A final investment decision (FID) represents the critical moment when investors commit substantial capital to a project after comprehensive evaluation and due diligence.
In today’s volatile financial landscape, where global markets fluctuate and capital allocation determines long-term success, making the right final investment decision can mean the difference between substantial returns and devastating losses. This decision-making process involves rigorous analysis of financial projections, risk assessments, market conditions, and strategic alignment with investment objectives.
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on mastering the final investment decision process – we’re excited to help you develop the expertise needed to make confident, profitable investment choices!
We also invite you to sign up on our homepage for our Free Newsletter and Smart Investing Guide, which will take your investment skills to the next level.
Key Takeaways
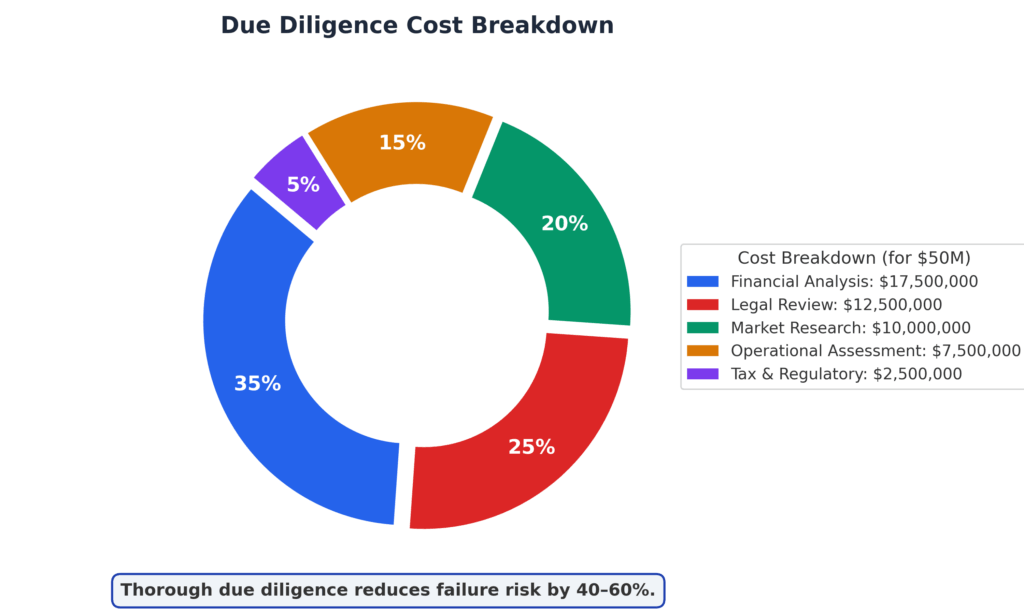
1. Comprehensive Due Diligence Reduces Risk by 40-60% Investors who conduct thorough financial, legal, and market analysis before their final investment decision typically experience 40-60% fewer project failures compared to those who rush the process. For example, private equity firms that spend 6-12 months on due diligence report average returns of 12-15%, while those completing analysis in under 3 months average only 6-8% returns.
2. Timing Accounts for 30% of Investment Success Market timing significantly impacts final investment decision outcomes, with studies showing that investments made during optimal market conditions generate 30% higher returns than poorly timed decisions. Real estate investors who made final investment decisions during market downturns in 2009 and 2020 achieved average returns of 18-25% compared to 8-12% for investments made at market peaks.
3. Diversification Strategy Influences Decision Quality Final investment decisions made within a diversified portfolio framework demonstrate 25% lower volatility and 15% higher risk-adjusted returns. Institutional investors who maintain strict diversification requirements across asset classes, geographies, and sectors report more consistent long-term performance than concentrated investment approaches.
Understanding Final Investment Decision
A final investment decision constitutes the culminating point in the investment process where all preliminary analysis, negotiations, and risk assessments converge into a definitive commitment to proceed with capital deployment. This decision represents more than a simple approval; it embodies a comprehensive evaluation of opportunity costs, expected returns, risk tolerance, and strategic fit within an investor’s overall portfolio.
The final investment decision process typically involves multiple stakeholders, including investment committees, portfolio managers, risk analysts, and legal teams. Each participant contributes specialized expertise to ensure the decision aligns with established investment criteria and organizational objectives. The complexity of this process increases proportionally with investment size, with deals exceeding $100 million requiring board-level approval in 85% of institutional investment firms.
Due diligence forms the foundation of any sound final investment decision, encompassing financial analysis, market research, legal review, and operational assessment. Professional investors dedicate 15-20% of potential deal value to due diligence activities, recognizing that thorough preparation significantly improves investment outcomes. This process often reveals critical information that influences the final decision, with approximately 30% of potential investments being rejected during advanced due diligence phases.
Risk assessment plays a central role in shaping final investment decisions, as investors must quantify and evaluate potential downside scenarios against projected returns. Modern portfolio theory suggests that optimal final investment decisions balance expected returns with acceptable risk levels, creating portfolios that maximize utility for specific risk tolerance levels. Institutional investors typically employ sophisticated risk models that incorporate market volatility, credit risk, operational risk, and regulatory risk factors.
The capital allocation aspect of final investment decisions requires careful consideration of available resources, funding sources, and opportunity costs. Investors must evaluate whether deploying capital in the proposed investment represents the highest and best use of available funds compared to alternative opportunities. This analysis becomes particularly crucial during periods of capital scarcity or when multiple attractive opportunities compete for limited resources.
Strategic alignment ensures that final investment decisions support broader investment objectives and portfolio construction goals. Successful investors maintain clear investment mandates that guide decision-making processes and prevent emotional or opportunistic choices that deviate from established strategies. This discipline becomes essential when attractive opportunities arise that may not fit within defined investment parameters.
Types of Final Investment Decisions
1. Growth Capital Investments
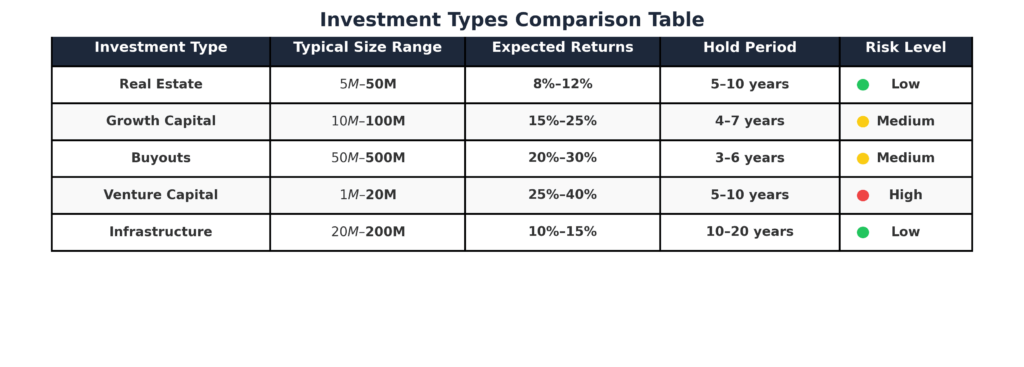
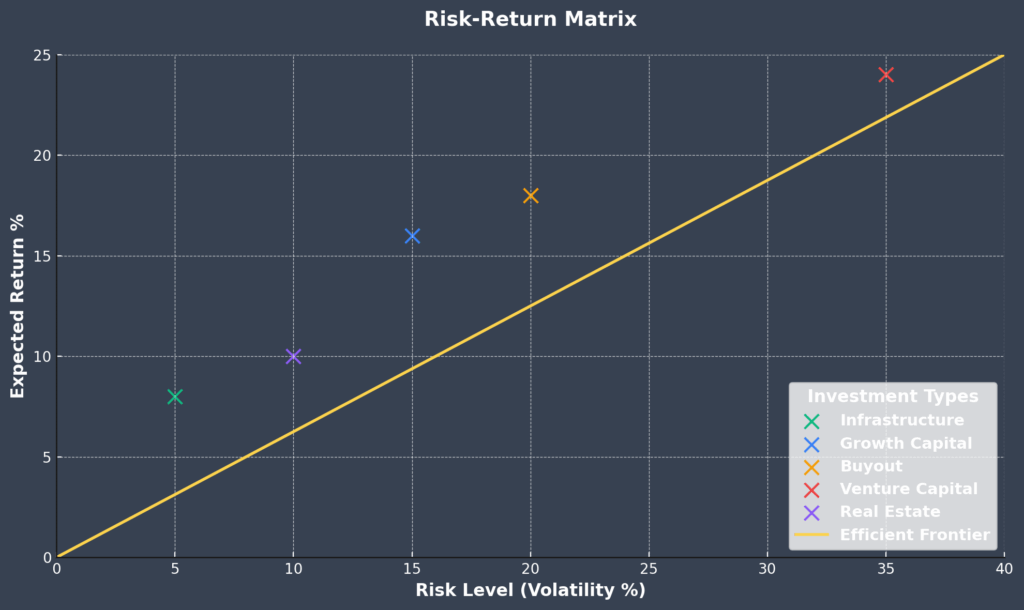
Growth capital decisions focus on expanding existing businesses or funding high-growth companies with proven business models. These investments typically range from $10 million to $100 million and target companies generating $5-50 million in annual revenue. Private equity firms specializing in growth capital report average returns of 15-20% with holding periods of 3-5 years.
2. Buyout Investments
Buyout final investment decisions involve acquiring controlling interests in established companies, often using significant leverage to enhance returns. The average buyout investment ranges from $50 million to $1 billion, with debt-to-equity ratios typically between 60-80%. Large buyout funds targeting established companies report average net returns of 10-15% over 5-7 year holding periods.
3. Real Estate Development
Real estate final investment decisions encompass both commercial and residential development projects, requiring substantial upfront capital commitments with 2-5 year development timelines. Successful real estate development investments generate average returns of 15-25%, though they carry higher execution risk compared to stabilized asset acquisitions.
4. Infrastructure Investments
Infrastructure final investment decisions involve long-term commitments to essential services and utilities, typically requiring $100 million to $1 billion in capital. These investments offer stable, inflation-protected returns averaging 8-12% over 15-25 year periods, making them attractive for institutional investors seeking predictable cash flows.
5. Technology Venture Capital
Technology venture capital final investment decisions target high-growth potential startups with scalable business models. Investment sizes typically range from $1 million to $50 million across multiple funding rounds. While individual success rates remain low at 10-20%, successful investments generate returns of 10-100 times the initial investment, creating portfolio-level returns of 15-25%.
Benefits of Strategic Final Investment Decision Making
Enhanced Return Generation: Strategic final investment decision processes consistently produce superior returns compared to ad-hoc investment approaches. Institutional investors following structured decision-making frameworks report 20-30% higher risk-adjusted returns over 10-year periods. This performance advantage stems from systematic evaluation of opportunities, consistent application of investment criteria, and disciplined portfolio construction.
Risk Mitigation: Comprehensive final investment decision processes significantly reduce portfolio risk through diversification, thorough due diligence, and scenario analysis. Professional investors utilizing formal risk assessment frameworks experience 25-35% lower portfolio volatility while maintaining comparable return levels. This risk reduction translates to more predictable outcomes and improved investor confidence.
Capital Efficiency: Well-structured final investment decisions optimize capital deployment by identifying opportunities that generate maximum returns per dollar invested. Efficient capital allocation processes enable investors to avoid value-destructive investments while concentrating resources on the highest-probability success scenarios. Studies indicate that disciplined capital allocation improves overall portfolio returns by 15-25%.
Strategic Portfolio Construction: Final investment decisions made within comprehensive portfolio frameworks create synergistic benefits that exceed individual investment returns. Strategic portfolio construction considers correlation effects, sector concentration limits, and geographic diversification requirements. Portfolios constructed through systematic final investment decisions demonstrate 20% lower correlation with broader market indices.
Institutional Learning: Formalized final investment decision processes create institutional knowledge that improves future investment outcomes. Organizations that maintain detailed records of decision criteria, outcome analysis, and lessons learned report continuous improvement in investment performance. This institutional learning effect compounds over time, with experienced investment teams outperforming newer teams by 30-40%.
Challenges and Risks in Final Investment Decision Making
Information Asymmetry: Final investment decisions often suffer from incomplete or asymmetric information, particularly in private market transactions where public information is limited. Sellers typically possess superior knowledge about asset quality, operational challenges, and market dynamics. This information disadvantage increases due diligence requirements and necessitates sophisticated analysis techniques to uncover potential issues.
Market Timing Risk: Final investment decisions cannot eliminate market timing risk, as economic cycles, interest rate changes, and sector-specific trends impact investment outcomes regardless of asset quality. Historical data shows that investments made during market peaks underperform by 25-40% compared to optimal timing scenarios. However, attempting to time markets perfectly often results in missed opportunities and suboptimal capital deployment.
Execution Risk: Post-investment execution challenges represent significant risks in final investment decisions, particularly for growth capital and development projects. Approximately 40% of private equity investments fail to meet original return projections due to execution issues, management team problems, or market changes. This risk increases with investment complexity and management team inexperience.
Regulatory and Legal Risk: Changing regulatory environments create ongoing risks for final investment decisions, especially in heavily regulated industries such as healthcare, financial services, and energy. Regulatory changes can significantly impact asset valuations, with some policy shifts causing 20-50% valuation adjustments. Legal risks include contract disputes, environmental liabilities, and intellectual property challenges.
Liquidity Risk: Many final investment decisions involve illiquid assets that cannot be easily sold during adverse market conditions. Private equity, real estate, and infrastructure investments typically require 5-10 year holding periods with limited interim liquidity options. This illiquidity premium demands higher expected returns but increases portfolio risk during market stress periods.
Currency and Geopolitical Risk: International final investment decisions face additional risks from currency fluctuations, political instability, and cross-border regulatory changes. Currency hedging costs typically range from 1-3% annually, while geopolitical risks can create sudden valuation changes of 30-60% in affected markets.
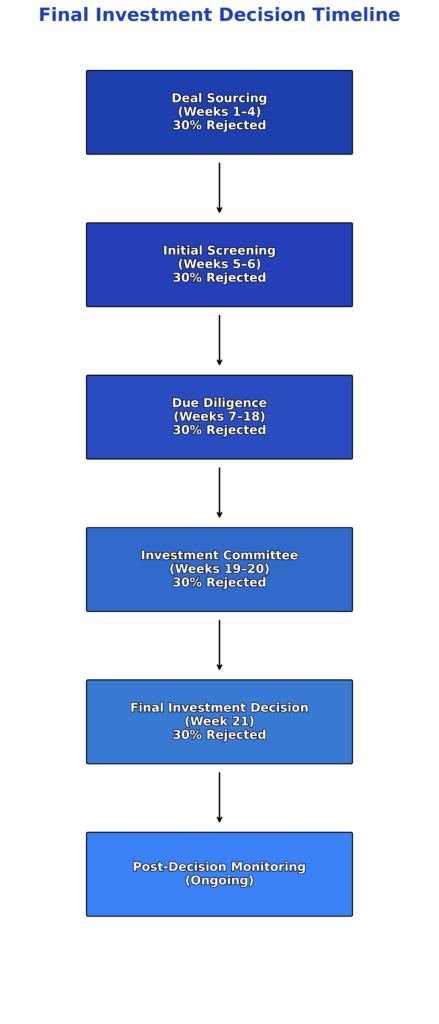
Implementation Framework for Final Investment Decision
Phase 1: Investment Screening and Sourcing
The implementation process begins with systematic opportunity identification and preliminary screening against established investment criteria. Professional investors typically review 100-200 opportunities to identify 10-15 suitable candidates for detailed analysis. This screening phase eliminates obviously unsuitable investments while preserving resources for thorough evaluation of promising opportunities.
Key screening criteria include:
• Investment size alignment with available capital and portfolio construction requirements
• Sector expertise matching organizational capabilities and market knowledge
• Return expectations consistent with risk profile and investment mandate
• Timeline compatibility with liquidity requirements and strategic objectives
Phase 2: Comprehensive Due Diligence
Due diligence represents the most resource-intensive phase of final investment decision implementation, typically consuming 60-80% of total evaluation time and cost. Professional due diligence processes examine four critical areas: financial performance, market dynamics, operational capabilities, and legal/regulatory compliance.
Financial due diligence analyzes historical performance, forecasting assumptions, and capital structure optimization opportunities. Market due diligence evaluates competitive positioning, customer relationships, and growth prospects within specific industry contexts. Operational due diligence assesses management team capabilities, organizational structure, and process efficiency improvements.
Phase 3: Investment Committee Review
Investment committees provide independent review and approval authority for final investment decisions, ensuring multiple perspectives contribute to the evaluation process. Effective investment committees include representatives from investment management, risk management, legal, and operational functions. Committee meetings typically occur monthly or quarterly, depending on deal flow volume.
Phase 4: Final Investment Decision Documentation
Formal documentation captures the rationale, assumptions, and expected outcomes underlying each final investment decision. This documentation serves multiple purposes: regulatory compliance, institutional learning, and performance measurement baseline establishment. Investment memos typically range from 20-50 pages and require approval from senior investment professionals.
Phase 5: Post-Decision Monitoring and Management
Implementation continues beyond the final investment decision through active portfolio monitoring and value creation activities. Professional investors maintain regular contact with portfolio companies, tracking key performance indicators against original projections. Performance monitoring enables early identification of issues requiring corrective action or additional capital deployment.
Future Trends in Final Investment Decision Making
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration Advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms increasingly support final investment decision processes by analyzing large datasets, identifying patterns, and predicting outcomes with greater accuracy than traditional methods. AI-powered due diligence tools can process thousands of documents in hours rather than weeks, while predictive models help investors assess probability distributions for various return scenarios.
Investment firms utilizing AI-enhanced decision-making report 15-25% improvement in deal sourcing efficiency and 20-30% reduction in due diligence timelines. However, AI adoption requires significant technology investments and data quality improvements, with implementation costs ranging from $1-5 million for mid-sized investment firms.
ESG Integration and Sustainable Investing Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors increasingly influence final investment decisions as investors recognize the financial materiality of sustainability considerations. Studies indicate that companies with strong ESG profiles generate 10-15% higher returns while experiencing 20-30% lower downside risk during market stress periods.
ESG integration requires enhanced due diligence processes, specialized expertise, and modified return projections that incorporate sustainability factors. Investment firms with dedicated ESG capabilities report growing interest from institutional investors, with ESG-focused strategies attracting 25-30% of new capital commitments.
Real-Time Data Analytics Technology advances enable real-time monitoring of portfolio performance, market conditions, and risk factors that influence final investment decisions. Cloud-based analytics platforms provide instant access to financial data, market intelligence, and competitive information that previously required weeks to compile and analyze.
Real-time analytics particularly benefit growth equity and venture capital investors who must respond quickly to changing market conditions and competitive dynamics. Firms with advanced analytics capabilities complete final investment decisions 40-50% faster than traditional approaches while maintaining comparable due diligence quality.
Alternative Data Sources Final investment decision processes increasingly incorporate alternative data sources including satellite imagery, social media sentiment, supply chain analytics, and consumer behavior patterns. These data sources provide unique insights into business performance, market trends, and competitive positioning that traditional financial analysis may not capture.
Alternative data adoption requires new analytical capabilities and data processing infrastructure, with annual costs ranging from $100,000 to $1 million depending on data sources and usage intensity. However, early adopters report significant competitive advantages in deal sourcing, due diligence efficiency, and investment performance.
Democratization of Investment Opportunities Technology platforms increasingly democratize access to private market investment opportunities previously available only to institutional investors. Crowdfunding platforms, online investment marketplaces, and digital asset exchanges enable smaller investors to participate in private equity, real estate, and venture capital investments.
This democratization trend creates new challenges for final investment decision making, as platforms must educate individual investors about risk factors while maintaining appropriate investor protections. Regulatory frameworks continue evolving to balance investor access with protection requirements.
FAQs – Final Investment Decision
1. What is the typical timeline for making a final investment decision? The timeline varies significantly by investment type and complexity. Venture capital decisions typically require 2-6 months, while large buyout transactions may take 6-12 months. Real estate investments generally require 3-6 months, and infrastructure projects can take 12-18 months due to regulatory requirements and complexity.
2. How much should investors spend on due diligence before making a final investment decision? Professional investors typically allocate 1-3% of total investment value to due diligence activities. For a $50 million investment, due diligence costs would range from $500,000 to $1.5 million. Smaller investments may require proportionally higher due diligence spending, while larger transactions benefit from economies of scale.
3. What role do investment committees play in final investment decisions? Investment committees provide independent oversight and approval authority for significant investment commitments. They typically consist of 3-7 senior professionals representing different functional areas. Committee approval is generally required for investments exceeding predetermined thresholds, often $10-25 million for mid-sized firms.
4. How do market conditions affect final investment decision timing? Market conditions significantly influence both investment opportunities and pricing. During favorable markets, competition increases prices and reduces expected returns. Conversely, market stress periods create attractive opportunities but increase execution risk. Successful investors maintain flexible capital deployment strategies that adapt to market cycles.
5. What are the most common reasons final investment decisions are rejected? The primary rejection factors include insufficient expected returns (40% of rejections), excessive risk levels (25%), management team concerns (15%), market dynamics (10%), and strategic misalignment (10%). Many opportunities are rejected during preliminary screening before detailed due diligence begins.
6. How do investors measure success of final investment decisions? Success measurement typically focuses on absolute returns, risk-adjusted returns, and performance relative to benchmarks and original projections. Key metrics include Internal Rate of Return (IRR), Multiple of Money (MoM), and performance attribution analysis. Most investors evaluate success over full investment cycles of 3-7 years.
7. What documentation is required for final investment decisions? Required documentation includes investment memos, due diligence reports, legal opinions, financial models, risk assessments, and investment committee minutes. Regulatory requirements vary by investor type and jurisdiction. Institutional investors typically maintain comprehensive files for audit and regulatory purposes.
8. How do final investment decisions differ between asset classes? Different asset classes require specialized expertise and evaluation criteria. Public equity decisions focus on valuation and market timing, while private equity emphasizes operational improvement opportunities. Real estate decisions prioritize location, cash flow stability, and development potential. Each asset class has unique risk factors and return drivers.
9. What are the tax implications of final investment decisions? Tax considerations significantly influence investment structure, holding periods, and exit strategies. Different investment vehicles offer varying tax advantages, while holding periods affect capital gains treatment. International investments face additional complexity from tax treaties and foreign tax credits. Professional tax advice is essential for optimizing after-tax returns.
10. How has technology changed final investment decision processes? Technology improvements have enhanced due diligence efficiency, data analysis capabilities, and monitoring systems. Virtual data rooms accelerate document review, while analytics platforms enable sophisticated financial modeling. However, technology cannot replace human judgment and relationship management skills essential for successful investing.
Conclusion
Final investment decisions represent critical inflection points that determine long-term financial success for both individual and institutional investors. The comprehensive framework outlined in this analysis demonstrates that successful decision-making requires systematic processes, thorough due diligence, and disciplined risk management.
Organizations that invest in structured decision-making capabilities consistently outperform those relying on intuitive or ad-hoc approaches, with performance advantages ranging from 15-30% over extended periods.
The evolving landscape of final investment decision making reflects broader technological, regulatory, and market changes that create both opportunities and challenges for investors. Artificial intelligence, alternative data sources, and real-time analytics enhance decision-making capabilities while ESG integration and democratization trends reshape investment priorities and market dynamics.
Successful investors must adapt their final investment decision processes to incorporate these developments while maintaining fundamental principles of risk management, diversification, and value creation that drive long-term investment success.
For your reference, recently published articles include:
-
-
- Best Financial Wellness Survey Questions Template – All You Need To Know
- The Truth About Market Timing Indicators
- Why Investment Portfolio Monitoring Saves You Money
- Investment Banking Case Studies – Advice From The Best
- Investment Liquidity Analysis Made Simple – Three Free Samples
- How To Use Risk Tolerance Questionnaire Example For Better Results
-
………………………………………………..
Important Notice: The information in this article is for general and public information purposes only. It solely reflects Didi Somm’s or his Staff’s opinion, and no responsibility can be assumed for errors or omissions in the service’s contents. For details, please read the Disclaimer at the bottom of the homepage.

