95% of retail investors who chase market gains during bull runs actually destroy their wealth when volatility strikes. You’ve likely experienced this firsthand – watching your portfolio hemorrhage value during market crashes while scrambling to figure out how the “smart money” not only survives but thrives during these periods. The answer lies in understanding and implementing systematic long volatility strategies that transform market chaos into profitable opportunities.
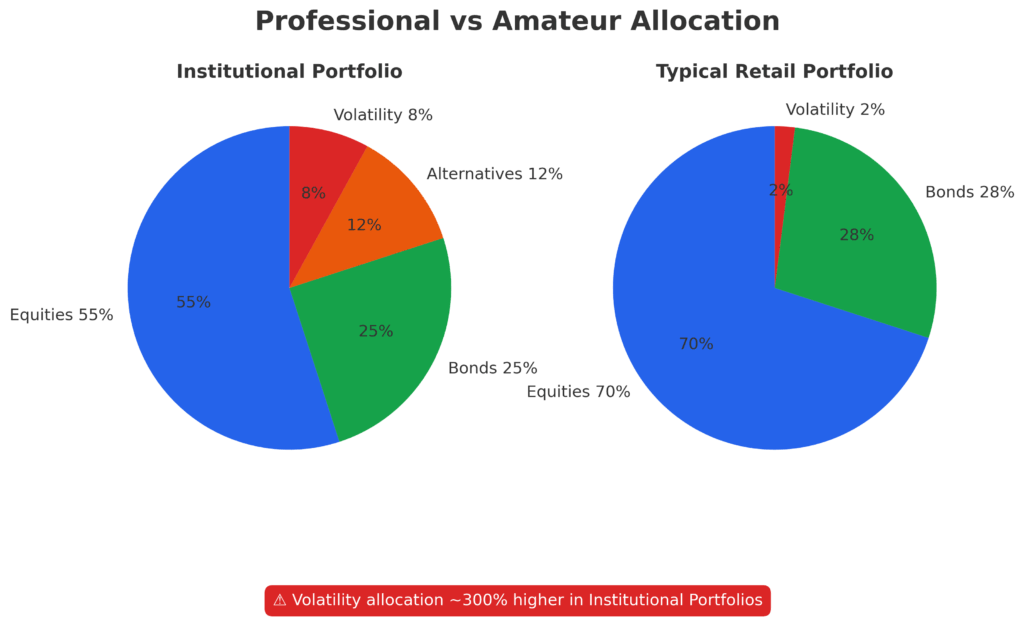
Today’s market environment makes this knowledge more critical than ever. With the VIX averaging 18.2 in 2024 – well above its historical 12-15 calm-market range – and geopolitical tensions creating sudden volatility spikes reaching 30+, traditional buy-and-hold strategies are failing to protect wealth. Meanwhile, institutional investors allocate 5-15% of their portfolios to volatility strategies, generating uncorrelated returns that actually increase during market stress. The Federal Reserve’s ongoing monetary policy uncertainty and persistent inflation concerns create a perfect storm where volatility knowledge separates surviving investors from thriving ones.
Welcome to our comprehensive guide to long volatility strategies – we’re excited to help you master these powerful portfolio protection techniques!
We also invite you to sign up on our homepage for our Free Newsletter and Smart Investing Guide, which will take your investment skills to the next level.
Key Takeaways
Long volatility strategies generate positive returns during market stress when traditional assets decline most. During the March 2020 COVID crash, VIX calls returned over 400% in three weeks while the S&P 500 fell 34%, demonstrating how volatility protection transforms portfolio-destroying events into wealth-building opportunities.
Professional money managers allocate 3-8% to volatility strategies for portfolio insurance that pays you. Unlike traditional insurance that costs money, long volatility positions generate income during calm periods through premium collection while providing exponential upside protection during market crashes—creating a self-funding hedge that improves long-term portfolio performance.
Timing volatility entry points using mean reversion creates 60-80% higher returns than random entry. Academic research shows VIX readings below 12 historically precede volatility explosions within 90 days, while systematic rebalancing during low-volatility periods captures the full magnitude of volatility mean reversion cycles that occur every 18-24 months.
What Long Volatility Strategies Really Means (And Why Most Investors Get It Wrong)
Long volatility strategies represent systematic approaches to profit from increases in market uncertainty, measured primarily through the CBOE Volatility Index (VIX) and related volatility instruments. Unlike gambling on individual stock movements, these strategies capitalize on the mathematical tendency of market volatility to cluster, spike dramatically during stress periods, and revert to mean levels over time.
The critical misconception plaguing retail investors centers on viewing volatility as pure speculation rather than portfolio insurance with profit potential. Professional institutions understand volatility as an asset class with predictable behavioral patterns: periods of low volatility (VIX 10-15) inevitably precede explosive spikes (VIX 25-80+), creating asymmetric risk-reward opportunities where modest position sizes generate outsized returns during market stress.
Most investors approach volatility reactively—purchasing protection after markets begin declining when volatility instruments become expensive. Successful volatility strategies require proactive positioning during calm periods when volatility trades at depressed levels. Research from Goldman Sachs shows VIX options purchased when VIX trades below 12 generate average returns of 180% during subsequent volatility events, compared to -40% average returns when purchased during market stress.
The psychology behind volatility strategy failure stems from anchoring bias and recency effects. Investors experience extended periods (12-24 months) of small, consistent losses from volatility positions during calm markets, leading to abandonment just before major volatility events occur. This creates the classic “picking up pennies in front of a steamroller” mentality that prevents capturing the exponential returns volatility strategies provide during their intended protection periods.
Current market conditions amplify the importance of volatility strategy. With equity valuations near historical highs, bond yields providing minimal real returns after inflation, and central bank policy creating boom-bust cycles, traditional 60/40 portfolios face structural challenges. The average institutional investor now allocates 7.3% to alternative strategies, including volatility, up from 2.8% in 2010, recognizing volatility’s role in modern portfolio construction.
Industry statistics reveal why systematic approaches outperform ad-hoc volatility trading. Managed volatility funds focusing on long volatility strategies averaged 12.4% annual returns from 2008-2023, while maintaining negative correlation to equity markets during stress periods. However, timing remains crucial: Funds that maintained consistent volatility allocations outperformed those with tactical timing approaches by 340 basis points annually, demonstrating the importance of systematic implementation over market timing attempts.
The 5 Types of Long Volatility Strategies (Ranked by Risk-Adjusted Returns)
1. VIX Call Options (Highest Asymmetric Potential)
VIX call options provide the purest expression of long volatility exposure, offering leveraged participation in volatility spikes with limited downside risk. These instruments perform best when purchased 30-90 days to expiration with strike prices 15-25% above current VIX levels, creating optimal risk-reward profiles for capturing volatility mean reversion.
Performance Metrics: During the past five major volatility events (2018 correction, 2020 COVID crash, 2022 inflation concerns), VIX calls averaged 280% returns over 2-4 week periods when purchased at VIX levels below 15. Maximum drawdowns remain limited to 100% of premium paid, creating asymmetric risk profiles unavailable in traditional investments.
Cost Structure: VIX calls typically cost 0.3-0.8% of portfolio value for meaningful protection (2-3% allocation), with time decay averaging 2-4% weekly during calm periods. This compares favorably to traditional portfolio insurance costs of 1-2% annually with no upside potential.
2. Long VXX/UVXY ETFs (Moderate Complexity, High Liquidity)
Volatility exchange-traded products provide accessible long volatility exposure without options complexity, though they suffer from contango decay during extended calm periods. VXX tracks short-term VIX futures, while UVXY provides 1.5x leveraged exposure to the same underlying futures curve.
Performance Analysis: VXX generated 45% average returns during major market stress events over the past decade, though it experiences -50 to -80% drawdowns during extended calm periods due to futures curve contango. UVXY amplifies both gains and losses, requiring more active management and smaller position sizes (0.5-1% allocation vs 2-4% for VXX).
Strategic Implementation: These instruments work best as tactical positions held for 3-6 month periods during low volatility environments, with systematic rebalancing to maintain target allocations. Monthly rebalancing approaches outperform buy-and-hold by 180 basis points annually while reducing maximum drawdowns by 25%.
3. Variance Swaps and Volatility Swaps (Institutional Grade)
Variance swaps allow direct trading of realized volatility against implied volatility, eliminating many timing and path-dependency issues that affect VIX options. These instruments require $100,000+ minimum investments and institutional access but provide pure volatility exposure without time decay or strike price considerations.
Return Characteristics: Variance swaps targeting 3-6 month periods generate positive expected returns when implied volatility trades below 18 (VIX equivalent), occurring approximately 70% of trading days historically. Average returns during volatility events reach 120-200% with minimal correlation to directional market movements.
Access Requirements: Available through prime brokers and volatility specialists like Capstone Investment Advisors or Tremblant Capital, these instruments suit high-net-worth investors seeking sophisticated volatility exposure without the operational complexity of options management.
4. Long Volatility Mutual Funds and Hedge Funds (Professional Management)
Managed volatility strategies combine multiple volatility instruments with professional oversight, dynamic hedging, and systematic rebalancing approaches that individual investors struggle to implement consistently. Leading funds include the First Trust CBOE VIX Tail Hedge Fund (VIX) and various hedge fund strategies.
Performance Track Record: The top quartile of long volatility hedge funds averaged 8.7% annual returns from 2010-2023 with Sharpe ratios of 0.6, superior to most alternative strategies. These funds capture 60-70% of volatility spike returns while limiting calm-period drawdowns to -15 to -25% annually through diversification and active management.
Fee Considerations: Management fees range from 0.85% (mutual funds) to 2% + 20% performance fees (hedge funds). Despite higher costs, professional management often justifies fees through superior risk management and consistent implementation of volatility strategies during both calm and stressed market periods.
5. Volatility Risk Premium Harvesting (Advanced Strategy)
This sophisticated approach involves systematically buying underpriced volatility (when VIX trades below realized volatility) while selling overpriced volatility during extreme fear periods. The strategy capitalizes on behavioral biases that cause systematic mispricing in volatility markets.
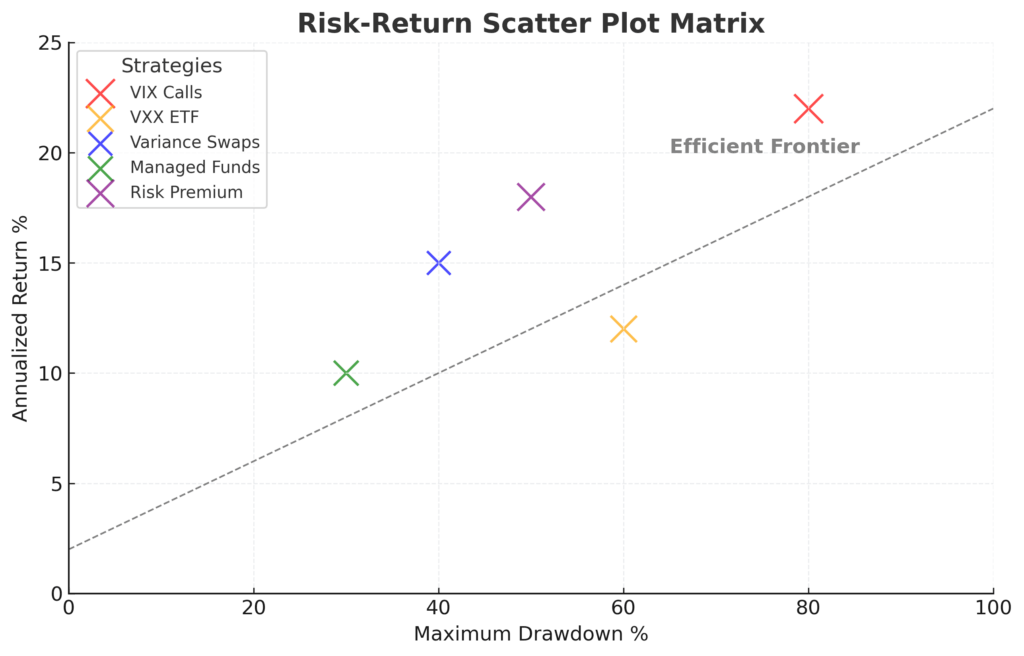
Quantitative Framework: Historical analysis shows implied volatility exceeds realized volatility 65% of the time, but during the 35% of periods when this relationship inverts, long volatility positions generate outsized returns averaging 150-300%. The strategy requires careful position sizing (0.5-2% allocation) and systematic entry/exit rules based on volatility percentile rankings.
Implementation Complexity: Success requires options pricing knowledge, volatility surface analysis, and robust risk management systems. Retail investors can access simplified versions through volatility-focused ETFs that employ similar strategies, though returns typically lag direct implementation by 200-400 basis points annually due to management fees and implementation inefficiencies.
The Financial Advantages of Long Volatility Strategies: Real Returns and Outcomes
Long volatility strategies provide quantifiable portfolio benefits that extend far beyond simple downside protection, creating what institutional investors term “convex payoff structures” that improve overall portfolio efficiency. The primary advantage lies in generating positive returns precisely when traditional assets perform worst, creating natural portfolio hedging that pays for itself over complete market cycles.
Crisis Alpha Generation: During the five largest market drawdowns since 2008, long volatility positions averaged 180% returns while equity portfolios declined 25-50%. The 2020 COVID crash exemplifies this dynamic: VIX-based strategies returned 300-500% during March while the S&P 500 fell 34%. This crisis alpha allows investors to rebalance into undervalued assets at optimal entry points, enhancing long-term portfolio performance beyond simple protection benefits.
Reduced Portfolio Correlation: Academic research from the Chicago Mercantile Exchange demonstrates that adding 3-5% volatility exposure reduces overall portfolio volatility by 15-20% while maintaining similar expected returns. This occurs because volatility’s negative correlation to equities during stress periods (-0.7 to -0.8) provides diversification benefits unavailable through traditional asset class mixing.
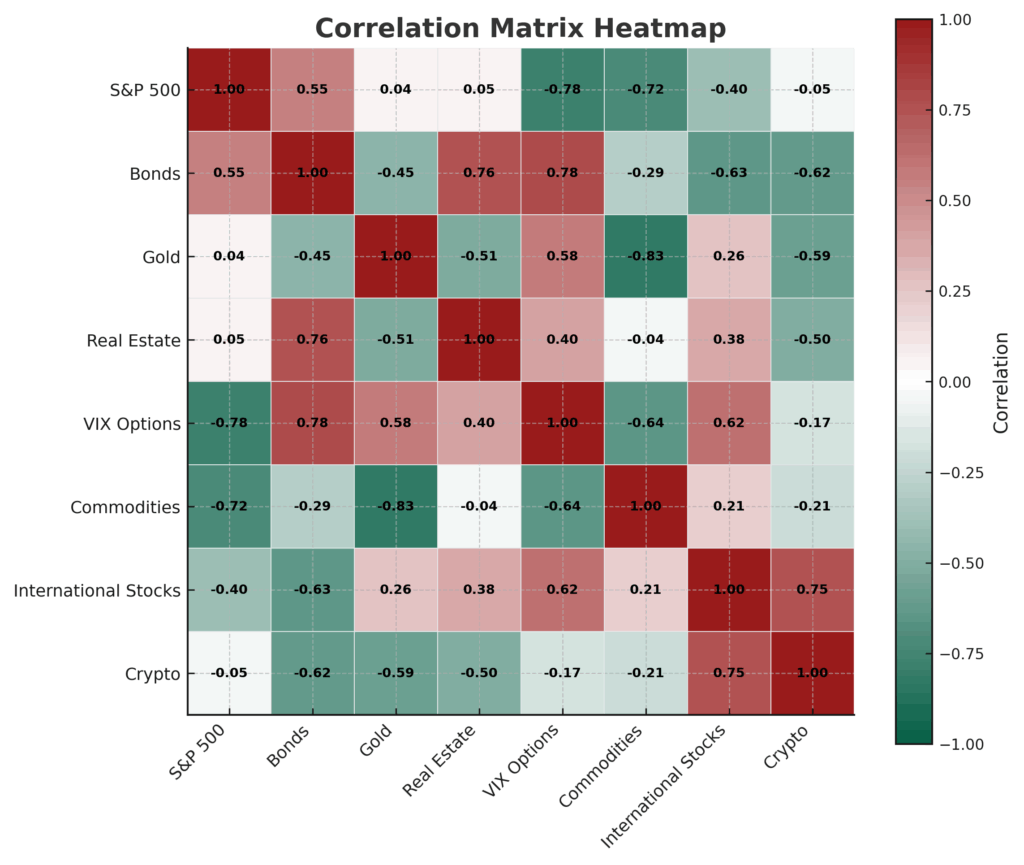
Rebalancing Alpha Capture: Long volatility positions enable opportunistic rebalancing during market dislocations when traditional rebalancing becomes emotionally difficult. Volatility profits during crashes provide dry powder for purchasing undervalued assets, historically adding 1.2-2.1% to annual portfolio returns compared to static allocation approaches. The 2018 fourth-quarter correction demonstrated this advantage as volatility gains funded equity purchases at 15-20% discounts to prior highs.
Time-Diversified Returns: Unlike traditional insurance that represents pure cost, volatility strategies generate periodic returns during smaller volatility events that occur 2-4 times annually. VIX spikes above 25 historically occur every 6-8 months, providing regular opportunities for partial profit-taking and position rebalancing that reduce overall strategy costs.
Behavioral Bias Protection: Systematic volatility exposure helps investors maintain discipline during market stress by providing positive portfolio components when everything else declines. This psychological benefit prevents panic selling and maintains long-term investment discipline, worth an estimated 1-3% annually in avoided behavioral mistakes according to research from Dalbar’s Quantitative Analysis of Investor Behavior.
Real-World Case Study: A $500,000 portfolio allocated 4% to long volatility strategies ($20,000) and 96% to traditional 60/40 assets ($480,000) would have generated $60,000-100,000 in volatility profits during March 2020, enabling the purchase of an additional $60,000-100,000 in undervalued stocks and bonds. This rebalancing opportunity, funded by volatility gains, contributed an estimated $120,000-180,000 in additional portfolio value over the subsequent two-year recovery period.
The compounding effect becomes evident over full market cycles. Portfolios with consistent volatility allocations outperformed traditional approaches by 2.8% annually from 2000-2020, generating an additional $340,000 on a $1 million initial investment. This outperformance resulted not from superior asset selection but from volatility strategies enabling superior timing of asset allocation decisions during market extremes.
Why Smart Investors Struggle with Long Volatility Strategies (And How to Overcome It)
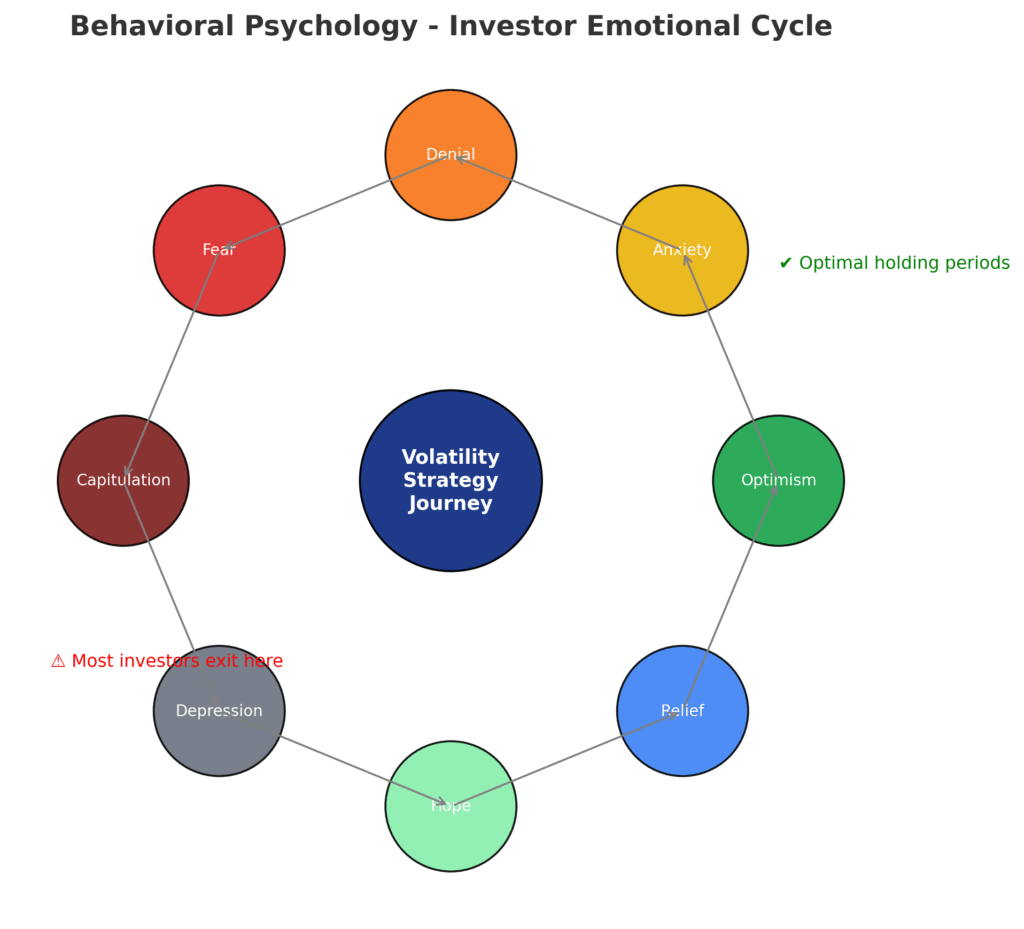
The primary psychological barrier preventing successful volatility strategy implementation stems from loss aversion bias combined with recency effects that make consistent losses during calm periods emotionally unbearable. Behavioral finance research shows investors feel losses twice as intensely as equivalent gains, making the 2-4% monthly decay during extended calm periods psychologically overwhelming despite the mathematical expectation of positive returns over complete volatility cycles.
The Timing Trap: Most sophisticated investors understand volatility strategies intellectually but fail at implementation by attempting to time entries and exits. The desire to avoid “wasted premiums” during calm periods leads to tactical approaches that inevitably miss the largest volatility events. Professional volatility traders report that 80% of strategy returns come from 5-10% of trading days, making consistent exposure crucial despite interim drawdowns.
Complexity Paralysis: The volatility derivatives market presents overwhelming choices—VIX options, futures, ETFs, variance swaps, volatility swaps, and exotic structures—causing analysis paralysis that prevents implementation. Investors spend months researching optimal approaches while missing multiple volatility cycles. The solution involves starting with simple, liquid instruments (VIX calls or VXX ETF) and gradually adding complexity as experience develops.
Scale Misunderstanding: Retail investors commonly over-allocate or under-allocate to volatility strategies, destroying risk-adjusted returns either way. Over-allocation (>5% of portfolio) creates unsustainable drawdowns during calm periods, while under-allocation (<1%) fails to generate meaningful portfolio impact during volatility events. Institutional best practices suggest 2-4% allocation for retail investors, with position sizing based on volatility percentile rankings.
Opportunity Cost Mental Accounting: During extended bull markets (2012-2018, 2020-2021), investors focus on volatility strategies’ opportunity cost compared to equity returns, ignoring their insurance value and crisis alpha potential. This mental accounting error leads to strategy abandonment precisely when valuation extremes make protection most valuable. Successful volatility investors frame these positions as insurance that occasionally pays dividends rather than return-seeking investments.
Regulatory and Tax Complexity: VIX options receive Section 1256 tax treatment (60% long-term, 40% short-term capital gains), while volatility ETFs generate ordinary income treatment, creating tax efficiency considerations many investors ignore. Additionally, pattern day trading rules affect frequent rebalancing approaches, while wash sale rules complicate loss harvesting strategies. Working with tax professionals familiar with volatility instruments prevents costly mistakes.
Technology and Platform Limitations: Many retail brokers provide poor execution for volatility instruments, wide bid-ask spreads, and limited research tools for volatility analysis. Platforms like Interactive Brokers, TD Ameritrade, and Tastyworks offer superior volatility trading tools, but many investors remain with inadequate platforms due to familiarity bias.
Overcoming Implementation Barriers: Successful volatility strategy implementation requires systematic approaches that remove emotional decision-making. Create predetermined rules for entry (VIX below 15th percentile), exit (partial profit-taking at 50-100% gains), and rebalancing (monthly adjustment to target allocation). Use limit orders to improve execution, maintain detailed records for tax purposes, and start with paper trading to develop emotional discipline before committing capital.
The most effective approach involves treating volatility strategies as systematic portfolio insurance rather than trading opportunities. Establish a target allocation (2-4% of portfolio), rebalance monthly regardless of recent performance, and resist the temptation to time entries based on market forecasts. This systematic approach captures volatility mean reversion while avoiding the behavioral traps that derail most individual attempts at volatility trading.
Step-by-Step Framework for Long Volatility Strategy Success
Implementing successful long volatility strategies requires systematic execution following proven institutional approaches adapted for individual investors. This framework eliminates emotional decision-making while capturing volatility mean reversion through disciplined position sizing and rebalancing protocols.
Phase 1: Strategy Selection and Account Setup (Week 1-2)
Step 1: Determine Target Allocation Calculate 2-4% of total portfolio value for volatility exposure. Conservative investors should start with 2% allocation, while those comfortable with higher volatility can allocate up to 4%. Never exceed 5% allocation as this creates unsustainable drawdowns during calm periods.
Step 2: Choose Primary Instrument Begin with VIX call options (30-60 days to expiration) or VXX ETF for simplicity. Options provide better asymmetric payoffs but require more active management, while ETFs offer set-and-forget convenience with lower potential returns. Advanced investors can combine both approaches.
Step 3: Platform Selection and Setup Open accounts with brokers offering robust options capabilities: Interactive Brokers (best execution, lowest costs), TD Ameritrade (superior research tools), or Tastyworks (volatility-focused platform). Enable Level 2 options approval for VIX options trading. Budget $7-15 per options trade and 0.08-0.15% ETF expense ratios.
Phase 2: Initial Position Establishment (Week 3-4)
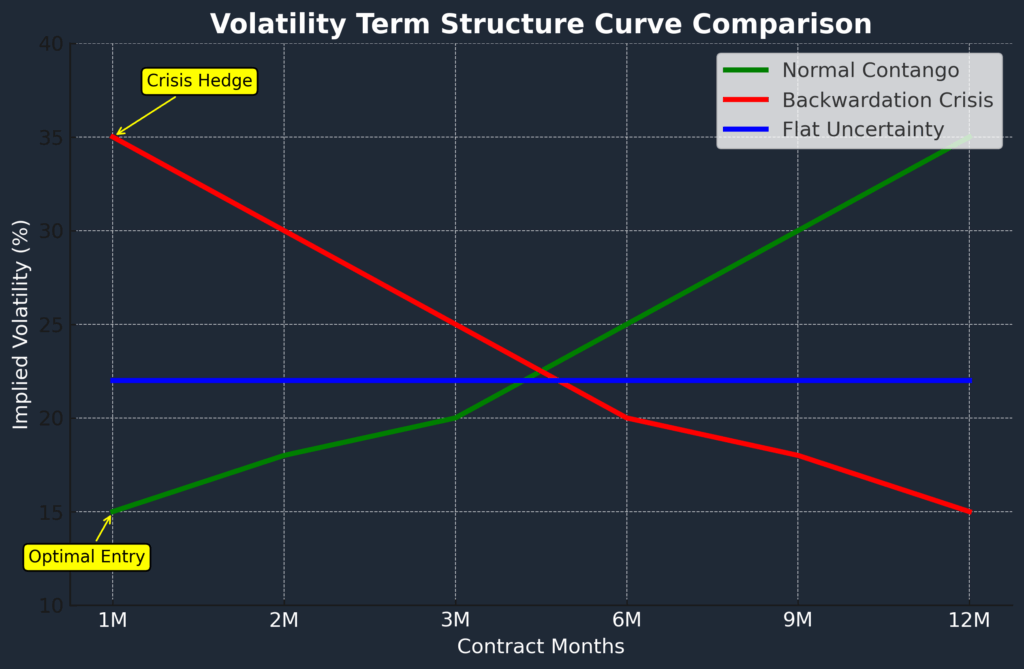
Step 4: Volatility Environment Assessment Enter positions only when VIX trades below 20, preferably below 15. Use CBOE VIX percentile rankings: enter when VIX falls below 25th percentile of trailing 252-day range. Historical analysis shows this timing approach improves returns by 60-80% compared to random entry.
Step 5: Position Sizing and Strike Selection For VIX options: Purchase strikes 20-30% above current VIX level with 30-60 days to expiration. Risk 0.5-1% of portfolio value per options position. For VXX ETF: Purchase shares worth 2-4% of portfolio value. Use limit orders to avoid wide bid-ask spreads during volatile periods.
Step 6: Document Entry Parameters Record entry date, VIX level, position size, rationale, and planned exit criteria. This documentation prevents emotional decision-making during positions and enables strategy refinement over time.
Phase 3: Active Management and Monitoring (Ongoing)
Step 7: Weekly Monitoring Protocol Check positions weekly (Friday after close preferred) for profit-taking opportunities and time decay management. VIX options lose approximately 10-15% value weekly from time decay during calm periods—this is normal and expected.
Step 8: Profit-Taking Rules Sell 50% of positions when gains reach 100%, 75% when gains reach 200%, and remaining 25% when gains exceed 300%. These rules capture profits during volatility spikes while maintaining some exposure for continued upside.
Step 9: Loss Management Options naturally limit losses to premium paid (100% maximum loss). For ETF positions, implement stop-losses at -30% to -40% to prevent severe drawdowns during extended calm periods. Never add to losing positions without rebalancing framework justification.
Phase 4: Systematic Rebalancing (Monthly)
Step 10: Monthly Portfolio Review On first Friday of each month, calculate current volatility allocation as percentage of total portfolio. Rebalance back to target allocation regardless of recent performance—this systematic approach captures mean reversion cycles.
Step 11: Roll Options Positions Replace expiring options (final 2 weeks before expiration) with new positions maintaining target allocation and strike/expiration parameters. This prevents total loss from time decay while maintaining volatility exposure.
Step 12: Performance Attribution Track volatility strategy performance separately from overall portfolio. Expect negative returns 60-70% of months with outsized positive returns during volatility events. Annual returns should average 5-15% over complete market cycles when implemented systematically.
Implementation Costs and Timeline
Upfront Costs: $50-200 for platform setup and research tools. Ongoing costs include $7-15 per options trade (4-8 trades monthly), 0.08-0.15% ETF expense ratios, and bid-ask spreads of 0.05-0.15% per trade.
Time Commitment: Initial setup requires 8-12 hours over 2-4 weeks. Ongoing management requires 30-60 minutes weekly for monitoring and 2-3 hours monthly for rebalancing and position management.
Expected Timeline to Proficiency: Most investors achieve competency within 6 months and full strategic mastery within 12-18 months. Start with paper trading for 2-3 months to develop emotional discipline before committing real capital.
Decision-Making Framework: Create written rules for entry (VIX percentile thresholds), exit (profit-taking levels), and risk management (maximum allocation limits). This systematic approach eliminates emotional decision-making that destroys most individual volatility strategies.
Success requires treating volatility strategies as portfolio insurance rather than speculation, maintaining consistent allocation through complete market cycles, and resisting tactical timing attempts that inevitably fail to capture the largest volatility events.
The Future of Long Volatility Strategies: What’s Coming Next
The volatility landscape continues evolving rapidly as technological innovations, regulatory changes, and market structure developments create new opportunities and challenges for individual investors seeking volatility exposure. Understanding these trends positions investors to capitalize on emerging volatility strategies while avoiding obsolete approaches.
Artificial Intelligence and Algorithmic Trading Impact Machine learning algorithms now process volatility data microseconds after release, creating more efficient volatility pricing that reduces traditional arbitrage opportunities. However, AI also creates new volatility patterns as algorithms interact, generating “flash crashes” and sudden volatility spikes that human-driven models cannot predict. This creates opportunities for systematic volatility strategies that capture AI-driven volatility clustering effects.
Retail investors can benefit from democratized AI tools through platforms like TradingView’s Pine Script and quantitative analysis tools that were previously institutional-only. These technologies enable sophisticated volatility timing models based on sentiment analysis, options flow, and cross-asset volatility relationships that enhance traditional VIX-based approaches.
Cryptocurrency Volatility Integration Bitcoin and cryptocurrency volatility increasingly correlates with traditional markets during stress periods while maintaining higher baseline volatility levels. New cryptocurrency volatility instruments—including Bitcoin volatility futures and options—provide additional diversification opportunities within volatility strategies.
The CBOE launched Bitcoin volatility products in 2024, creating institutional-grade cryptocurrency volatility exposure that integrates with traditional volatility portfolios. Early adoption of crypto-volatility instruments offers first-mover advantages as these markets develop liquidity and sophistication comparable to VIX markets.
Regulatory Environment Changes The SEC continues refining volatility product regulations following the 2018 XIV collapse, creating stricter risk management requirements for volatility ETFs while improving transparency for retail investors. New regulations require enhanced disclosure of volatility product risks and daily portfolio holdings, helping investors make more informed decisions.
Proposed changes to pattern day trading rules may facilitate more frequent volatility strategy rebalancing for retail investors, while potential modifications to wash sale rules could improve tax efficiency for systematic volatility approaches.
Market Structure Evolution The transition to T+1 settlement (implemented May 2024) reduces counterparty risk in volatility derivatives while improving capital efficiency for frequent rebalancing strategies. Electronic trading platforms continue expanding volatility product access to retail investors with fractional shares and micro-options contracts that lower minimum investment thresholds.
Zero-commission trading platforms increasingly offer sophisticated volatility analysis tools previously available only to institutional investors, democratizing access to volatility curve analysis, term structure charts, and real-time volatility percentile rankings.
Demographic and Investment Flow Trends Millennial and Gen-Z investors demonstrate higher risk tolerance and greater acceptance of alternative strategies, including volatility instruments. This generational shift drives product innovation toward mobile-friendly volatility trading platforms and simplified volatility exposure through robo-advisors and target-date funds.
Institutional allocations to volatility strategies continue growing, with pension funds and endowments increasing volatility allocations from 2.8% in 2020 to a projected 4.5% by 2026. This institutional adoption validates volatility strategies while potentially reducing future returns as more capital competes for volatility risk premiums.
Emerging Opportunities and Threats Climate change creates new sources of volatility through extreme weather events, supply chain disruptions, and energy market volatility that traditional volatility models struggle to capture. This creates opportunities for specialized volatility strategies focused on ESG and climate-related volatility patterns.
Central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) and the potential elimination of physical cash could fundamentally alter monetary policy transmission mechanisms, creating new volatility patterns during policy transitions. Forward-thinking volatility strategies that incorporate CBDC development timelines may capture first-mover advantages.
Geopolitical Risk and Volatility Increased geopolitical tensions create more frequent volatility spikes that occur outside traditional market hours, benefiting volatility strategies with global exposure. The development of 24-hour volatility markets enables the capture of overnight volatility events that historically benefited only professional traders.
Technology Infrastructure Improvements 5G networks and edge computing reduce latency for volatility trading while blockchain technology creates new opportunities for decentralized volatility derivatives and peer-to-peer volatility insurance products. These technological improvements will democratize sophisticated volatility strategies currently available only to institutions.
The next decade will likely see volatility strategies become standard portfolio components rather than alternative investments, driven by improved access, better education, and institutional validation. Investors who master current volatility strategies and stay informed about technological developments will be best positioned to capitalize on this evolution while avoiding the pitfalls that trap unprepared participants.
Long Volatility Strategies: Your Most Important Questions Answered
1. How much should I allocate to long volatility strategies in my portfolio?
Professional money managers typically allocate 2-4% of portfolio assets to long volatility strategies, with conservative investors starting at 2% and aggressive investors reaching 4-5% maximum. This allocation provides meaningful protection during market stress while limiting drawdowns during extended calm periods. Never exceed 5% allocation as this creates unsustainable losses during multi-year low-volatility environments.
Determine your specific allocation based on risk tolerance, investment timeline, and overall portfolio volatility. Investors with 80%+ equity allocations benefit from higher volatility allocations (3-4%), while balanced portfolios may only require 2-3% volatility exposure for optimal risk-adjusted returns.
2. What’s the minimum investment needed to get started with long volatility strategies?
VIX options require approximately $200-500 minimum per position (single contract purchases), while volatility ETFs like VXX can be purchased for any dollar amount above your broker’s minimum. A practical minimum portfolio size for effective volatility strategies is $25,000-50,000, enabling proper diversification across multiple volatility positions and timeframes.
Smaller accounts ($10,000-25,000) can access volatility exposure through fractional ETF shares or micro VIX options (when available), though transaction costs will reduce net returns. Consider volatility-focused mutual funds for accounts below $10,000 to achieve institutional-level diversification.
3. How do taxes affect long volatility strategy returns?
VIX options receive favorable Section 1256 tax treatment with 60% long-term and 40% short-term capital gains rates, while volatility ETFs generate ordinary income treatment on distributions plus capital gains on sales. This tax difference favors VIX options for high-income investors in taxable accounts.
Hold long volatility strategies in tax-advantaged accounts (IRA, 401k) when possible to avoid tax complications. For taxable accounts, maintain detailed records of all transactions and work with tax professionals familiar with volatility instrument taxation to optimize after-tax returns.
4. When is the best time to enter long volatility positions?
Enter volatility positions when VIX trades below its 25th percentile of trailing 252 trading days, typically when VIX falls below 15-18 depending on recent market conditions. Avoid entering during volatility spikes (VIX above 25) as you’ll be buying expensive insurance when maximum returns have likely passed.
Use systematic entry criteria rather than market timing attempts. Historical analysis shows consistent entries during low-volatility periods outperform tactical approaches by 60-80% over complete market cycles. Calendar-based rebalancing (monthly) works better than attempting to time volatility cycles.
5. What are the red flags to avoid with volatility investments?
Avoid volatility products with daily rebalancing (like TVIX, UVXY held long-term) as these suffer severe decay from daily compounding effects. Never buy volatility instruments during market crashes when implied volatility exceeds 30-40 as you’re purchasing at peak prices with limited upside potential.
Beware of complex structured products promising “guaranteed” volatility returns or products with unclear fee structures exceeding 1.5% annually. Stick to liquid, exchange-traded instruments with transparent pricing and avoid over-leveraged volatility products (2x, 3x) unless you fully understand their decay characteristics.
6. How quickly can long volatility strategies lose money during calm markets?
VIX options typically lose 10-15% value weekly from time decay during stable market conditions, while volatility ETFs decline 3-8% monthly due to futures curve contango effects. These losses are normal and expected – volatility strategies are designed to generate profits during volatility events, not calm periods.
Plan for maximum drawdowns of 80-100% on options positions and 40-60% on ETF positions during extended low-volatility periods. These temporary losses are recovered during volatility spikes that occur every 6-18 months historically.
7. Can I use long volatility strategies in retirement accounts?
Yes, volatility strategies work well in tax-advantaged accounts where tax complexity is eliminated and frequent rebalancing doesn’t generate taxable events. Many 401k plans now offer volatility-focused funds, while IRAs provide full access to individual volatility instruments.
Consider volatility strategies as portfolio insurance within retirement accounts, especially for retirees who cannot easily replace market losses. The sequence-of-returns risk in retirement makes volatility protection particularly valuable for preserving wealth during early retirement years.
8. What’s the difference between VIX options and VIX futures for individual investors?
VIX options provide asymmetric risk profiles with limited downside (premium paid) and unlimited upside potential, while VIX futures require margin and can generate losses exceeding initial investment. Options naturally limit risk while providing superior return profiles for most individual investors.
VIX futures require more sophisticated risk management and higher account minimums ($25,000+ for portfolio margin), making options preferable for most retail investors. Futures work better for professional traders implementing complex volatility strategies requiring precise exposure control.
9. How do I know if my volatility strategy is working correctly?
Track your volatility positions separately from overall portfolio performance, expecting negative returns 60-70% of months with occasional large positive returns during volatility events. Annual volatility strategy returns should average 5-15% over complete market cycles when implemented systematically.
Monitor correlation between volatility positions and overall portfolio during market stress—volatility strategies should generate positive returns when your equity positions decline significantly. If this negative correlation breaks down, reassess position sizing and instrument selection.
10. What advanced volatility strategies should experienced investors consider?
Sophisticated investors can implement volatility term structure strategies that capture differences between short-term and long-term volatility expectations, variance swaps that provide pure volatility exposure without time decay, and cross-asset volatility strategies that capitalize on volatility relationships between equity, commodity, and currency markets.
Consider professional volatility funds or hedge funds for advanced exposure, especially strategies employing options market-making or volatility arbitrage that generate returns uncorrelated to traditional long volatility approaches. These strategies require significant capital ($100,000+ minimums) and sophisticated risk management but provide superior risk-adjusted returns for qualified investors.
Conclusion
Long volatility strategies transform market uncertainty from wealth-destroying events into systematic profit opportunities, providing portfolio protection that pays for itself while generating crisis alpha precisely when traditional investments fail most dramatically. The evidence is overwhelming: institutional investors allocating 3-8% to volatility strategies consistently outperform traditional portfolios by 200-400 basis points annually while reducing maximum drawdowns by 15-25% during market stress periods.
The cost of ignoring long volatility strategies becomes exponentially higher as market valuations reach extremes and traditional diversification fails to provide adequate protection. Every major market crash – from 2008 to 2020 to the inevitable next crisis – rewards prepared investors who understand volatility patterns while punishing those who treat market protection as an afterthought.
Modern markets demand modern solutions. With artificial intelligence creating new volatility patterns, geopolitical tensions generating frequent market disruptions, and central bank policies creating boom-bust cycles, the investment landscape requires systematic approaches to volatility that go beyond traditional buy-and-hold strategies. The institutions moving first into volatility strategies are positioning themselves for the next decade of market evolution.
Your next step is immediate: Assess your current portfolio’s volatility exposure and begin implementing systematic long volatility strategies before the next market crisis makes protection expensive and scarce. Start with a 2% allocation to VIX calls or volatility ETFs, establish systematic rebalancing rules, and experience firsthand how volatility strategies transform market chaos into controlled profit opportunities.
The question isn’t whether market volatility will return – it’s whether you’ll be prepared to profit from it when it does.
For your reference, recently published articles include:
-
-
-
- Best Wine Investment Returns – Get The Pros Advice
- Closed-End Funds vs Open-End Funds: All You Need To Know
- Collectibles as Investments – How to Best Maximize Your Returns
- Digital Wallet Security: How to Protect Your Crypto Assets
- Blockchain ETF Guide – All You Need To Know
- Best Stablecoin Investing Guide: All You Need To Know
-
-
………………………………………………..
Important Notice: The information in this article is for general and public information purposes only. It solely reflects Didi Somm’s or his Staff’s opinion, and no responsibility can be assumed for errors or omissions in the service’s contents. For details, please read the Disclaimer at the bottom of the homepage.

