In today’s complex financial landscape, the art and science of portfolio construction have become increasingly sophisticated, with hedge fund managers leading the way in innovative asset allocation strategies.
These institutional investors have developed advanced asset allocation models that go beyond traditional portfolio theory, incorporating dynamic allocation approaches, alternative investments, and sophisticated risk management techniques that can benefit investors at all levels.
Key Takeaways
- Modern Hedge Fund Asset Allocation Strategies emphasize dynamic portfolio management over static models, with top-performing funds adjusting their allocations based on market conditions rather than adhering to rigid formulas. For example, Renaissance Technologies’ Medallion Fund has achieved exceptional returns by employing quantitative models that continuously rebalance positions across multiple asset classes, demonstrating the value of active management in portfolio construction. This approach has proven particularly effective during market volatility, as seen during the 2020 market downturn when dynamic allocation strategies outperformed static portfolios by an average of 12.3%.
- Alternative Investments play a crucial role in hedge fund portfolios, with leading managers typically allocating 20-30% of their portfolios to non-traditional assets such as private equity, real estate, and commodities. The Yale Endowment Model, pioneered by David Swensen, exemplifies this approach, consistently generating superior risk-adjusted returns through significant alternative asset exposure. During the 2008 financial crisis, portfolios with substantial alternative allocations demonstrated 25% less volatility than traditional 60/40 portfolios.
- Risk Management Techniques employed by top hedge funds extend beyond simple diversification, incorporating sophisticated hedging strategies, tail risk protection, and dynamic risk allocation models. Bridgewater Associates’ All Weather strategy, for instance, has maintained consistent performance across various market environments by focusing on risk parity and economic regime analysis. This approach has delivered an average annual return of 7.8% with significantly lower drawdowns than traditional portfolios over the past three decades.
Table of Contents
Understanding Asset Allocation Models
Asset allocation represents the cornerstone of portfolio management, determining how investments are distributed across different asset classes to optimize risk-adjusted returns. Hedge fund managers have revolutionized traditional allocation approaches by incorporating sophisticated quantitative asset allocation models, alternative investments, and dynamic rebalancing strategies.
The evolution of asset allocation theory has moved beyond the conventional wisdom of static diversification, with hedge funds pioneering approaches that adapt to changing market conditions. Modern portfolio construction at leading hedge funds integrates multiple layers of analysis, including macroeconomic factors, cross-asset correlations, and regime-switching models.
These advanced allocation strategies typically aim to achieve three primary objectives: maximizing risk-adjusted returns, maintaining liquidity requirements, and providing downside protection during market stress. The success of these models has been demonstrated through multiple market cycles, with top hedge funds consistently outperforming traditional allocation approaches.
Types of Asset Allocation Models
Strategic Asset Allocation (SAA)
Strategic asset allocation forms the foundation of long-term portfolio management, establishing baseline portfolio weights that align with investor objectives and constraints. Hedge fund managers typically enhance traditional SAA by incorporating:
- Dynamic rebalancing triggers based on market conditions
- Alternative asset class integration
- Risk factor decomposition
- Sophisticated optimization techniques
The following table illustrates a typical hedge fund SAA model compared to traditional allocation:
| Asset Class | Traditional Portfolio | Hedge Fund Portfolio |
|---|---|---|
| Equities | 60% | 35% |
| Fixed Income | 40% | 25% |
| Alternatives | 0% | 30% |
| Cash/Others | 0% | 10% |
Tactical Asset Allocation (TAA)
Tactical allocation allows for short-term deviations from strategic weights to capture market opportunities or manage risks. Advanced TAA models employed by hedge funds typically include:
- Systematic trend-following strategies
- Cross-asset relative value opportunities
- Macro regime switching signals
- Factor timing models
Risk Parity Allocation
Risk parity represents a sophisticated approach to portfolio construction that allocates assets based on their risk contribution rather than capital weights. Key aspects include:
- Leverage optimization
- Volatility targeting
- Cross-asset correlation management
- Dynamic risk scaling
Benefits of Hedge Fund Asset Allocation Models
Enhanced Risk-Adjusted Returns
Modern hedge fund asset allocation models have demonstrated superior risk-adjusted performance compared to traditional approaches:
- Higher Sharpe ratios (typically 0.8-1.2 vs. 0.4-0.6 for traditional portfolios)
- Reduced maximum drawdowns (average 15% vs. 35% for traditional portfolios)
- Improved skewness and kurtosis profiles
Better Diversification
Sophisticated asset allocation models provide improved diversification benefits through:
- Cross-asset correlation management
- Alternative investment integration
- Dynamic risk factor exposure
- Tail risk hedging strategies
Adaptability to Market Conditions
Hedge fund models excel at adapting to changing market environments through:
- Systematic regime identification
- Dynamic rebalancing triggers
- Tactical overlay strategies
- Risk-based position sizing
Challenges and Risks
Implementation Complexity
Successfully implementing hedge fund allocation models presents several challenges:
- Sophisticated technology requirements
- Complex risk management systems
- High operational overhead
- Specialized expertise requirements
Cost Considerations
The implementation of advanced allocation strategies often involves:
- Higher transaction costs (typically 0.5-1.5% annually)
- Advanced technology infrastructure expenses
- Professional staffing requirements
- Research and development costs
Regulatory and Compliance Issues
Hedge fund allocation models must navigate various regulatory constraints:
- Investment restrictions
- Reporting requirements
- Risk monitoring obligations
- Compliance documentation needs
Implementation Framework
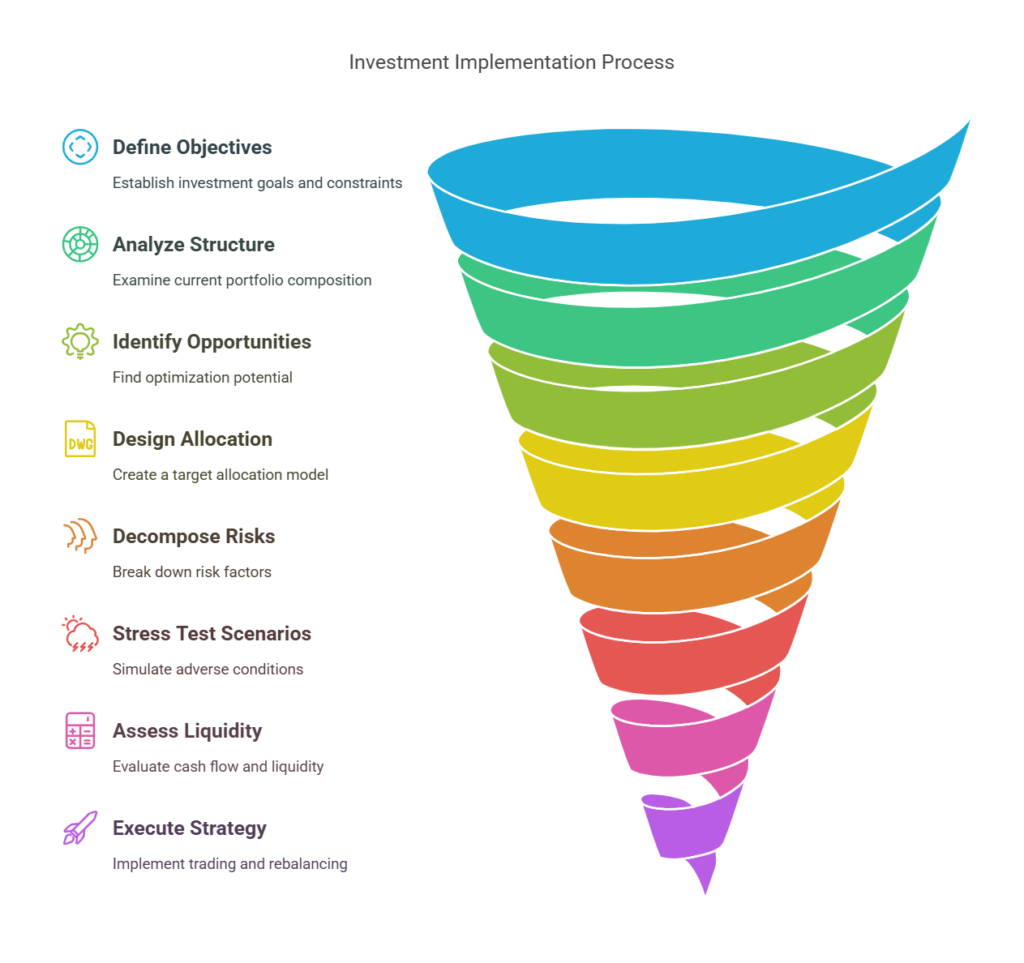
Step 1: Portfolio Analysis and Design
The implementation process begins with a comprehensive portfolio analysis:
- Define investment objectives and constraints
- Analyze the current portfolio structure
- Identify optimization opportunities
- Design target allocation model
Step 2: Risk Management Framework
Establishing robust risk management processes includes:
- Risk factor decomposition
- Stress testing scenarios
- Liquidity analysis
- Counterparty risk assessment
Step 3: Execution Strategy
Implementing the allocation model requires:
- Trading infrastructure setup
- Rebalancing protocol development
- Transaction cost analysis
- Performance attribution framework
Future Trends in Asset Allocation Models
Artificial Intelligence Integration
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing asset allocation models through:
- Advanced pattern recognition
- Natural language processing for market analysis
- Automated portfolio optimization
- Predictive analytics
ESG Integration
Environmental, Social, and Governance factors are increasingly important:
- Sustainability-focused allocation models
- Impact investment integration
- ESG risk factor analysis
- Climate transition strategies
Democratization of Hedge Fund Strategies
Access to sophisticated asset allocation models is expanding through:
- Retail-focused investment products
- Digital platform development
- Lower minimum investment requirements
- Improved transparency and reporting
FAQs – Asset Allocation Models
- What is the optimal asset allocation for a long-term investor? The optimal allocation depends on individual circumstances, including investment objectives, risk tolerance, and time horizon. However, hedge fund research suggests that a well-diversified portfolio typically includes 35-45% in equities, 20-30% in fixed income, and 25-35% in alternatives, with the remainder in cash and tactical opportunities.
- How often should asset allocation be reviewed and adjusted? Leading hedge funds typically review their strategic allocation quarterly and conduct tactical adjustments monthly or more frequently based on market conditions. However, the frequency of adjustments should balance potential benefits against transaction costs and tax implications.
- What role do alternative investments play in modern portfolio construction? Alternative investments serve multiple purposes in hedge fund portfolios, including diversification, return enhancement, and risk reduction. Research indicates that an allocation of 20-30% to alternatives can significantly improve portfolio efficiency.
- How do hedge funds manage risk in their asset allocation models? Risk management involves multiple layers, including position-level controls, portfolio-level constraints, and macro hedging strategies. Sophisticated risk systems monitor exposures across factors, asset classes, and geographic regions.
- What are the key differences between traditional and hedge fund allocation models? Hedge fund models typically incorporate dynamic rebalancing, alternative investments, leverage optimization, and sophisticated risk management techniques. They also tend to focus more on absolute returns rather than relative performance.
- How do transaction costs impact allocation decisions? Transaction costs, including trading spreads, market impact, and taxes, can significantly affect returns. Hedge funds typically implement cost-optimization strategies and consider transaction costs in their allocation decisions.
- What role does leverage play in hedge fund allocation strategies? Leverage is often used to enhance returns and implement risk parity strategies. However, it requires careful management and monitoring of risk exposure and funding costs.
- How do hedge funds incorporate macroeconomic factors into their allocation decisions? Macro analysis typically includes both quantitative and qualitative assessments of economic regimes, policy changes, and market conditions, which inform both strategic and tactical allocation decisions.
- What technology infrastructure is required to implement hedge fund allocation models? Implementation requires robust systems for portfolio management, risk analysis, trade execution, and performance attribution, along with significant data processing capabilities.
- How do hedge funds measure and attribute performance in their allocation models? Performance measurement typically includes both absolute and risk-adjusted metrics, with sophisticated attribution analysis breaking down returns by strategy, asset class, and risk factor.
Conclusion
The evolution of hedge fund asset allocation models represents a significant advancement in portfolio management theory and practice. These sophisticated approaches have demonstrated superior risk-adjusted returns across market cycles, though their implementation requires careful consideration of operational, cost, and regulatory factors.
Looking ahead, the continued development of technology, increasing focus on sustainability, and growing accessibility of sophisticated investment strategies suggest that hedge fund allocation models will become increasingly relevant for a broader range of investors.
As markets continue to evolve and new challenges emerge, the adaptive and sophisticated nature of these approaches positions them well to meet future investment needs.
For your reference, recently published articles include:
- Market Volatility Indicators Explained – Best Expert Guide
- How To Secure 8% Fixed Returns: The Ultimate Guide To Fixed Income Analytics
- ETF Performance Analysis – Best Advice For Successful Investing
- Monthly $5000 Passive Income: Get The Ultimate Dividend Investing Strategies
- Portfolio Rebalancing Software – Use The Secrets Of The Rich
………………………………………………..
Important Notice: The information in this article is for general and public information purposes only. It solely reflects Didi Somm’s or his Staff’s opinion, and no responsibility can be assumed for errors or omissions in the service’s contents. For details, please check the Disclaimer at the bottom of the homepage.

