opportunities in the changing financial ecosystem.
The ultimate passive income blueprint isn’t merely about reaching a specific monthly dollar figure – it’s about creating a resilient, adaptable financial system that provides sustainable freedom and security in an increasingly uncertain economic environment.
For your reference, recently published articles include:
- Investment Research Platforms That Give You the Edge: Institutional Tools for Exceptional Returns
- Alternative Data Analytics: All You Need To Know About Wall Street’s Best-Kept Secret
- Outperform 90% Of Investors: Best Advice On Investment Benchmarking Tools
- Trading Fee Comparison: Your 2025 Guide to Commission-Free Platforms
- Investment Tax Optimization: The Ultimate Guide To Save Legally
………………………………………………..
Important Notice: The information in this article is for general and public information purposes only. It solely reflects Didi Somm’s or his Staff’s opinion, and no responsibility can be assumed for errors or omissions in the service’s contents. For details, please check the Disclaimer at the bottom of the homepage.

