Investment portfolio monitoring represents the systematic tracking and analysis of investment holdings to optimize performance and minimize losses.
In today’s volatile financial markets, where global events can trigger 10-20% market swings within days, active portfolio oversight has become essential for preserving wealth. Professional investors who implement comprehensive monitoring systems typically outperform passive strategies by 2-4% annually, translating to substantial long-term wealth accumulation.
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on investment portfolio monitoring – we’re excited to help you master these essential wealth-building strategies!
Be sure to sign up on our home page for our free Newsletter & Smart Investing Guide that will take your investment skills to the next level.
Key Takeaways
1. Early Risk Detection Prevents Major Losses. Investment portfolio monitoring enables investors to identify declining assets before catastrophic losses occur. For instance, investors who monitored their technology holdings during the 2022 tech downturn could have limited losses to 15-20% rather than experiencing the sector’s full 35% decline by implementing stop-loss strategies.
2. Rebalancing Optimization Enhances Returns. Regular portfolio monitoring facilitates timely rebalancing, which studies show can improve annual returns by 1.5-2.5%. A $500,000 portfolio monitored and rebalanced quarterly can generate an additional $7,500-$12,500 annually compared to a buy-and-hold approach.
3. Tax Efficiency Through Loss Harvesting. Systematic monitoring enables strategic tax-loss harvesting, which can reduce tax liability by 0.5-1.5% annually. This practice involves selling losing positions to offset gains, potentially saving investors thousands in taxes while maintaining portfolio exposure.
Understanding Investment Portfolio Monitoring
Investment portfolio monitoring encompasses the continuous observation, analysis, and adjustment of investment holdings to maintain optimal performance and risk levels. This process involves tracking asset performance, analyzing market conditions, assessing portfolio allocation, and making strategic adjustments based on predetermined criteria.
The foundation of effective portfolio monitoring lies in establishing clear benchmarks and performance metrics. These typically include target asset allocation percentages, risk tolerance thresholds, and performance benchmarks such as the S&P 500 or relevant sector indices. Professional portfolio managers utilize sophisticated software systems that provide real-time data feeds, automated alerts, and comprehensive analytics to maintain oversight of millions of dollars in assets.
Modern portfolio monitoring extends beyond simple performance tracking to include risk assessment, correlation analysis, and scenario modeling. Advanced systems can simulate how portfolios might perform under various market conditions, enabling proactive adjustments rather than reactive responses to market volatility.
The frequency of monitoring varies based on investment strategy and market conditions. Day traders monitor positions continuously, while long-term investors may review portfolios weekly or monthly. However, even conservative investors benefit from quarterly comprehensive reviews to ensure alignment with financial goals and risk tolerance.
Technology has revolutionized portfolio monitoring capabilities, with artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms now capable of identifying patterns and anomalies that human analysts might miss. These systems can process vast amounts of market data, news sentiment, and economic indicators to provide early warning signals for potential portfolio impacts.
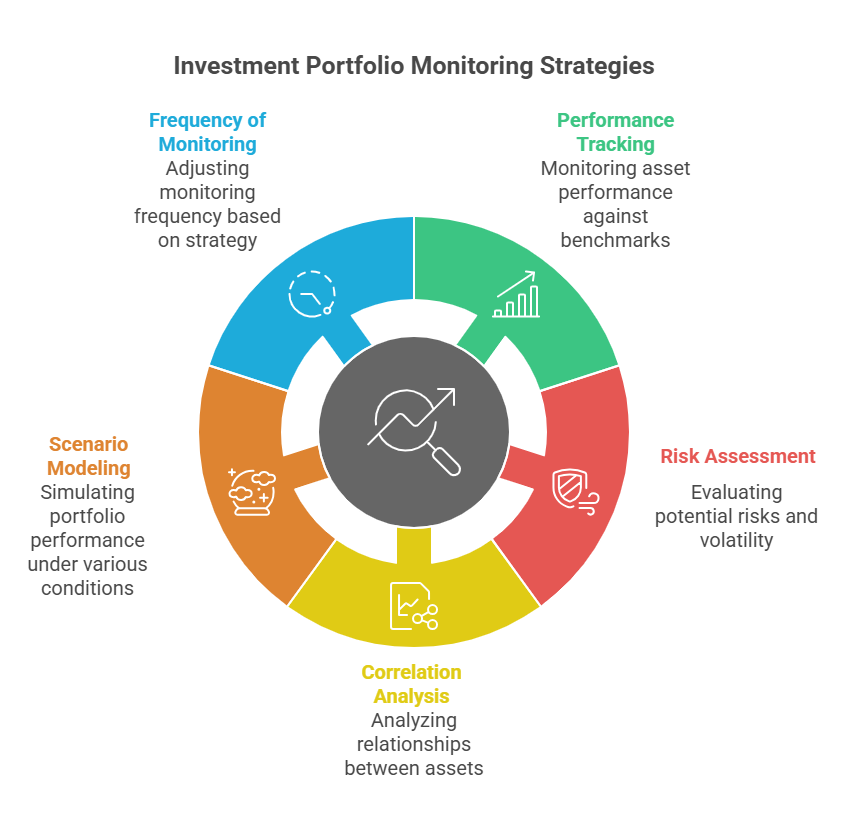
Types of Portfolio Monitoring Systems
| Monitoring Type | Frequency | Best For | Average Cost | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Monitoring | Continuous | Active traders, large portfolios | $50-$200/month | Live updates, instant alerts, advanced analytics |
| Daily Monitoring | End-of-day | Moderate traders, professionals | $20-$100/month | Daily summaries, performance reports, risk metrics |
| Weekly Monitoring | Weekly reviews | Long-term investors | $10-$50/month | Trend analysis, allocation tracking, basic alerts |
| Monthly Monitoring | Monthly reports | Conservative investors | $5-$25/month | Performance summaries, rebalancing recommendations |
| Quarterly Monitoring | Quarterly reviews | Passive investors | Free-$15/month | Basic reporting, annual performance tracking |
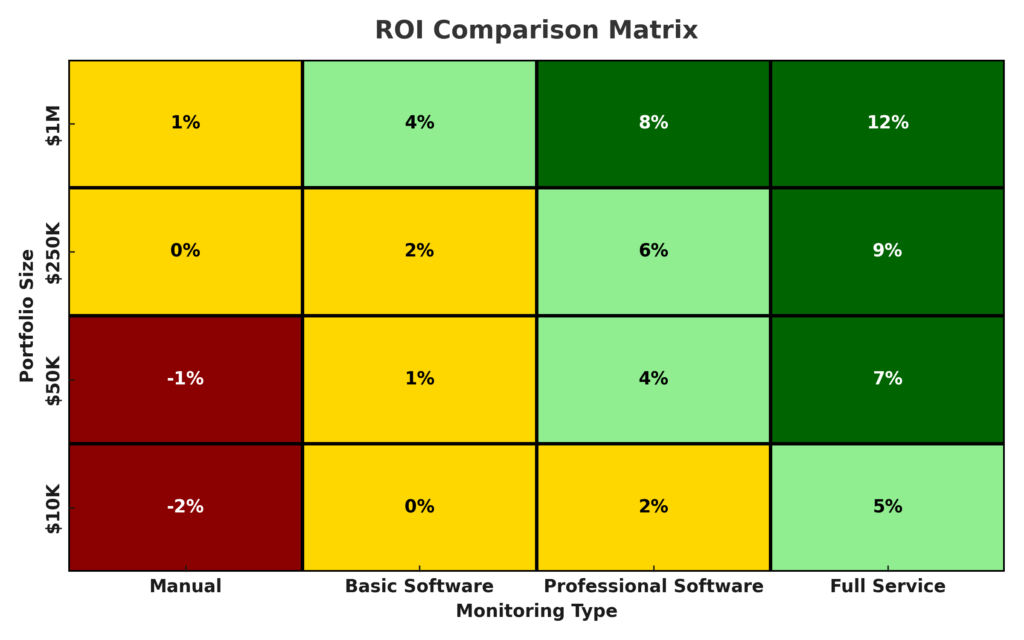
Manual vs. Automated Monitoring
Manual monitoring involves personally reviewing portfolio performance, reading financial statements, and making adjustment decisions. While cost-effective, this approach requires significant time investment and financial knowledge. Studies indicate that individual investors using manual monitoring methods often underperform market indices by 1-3% annually due to emotional decision-making and delayed responses to market changes.
Automated monitoring systems utilize algorithms and predetermined rules to track portfolio performance and execute trades. These systems can process information faster than human analysts and remove emotional bias from investment decisions. Automated systems typically cost between $20-$200 monthly but can improve portfolio performance by 1-4% annually through optimized timing and reduced transaction costs.
Benefits of Investment Portfolio Monitoring
Enhanced Performance Optimization
Regular monitoring enables investors to identify underperforming assets and reallocate resources to higher-performing investments. Research by Vanguard indicates that investors who monitor and rebalance portfolios quarterly achieve 1.8% higher annual returns compared to those who review portfolios annually. This translates to approximately $18,000 in additional returns over 10 years for a $100,000 initial investment.
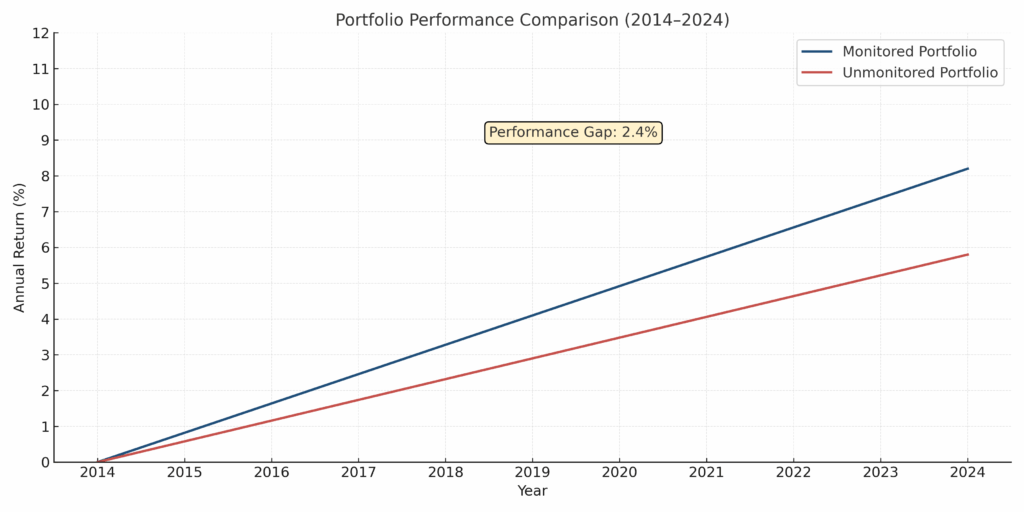
Risk Mitigation and Loss Prevention
Portfolio monitoring systems provide early warning indicators for potential losses through volatility tracking, correlation analysis, and market trend identification. Professional risk management systems can reduce portfolio volatility by 15-25% while maintaining similar return potential. During the 2008 financial crisis, investors with active monitoring systems limited losses to 20-30% compared to the market’s 37% decline.
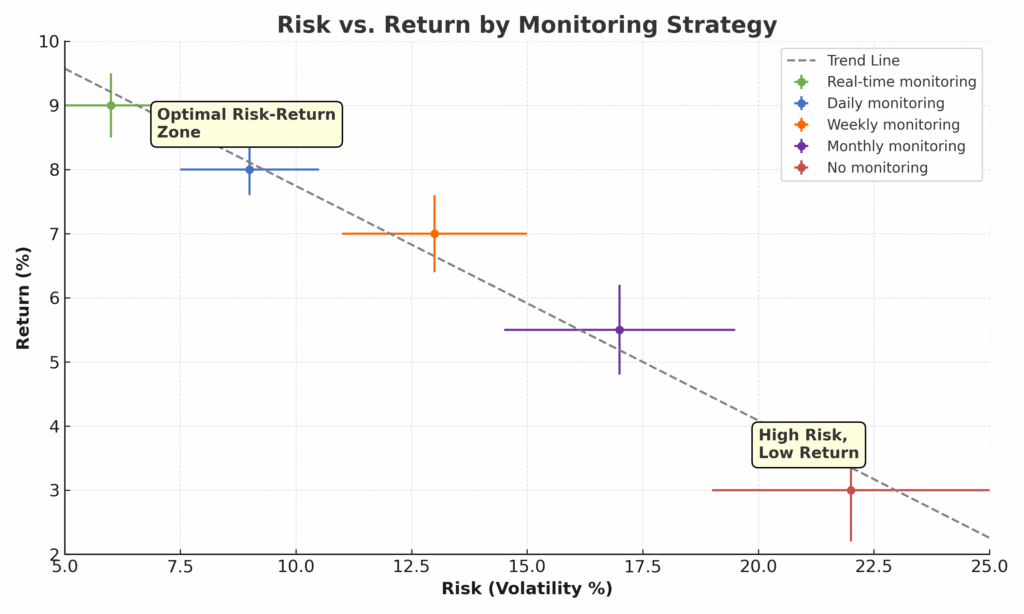
Tax Optimization Benefits
Strategic monitoring facilitates tax-loss harvesting opportunities, where investors sell losing positions to offset taxable gains. This practice can reduce annual tax liability by 0.5-1.5%, resulting in substantial savings over time. Additionally, monitoring enables optimal timing for long-term capital gains treatment, reducing tax rates from ordinary income levels to preferential capital gains rates.
Improved Asset Allocation
Monitoring systems track portfolio drift and alert investors when allocations deviate from target percentages. Without regular rebalancing, portfolios can become significantly overweight in certain sectors. For example, technology stocks comprised 22% of the S&P 500 in 2020 but grew to 28% by 2021 without rebalancing, creating unintended concentration risk.
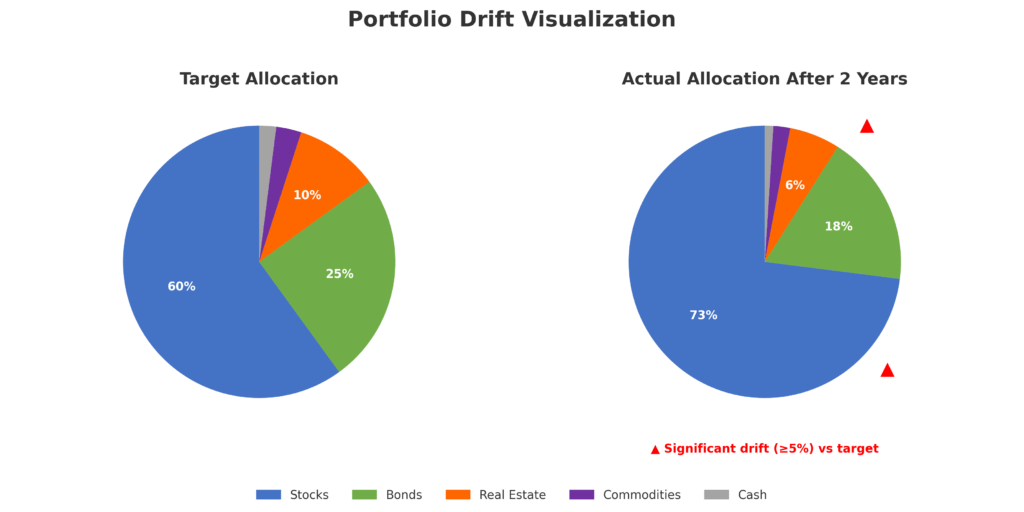
Challenges and Risks in Portfolio Monitoring
Information Overload and Analysis Paralysis
Modern monitoring systems generate vast amounts of data, reports, and alerts that can overwhelm investors. Studies show that investors exposed to excessive information often make more frequent, less profitable trades. The average individual investor who receives daily portfolio updates trades 75% more frequently than those receiving monthly updates, resulting in 0.8% lower annual returns due to increased transaction costs.
Technology Dependence and System Failures
Automated monitoring systems face risks from technical failures, data errors, and cybersecurity threats. In 2020, several major trading platforms experienced outages during high-volatility periods, preventing investors from accessing their portfolios or executing trades. These incidents highlight the importance of backup systems and manual oversight capabilities.
False Signals and Overactive Trading
Monitoring systems can generate false alerts during normal market fluctuations, leading to unnecessary trading activity. Overactive trading reduces returns through increased transaction costs and tax implications. Research indicates that investors who trade based on short-term signals underperform buy-and-hold strategies by 2-4% annually.
Cost Considerations
Comprehensive monitoring systems require ongoing subscription fees, trading costs, and potential advisory fees. These expenses can range from $100-$2,000 annually, depending on portfolio size and service level. Investors must ensure that monitoring benefits exceed these costs to achieve net positive returns.
Implementation and How Portfolio Monitoring Works
Setting Up Monitoring Systems
Effective portfolio monitoring begins with establishing clear objectives, risk tolerance levels, and performance benchmarks. Investors should define specific criteria for buy/sell decisions, rebalancing triggers, and alert thresholds. Professional advisors typically recommend monitoring systems that track:
- Asset allocation percentages with 5-10% drift tolerance
- Individual position sizes not exceeding 5-10% of the total portfolio
- Sector concentration limits to prevent overexposure
- Performance tracking against relevant benchmarks
- Risk metrics, including volatility, beta, and correlation coefficients
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
| KPI Category | Metric | Target Range | Monitoring Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Returns | Annual return vs. benchmark | +/- 2% of benchmark | Monthly |
| Risk | Portfolio volatility | 10-20% annually | Weekly |
| Allocation | Asset class drift | +/- 5% of targets | Monthly |
| Liquidity | Cash position | 5-10% of portfolio | Daily |
| Concentration | Single position limit | Maximum 10% | Continuous |
Monitoring Workflow Process
The systematic monitoring process follows a structured approach:
- Daily price updates and performance calculations
- Weekly risk assessment and volatility analysis
- Monthly allocation review and rebalancing evaluation
- Quarterly comprehensive analysis including tax implications
- Annual strategy review and goal reassessment
Technology Integration
Modern portfolio monitoring integrates multiple data sources, including market feeds, economic indicators, and news sentiment analysis. Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) connect various financial platforms to provide consolidated reporting and automated trade execution capabilities.
Future Trends in Portfolio Monitoring
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI-powered monitoring systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated, utilizing natural language processing to analyze news sentiment and predict market movements. These systems can identify patterns in vast datasets that human analysts cannot detect, potentially improving portfolio performance by 2-5% annually through better timing and risk management.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Integration
ESG monitoring is becoming standard practice, with 85% of institutional investors incorporating ESG factors into investment decisions. Monitoring systems now track ESG scores, carbon footprints, and social impact metrics alongside traditional financial metrics. This integration helps investors align portfolios with personal values while potentially reducing long-term risk.
Robo-Advisory Evolution
Robo-advisors are expanding beyond basic portfolio management to offer sophisticated monitoring capabilities previously available only to high-net-worth clients. These platforms typically charge 0.25-0.50% annually and provide continuous monitoring, automatic rebalancing, and tax optimization for portfolios as small as $500.
Blockchain and Cryptocurrency Integration
Portfolio monitoring systems are incorporating cryptocurrency and blockchain-based assets, requiring new risk models and regulatory compliance frameworks. As digital assets become more mainstream, monitoring systems must adapt to 24/7 market conditions and extreme volatility patterns.
FAQs – Investment Portfolio Monitoring
1. How often should I monitor my investment portfolio? The optimal monitoring frequency depends on your investment strategy and risk tolerance. Active traders should monitor daily, while long-term investors can review portfolios monthly or quarterly. Most financial advisors recommend at least quarterly reviews to ensure alignment with financial goals and risk parameters.
2. What percentage of my portfolio should trigger a rebalancing alert? Most professionals recommend rebalancing when asset allocations drift 5-10% from target percentages. For example, if your target allocation is 60% stocks and 40% bonds, consider rebalancing when stocks exceed 66% or fall below 54% of the portfolio.
3. How much does professional portfolio monitoring cost? Professional monitoring services typically cost 0.25-1.5% of portfolio value annually. Robo-advisors charge 0.25-0.50%, while full-service human advisors charge 0.75-1.5%. DIY monitoring software ranges from $10-$200 monthly, depending on features and portfolio size.
4. Can portfolio monitoring help reduce taxes? Yes, systematic monitoring enables tax-loss harvesting, which can reduce annual tax liability by 0.5-1.5%. This involves selling losing positions to offset gains and strategically timing transactions to qualify for favorable long-term capital gains treatment.
5. What are the key metrics I should track in my portfolio? Essential metrics include total return, volatility, Sharpe ratio, beta, asset allocation percentages, and performance versus benchmarks. Additionally, track individual position sizes, sector concentration, and correlation coefficients to manage risk effectively.
6. How do I know if my monitoring system is working effectively? Effective monitoring systems should provide clear, actionable insights and measurable improvements in portfolio performance. Key indicators include reduced volatility, improved risk-adjusted returns, timely rebalancing, and successful tax optimization compared to passive strategies.
7. What technology do I need for effective portfolio monitoring? Basic monitoring requires internet access and portfolio tracking software or apps. Advanced monitoring may include real-time data feeds, automated trading platforms, and analytical tools. Many effective solutions are available through standard web browsers and mobile applications.
8. How does market volatility affect monitoring strategies? High volatility periods require more frequent monitoring and potentially tighter risk controls. During volatile markets, consider daily monitoring instead of weekly reviews, and implement stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. Automated systems can help manage emotions during turbulent periods.
9. Should I use automated or manual portfolio monitoring? The choice depends on your time availability, technical expertise, and portfolio complexity. Automated systems excel at processing large amounts of data quickly and removing emotional bias, while manual monitoring provides more control and customization options. Many successful investors combine both approaches.
10. What are the biggest mistakes to avoid in portfolio monitoring? Common mistakes include overreacting to short-term market movements, ignoring transaction costs, failing to maintain adequate diversification, and not updating monitoring criteria as financial situations change. Additionally, avoid analysis paralysis from excessive data and maintain focus on long-term objectives.
Conclusion
Investment portfolio monitoring represents a critical component of successful wealth management, offering substantial benefits through enhanced performance optimization, risk mitigation, and tax efficiency.
The evidence clearly demonstrates that systematic monitoring can improve annual returns by 1.5-4% while reducing volatility and tax liability. Professional investors who implement comprehensive monitoring systems consistently outperform passive strategies through timely rebalancing, loss prevention, and strategic tax management.
The evolution of portfolio monitoring technology continues to democratize sophisticated investment management tools, making professional-grade monitoring accessible to investors of all portfolio sizes. As artificial intelligence, ESG integration, and blockchain technologies advance, monitoring systems will become even more powerful and cost-effective.
Investors who embrace these technologies and implement systematic monitoring approaches position themselves for superior long-term financial outcomes. The key to success lies in selecting appropriate monitoring tools, establishing clear criteria, and maintaining discipline in following systematic processes while avoiding the pitfalls of overactive trading and information overload.
For your reference, recently published articles include:
-
-
- Investment Banking Case Studies – Advice From The Best
- Investment Liquidity Analysis Made Simple – Three Free Samples
- How To Use Risk Tolerance Questionnaire Example For Better Results
- Master Your Wealth: Financial Disclaimers Explained
- Rate Volume Analysis: Best Expert Advice For Your Success
- Irrational Investing: Why Emotions Destroy Your Portfolio
-
………………………………………………..
Important Notice: The information in this article is for general and public information purposes only. It solely reflects Didi Somm’s or his Staff’s opinion, and no responsibility can be assumed for errors or omissions in the service’s contents. For details, please read the Disclaimer at the bottom of the homepage.

