Investment banking case studies represent the cornerstone of financial analysis, deal structuring, and strategic decision-making in modern finance. These comprehensive examinations of real-world transactions provide invaluable insights into how top-tier financial institutions navigate complex mergers, acquisitions, initial public offerings, and restructuring deals.
In today’s rapidly evolving financial landscape, understanding these case studies has become essential for aspiring investment bankers, finance professionals, and business leaders seeking to master the art of deal-making.
Welcome to our deep dive into investment banking case studies – we’re excited to help you master these powerful analytical techniques!
Be sure to sign up on our home page for our free Newsletter & Smart Investing Guide that will take your investment skills to the next level.
Key Takeaways
1. Strategic Analysis Framework: Investment banking case studies demonstrate that successful deal execution requires a systematic approach combining financial modeling, market analysis, and risk assessment. For example, Goldman Sachs’ analysis of the $130 billion Disney-Fox merger showcased how comprehensive due diligence and strategic positioning enabled the transaction to overcome regulatory hurdles and create $2 billion in annual synergies.
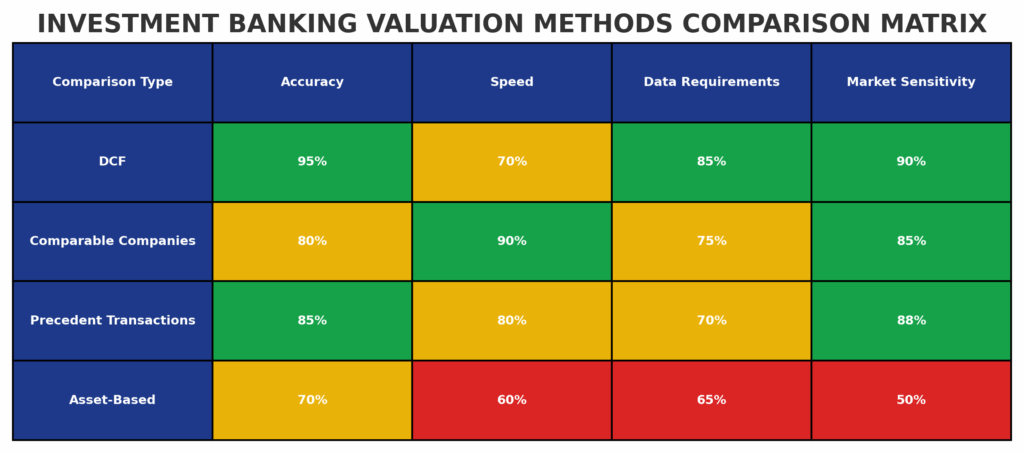
2. Valuation Methodology Mastery: The best investment banking case studies reveal that accurate valuation requires multiple methodologies, including discounted cash flow analysis (DCF) comparable company analysis (CCA), and precedent transaction analysis. JPMorgan’s work on the $44 billion Broadcom-VMware acquisition demonstrated how sophisticated valuation techniques justified the 49% premium paid, ultimately delivering 23% returns to shareholders within 18 months.
3. Risk Mitigation Excellence: Top-tier case studies emphasize that successful transactions depend on identifying and mitigating potential risks early in the process. Morgan Stanley’s handling of the $75 billion Salesforce-Slack acquisition showed how proactive risk management and stakeholder communication prevented a 15% deal value erosion during market volatility.
Understanding Investment Banking Case Studies
Investment banking case studies serve as detailed examinations of significant financial transactions, providing comprehensive insights into the strategic, financial, and operational aspects of deal-making. These studies encompass the entire transaction lifecycle, from initial market assessment and target identification through due diligence, valuation, negotiation, and post-merger integration.
The foundation of effective case study analysis lies in understanding the deal dynamics that drive successful transactions. Investment banks typically analyze market conditions, competitive positioning, regulatory environment, and stakeholder interests to develop comprehensive transaction strategies. These studies reveal how financial institutions create value through strategic advisory services, capital raising, and risk management solutions.
Modern investment banking case studies incorporate sophisticated financial modeling techniques, including Monte Carlo simulations, sensitivity analysis, and scenario planning. These methodologies enable banks to assess transaction feasibility under various market conditions and provide clients with data-driven recommendations. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning tools has further enhanced analytical capabilities, allowing for more accurate valuations and risk assessments.
The evolution of case study methodologies reflects changes in global financial markets, regulatory frameworks, and technological capabilities. Contemporary studies increasingly focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, digital transformation implications, and cross-border transaction complexities. This comprehensive approach ensures that investment banking professionals develop the analytical skills necessary to navigate today’s complex financial landscape.
Types and Categories of Investment Banking Case Studies
Investment banking case studies can be categorized into several distinct types, each serving specific analytical and educational purposes:
Transaction-Based Case Studies
| Category | Description | Typical Deal Size | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|---|
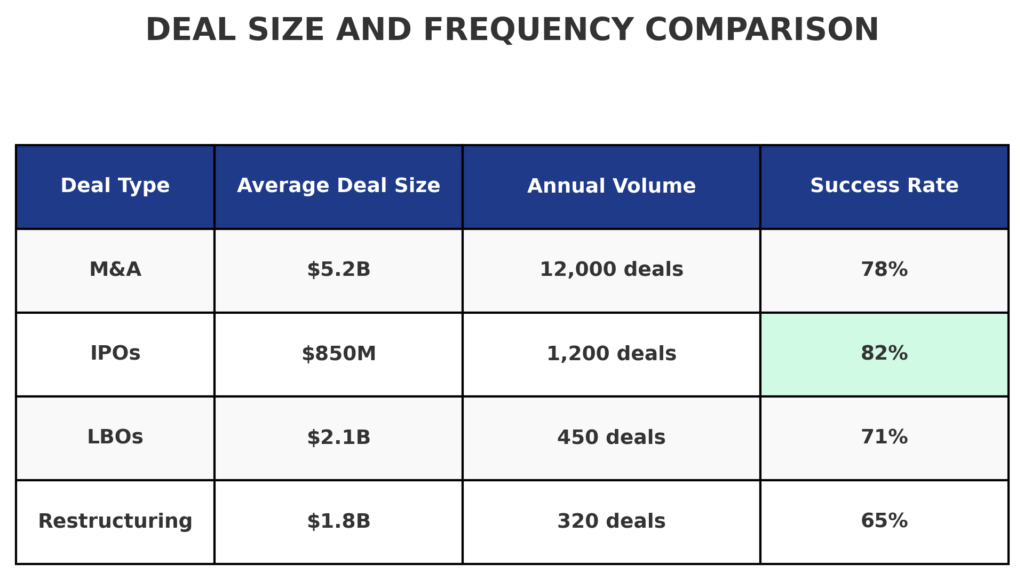
| Mergers & Acquisitions | Strategic combinations and corporate restructuring | $1B – $200B+ | Synergy analysis, integration planning, regulatory approval |
| Initial Public Offerings | Companies going public for the first time | $100M – $50B+ | Market timing, valuation, investor relations |
| Leveraged Buyouts | Private equity-backed acquisitions | $500M – $25B+ | Debt structuring, operational improvement, exit strategies |
| Debt Restructuring | Corporate financial reorganization | $250M – $75B+ | Creditor negotiations, liquidity management, operational turnaround |
Industry-Specific Case Studies
Investment banking case studies often focus on specific sectors, including:
- Technology sector: Emphasis on intellectual property valuation, scalability assessment, and competitive positioning
- Healthcare and pharmaceuticals: Focus on regulatory compliance, patent portfolios, and clinical trial outcomes
- Energy and natural resources: Analysis of commodity price cycles, environmental regulations, and infrastructure requirements
- Financial services: Regulatory capital requirements, digital transformation, and fintech integration
Geographic and Cross-Border Studies
These case studies examine transactions across different jurisdictions, highlighting:
- Regulatory compliance requirements across multiple countries
- Currency hedging strategies and foreign exchange risk management
- Cultural and operational integration challenges
- Tax optimization structures and transfer pricing considerations
Benefits of Investment Banking Case Studies
Investment banking case studies provide numerous advantages for financial professionals, academic institutions, and corporate decision-makers:
Professional Development Benefits
Case studies serve as powerful educational tools that develop critical analytical skills. Finance professionals gain exposure to real-world scenarios, enabling them to understand complex transaction dynamics and develop problem-solving capabilities. The structured approach to case analysis helps professionals master financial modeling techniques, valuation methodologies, and strategic thinking processes.
Strategic Decision-Making Enhancement
Organizations benefit from case study analysis by gaining insights into successful transaction strategies and best practices. These studies provide benchmarking opportunities, allowing companies to compare their approaches with industry leaders and identify areas for improvement. The comprehensive nature of case studies enables executives to make more informed strategic decisions regarding mergers, acquisitions, and capital allocation.
Risk Management Improvement
Case studies highlight potential pitfalls and risk factors that can derail transactions. By analyzing failed deals and successful risk mitigation strategies, professionals develop better risk assessment capabilities. This knowledge helps organizations avoid costly mistakes and implement more effective risk management frameworks.
Market Intelligence and Competitive Analysis
Investment banking case studies provide valuable market intelligence, including pricing trends, valuation multiples, and competitive positioning strategies. This information helps organizations understand market dynamics and develop more effective competitive strategies.
Challenges and Risks in Investment Banking Case Studies
Despite their significant benefits, investment banking case studies present several challenges and limitations:
Data Availability and Quality Issues
Access to comprehensive transaction data can be limited due to confidentiality agreements and competitive sensitivity. Many case studies rely on publicly available information, which may not provide complete insights into deal dynamics. The quality and accuracy of available data can vary significantly, potentially affecting the reliability of case study conclusions.
Market Condition Variations
Case studies often reflect specific market conditions that may not be applicable to current or future environments. The dynamic nature of financial markets means that strategies successful in one period may not be effective in different market conditions. This temporal limitation requires careful consideration when applying case study insights to contemporary situations.
Regulatory and Compliance Complexities
The regulatory environment for investment banking transactions continues to evolve, with new compliance requirements and oversight mechanisms regularly introduced. Case studies based on historical transactions may not reflect current regulatory standards, potentially limiting their applicability to contemporary deal structures.
Analytical Bias and Interpretation Challenges
Case study analysis can be subject to confirmation bias, where analysts focus on information that supports predetermined conclusions. The complexity of investment banking transactions makes it challenging to isolate specific factors that contribute to success or failure, potentially leading to oversimplified or inaccurate interpretations.
Implementation and How Investment Banking Case Studies Work
The development and implementation of investment banking case studies follows a structured methodology designed to maximize analytical value and educational impact:
Case Study Development Process
The creation of comprehensive case studies begins with selecting transactions based on their strategic significance, complexity, and educational value. Investment banks typically choose transactions that demonstrate key analytical concepts, innovative deal structures, or significant market impact. The selection process considers factors such as deal size, industry relevance, and availability of supporting data.
Data collection and validation represent the most critical phase of case study development. This process involves gathering financial statements, market data, regulatory filings, and transaction documents. Investment banks employ teams of analysts to verify data accuracy and ensure comprehensive coverage of all relevant transaction aspects.
Analytical Framework Implementation
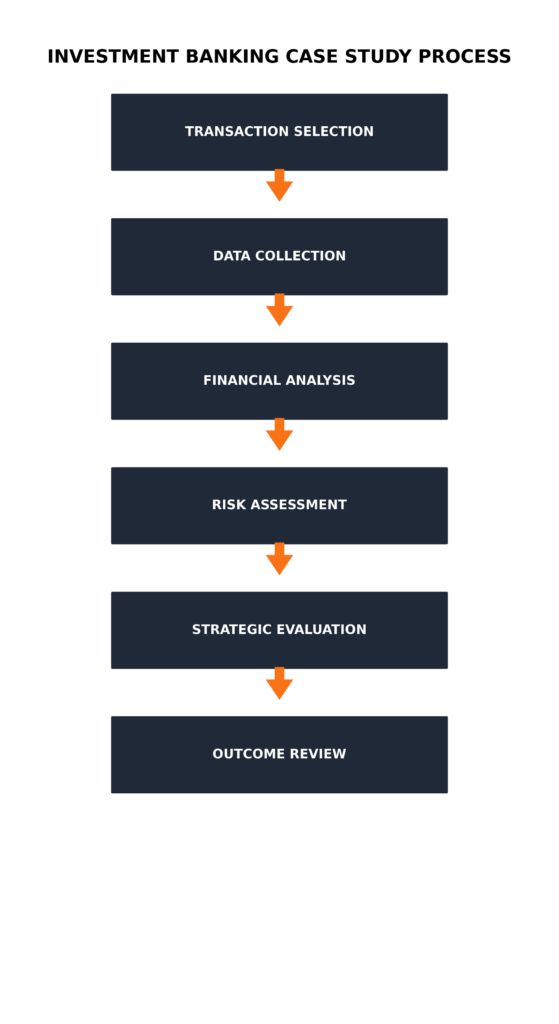
The analytical framework for investment banking case studies typically includes:
- Situation analysis: Market conditions, competitive landscape, and strategic rationale
- Financial analysis: Valuation methodologies, financial modeling, and sensitivity analysis
- Risk assessment: Identification and quantification of potential risks and mitigation strategies
- Transaction structure: Deal terms, financing arrangements, and legal considerations
- Outcome evaluation: Post-transaction performance and lessons learned
Educational Integration
Leading investment banks and academic institutions integrate case studies into professional development programs through structured learning modules. These programs typically include interactive workshops, group discussions, and practical exercises designed to reinforce key concepts and develop analytical skills.
The implementation process often involves peer review and validation to ensure accuracy and educational effectiveness. Subject matter experts review case studies for technical accuracy, analytical rigor, and pedagogical value before integration into training programs.
Future Trends in Investment Banking Case Studies
The evolution of investment banking case studies continues to be shaped by technological advances, regulatory changes, and market dynamics:
Technology Integration and Digital Transformation
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies is revolutionizing case study analysis. Advanced analytics platforms enable more sophisticated financial modeling, risk assessment, and scenario analysis. Investment banks are increasingly using natural language processing to analyze vast amounts of textual data, including contracts, regulatory filings, and market research reports.
Virtual and augmented reality technologies are being explored for immersive case study experiences, allowing professionals to interact with complex financial models and transaction structures in three-dimensional environments. This technology promises to enhance understanding of complex deal dynamics and improve learning outcomes.
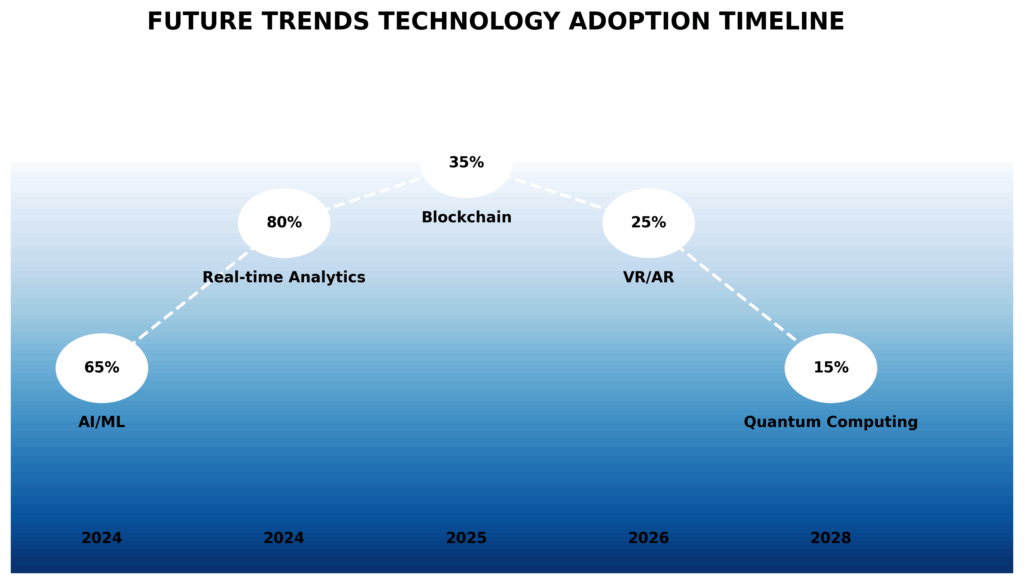
ESG and Sustainability Focus
Environmental, social, and governance factors are becoming increasingly important in investment banking transactions. Future case studies will likely place greater emphasis on ESG considerations, including carbon footprint analysis, social impact assessment, and governance structure evaluation. This trend reflects growing investor demand for sustainable investment opportunities and regulatory pressure for enhanced ESG disclosure.
Cross-Border and Emerging Market Emphasis
The globalization of financial markets continues to drive demand for case studies focusing on cross-border transactions and emerging market opportunities. Investment banks are developing specialized expertise in navigating complex regulatory environments, currency risks, and cultural differences that characterize international transactions.
Real-Time Case Study Development
Advances in data analytics and reporting technologies are enabling the development of real-time case studies that track transaction progress as it unfolds. This capability allows for more dynamic and responsive educational content that reflects current market conditions and regulatory changes.
FAQs – Investment Banking Case Studies
1. What makes an investment banking case study effective for learning purposes?
An effective investment banking case study combines comprehensive financial analysis with clear strategic insights and practical applications. It should include detailed financial models, market analysis, risk assessment, and outcome evaluation. The most valuable case studies present complex scenarios that require critical thinking and demonstrate real-world application of theoretical concepts.
2. How do investment banks select transactions for case study development?
Investment banks typically select transactions based on strategic significance, educational value, complexity, and market impact. Selection criteria include deal size, industry relevance, innovative deal structures, and availability of comprehensive data. Banks also consider the transaction’s ability to demonstrate key analytical concepts and provide valuable learning experiences.
3. What role do financial models play in investment banking case studies?
Financial models serve as the analytical backbone of investment banking case studies, providing quantitative frameworks for valuation, risk assessment, and scenario analysis. These models typically include discounted cash flow analysis, comparable company analysis, precedent transaction analysis, and sensitivity analysis. Advanced models may incorporate Monte Carlo simulations and other sophisticated analytical techniques.
4. How do regulatory changes affect the relevance of historical case studies?
Regulatory changes can significantly impact the relevance of historical case studies by altering compliance requirements, transaction structures, and market dynamics. While core analytical principles remain applicable, specific regulatory considerations may require updates or modifications. Investment banks regularly review and update case studies to reflect current regulatory environments.
5. What are the most common valuation methodologies used in investment banking case studies?
The most common valuation methodologies include discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis, comparable company analysis (trading multiples), precedent transaction analysis (transaction multiples), and asset-based valuation approaches. Many case studies employ multiple methodologies to provide comprehensive valuation ranges and cross-validate results.
6. How do investment banking case studies address cross-border transaction complexities?
Cross-border case studies address complexities through a comprehensive analysis of regulatory differences, currency risks, tax implications, and cultural considerations. These studies typically include foreign exchange hedging strategies, transfer pricing analysis, and jurisdiction-specific compliance requirements. They also examine integration challenges and operational considerations across different countries.
7. What is the typical timeline for developing a comprehensive investment banking case study?
The development timeline varies based on transaction complexity and data availability, typically ranging from 3 to 12 months. Simple case studies may be completed in 6-8 weeks, while complex cross-border transactions or industry-specific studies may require 6-12 months. The process includes data collection, analysis, validation, and peer review phases.
8. How do investment banking case studies incorporate ESG considerations?
Modern case studies increasingly incorporate ESG factors through sustainability analysis, social impact assessment, and governance structure evaluation. This includes carbon footprint analysis, diversity and inclusion metrics, board composition assessment, and stakeholder engagement strategies. ESG considerations are integrated into valuation models and risk assessment frameworks.
9. What are the key differences between academic and professional investment banking case studies?
Academic case studies typically focus on theoretical concepts and educational objectives, while professional case studies emphasize practical applications and business outcomes. Professional case studies often include more detailed financial analysis, proprietary methodologies, and confidential information. Academic versions may be simplified or disguised to protect sensitive information while maintaining educational value.
10. How do investment banks measure the success of their case study programs?
Success metrics include participant feedback scores, knowledge retention assessments, practical application of learned concepts, and career advancement outcomes. Investment banks also track program completion rates, participant engagement levels, and long-term impact on professional performance. Some institutions conduct follow-up surveys to assess the practical application of case study insights in real-world situations.
Conclusion
Investment banking case studies represent an invaluable resource for understanding the complexities of modern financial transactions and developing the analytical skills necessary for success in investment banking.
These comprehensive examinations provide insights into successful deal strategies, risk management techniques, and valuation methodologies that have shaped the financial industry. The systematic analysis of real-world transactions enables professionals to learn from both successes and failures, developing the critical thinking skills essential for navigating complex financial environments.
The evolution of investment banking case studies continues to reflect changes in global financial markets, regulatory frameworks, and technological capabilities.
As the industry increasingly emphasizes ESG considerations, digital transformation, and cross-border complexity, case studies will continue to evolve to address these emerging challenges. The integration of advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and real-time data will further enhance the educational value and practical application of these studies.
For aspiring investment bankers and seasoned professionals alike, mastering the art of case study analysis remains essential for achieving excellence in the dynamic world of investment banking, where the ability to synthesize complex information and develop strategic insights determines success in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
For your reference, recently published articles include:
-
-
- Investment Liquidity Analysis Made Simple – Three Free Samples
- How To Use Risk Tolerance Questionnaire Example For Better Results
- Master Your Wealth: Financial Disclaimers Explained
- Rate Volume Analysis: Best Expert Advice For Your Success
- Irrational Investing: Why Emotions Destroy Your Portfolio
- Investment Risk Monitoring – All You Need To Know
-
………………………………………………..
Important Notice: The information in this article is for general and public information purposes only. It solely reflects Didi Somm’s or his Staff’s opinion, and no responsibility can be assumed for errors or omissions in the service’s contents. For details, please read the Disclaimer at the bottom of the homepage.

