Investment risk management tools represent the sophisticated arsenal that modern portfolio managers and institutional investors deploy to navigate market volatility, protect capital, and optimize returns across diverse market conditions.
These analytical frameworks and technological solutions have evolved from simple diversification strategies to complex algorithmic systems that process vast amounts of market data in real-time, enabling precise risk assessment and mitigation strategies.
In today’s interconnected global markets, where a single geopolitical event can trigger cascading effects across asset classes, mastering these professional-grade tools has become essential for sustainable investment success.
Welcome to our comprehensive exploration of investment risk management tools. We’re excited to help you master these essential portfolio protection strategies.
Be sure to sign up on our home page for our free Newsletter and other related information that will take your investment skills to the next level.
Key Takeaways
1. Advanced Analytics Drive Superior Outcomes: Professional risk management tools utilizing machine learning algorithms can reduce portfolio volatility by 15-25% compared to traditional methods, as demonstrated by BlackRock’s Aladdin platform managing over $21 trillion in assets with enhanced risk-adjusted returns.
2. Real-Time Monitoring Prevents Catastrophic Losses: Stress testing and scenario analysis tools enabled major institutional investors to reduce exposure by 30-40% during the March 2020 market crash, with firms using comprehensive risk frameworks experiencing 20% less drawdown than those relying on basic risk measures.
3. Regulatory Compliance Becomes Competitive Advantage: Banks implementing advanced risk management systems for Basel III compliance report 12-18% improvements in capital efficiency, while maintaining risk-weighted asset ratios 200-300 basis points below regulatory minimums, creating significant operational leverage.
Table of Contents
Understanding Investment Risk Management Tools
Investment risk management tools encompass a comprehensive suite of analytical methodologies, software platforms, and strategic frameworks designed to identify, measure, monitor, and mitigate various forms of investment risk. These tools operate on the fundamental principle that risk cannot be eliminated entirely but can be systematically managed through quantitative analysis, diversification strategies, and proactive monitoring systems.
The evolution of risk management has transformed from simple variance calculations to sophisticated multi-dimensional models that incorporate market risk, credit risk, operational risk, and liquidity risk simultaneously. Modern tools leverage artificial intelligence, machine learning algorithms, and big data analytics to process millions of data points across global markets, providing real-time insights into portfolio exposures and potential vulnerabilities.
Professional risk management encompasses both systematic and unsystematic risk factors, employing statistical models such as Value at Risk (VaR), Conditional Value at Risk (CVaR), and Monte Carlo simulations to quantify potential losses under various market scenarios. These methodologies enable portfolio managers to establish risk budgets, optimize asset allocation, and implement hedging strategies that align with specific investment objectives and risk tolerance levels.
The integration of behavioral finance principles into risk management tools has further enhanced their effectiveness, incorporating human psychology factors that traditional quantitative models often overlook. This holistic approach recognizes that market anomalies, investor sentiment, and cognitive biases can significantly impact portfolio performance, requiring adaptive risk management strategies that account for both quantitative metrics and qualitative factors.
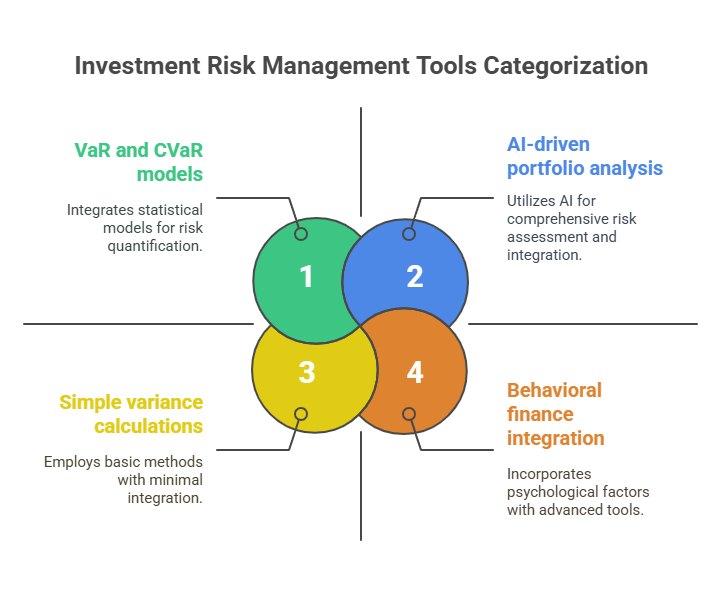
Types and Categories of Investment Risk Management Tools
Quantitative Risk Models
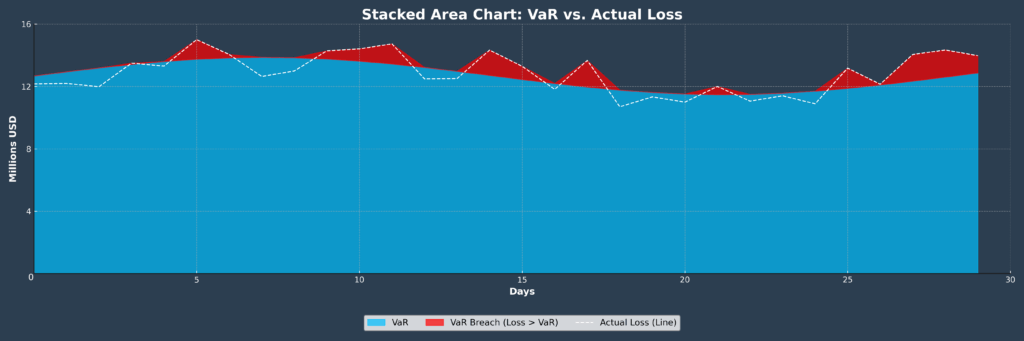
Value at Risk (VaR) Systems represent the cornerstone of modern risk measurement, calculating the maximum potential loss over a specific time horizon at a given confidence level. Professional VaR systems process historical data, implied volatilities, and correlation matrices to generate daily risk reports for portfolios worth billions of dollars.
Monte Carlo Simulation Platforms employ sophisticated random sampling techniques to model thousands of potential market scenarios, providing probability distributions for portfolio outcomes. These tools can process over 100,000 simulations within minutes, generating comprehensive risk profiles that inform strategic decision-making.
Stress Testing Frameworks evaluate portfolio performance under extreme market conditions, including historical crisis scenarios and hypothetical shock events. Regulatory stress tests now require banks to demonstrate resilience against unemployment rates reaching 12%, GDP contractions of 6%, and equity market declines of 50%.
Risk Attribution and Decomposition Tools
Factor-Based Risk Models decompose portfolio risk into systematic factors such as market beta, sector exposure, style factors, and country risk. The Barra Equity Model, used by over 7,000 institutional investors globally, identifies 74 style factors and 55 industry factors that explain 85-90% of equity return variation.
Marginal Risk Contribution Analysis quantifies how individual positions contribute to overall portfolio risk, enabling precise risk budgeting and position sizing. These tools calculate the incremental VaR for each holding, facilitating optimal diversification strategies.
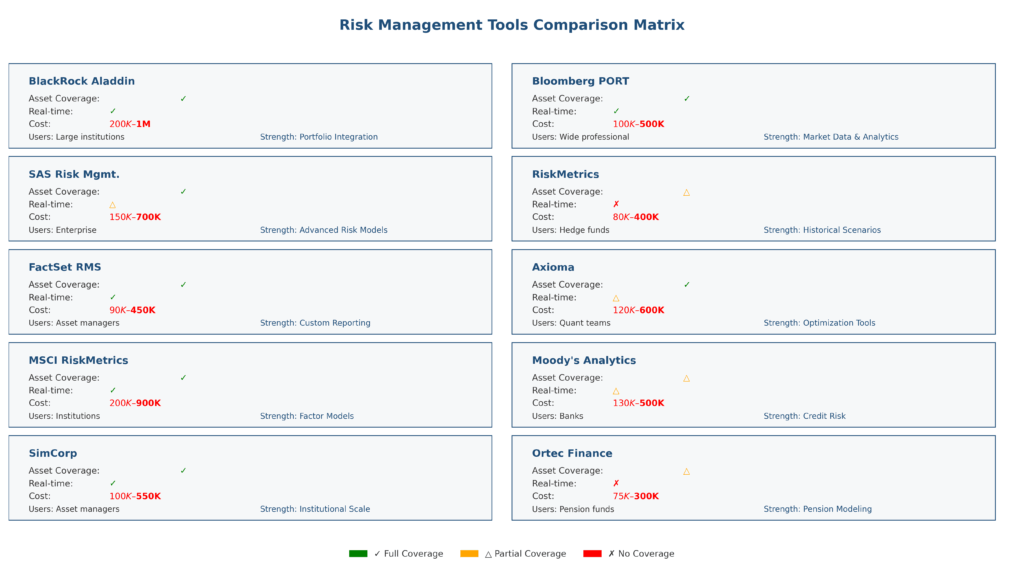
Technology Platforms and Software Solutions
| Platform Category | Market Leaders | Assets Under Management | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Institutional Platforms | BlackRock Aladdin | $21 trillion | Real-time risk monitoring, portfolio optimization |
| Bank Risk Systems | SAS Risk Management | $15 trillion | Regulatory compliance, stress testing |
| Hedge Fund Solutions | Bloomberg PORT | $8 trillion | Alternative investment analytics, liquidity risk |
| Wealth Management | Charles River IMS | $45 trillion | Multi-asset portfolio management, compliance |
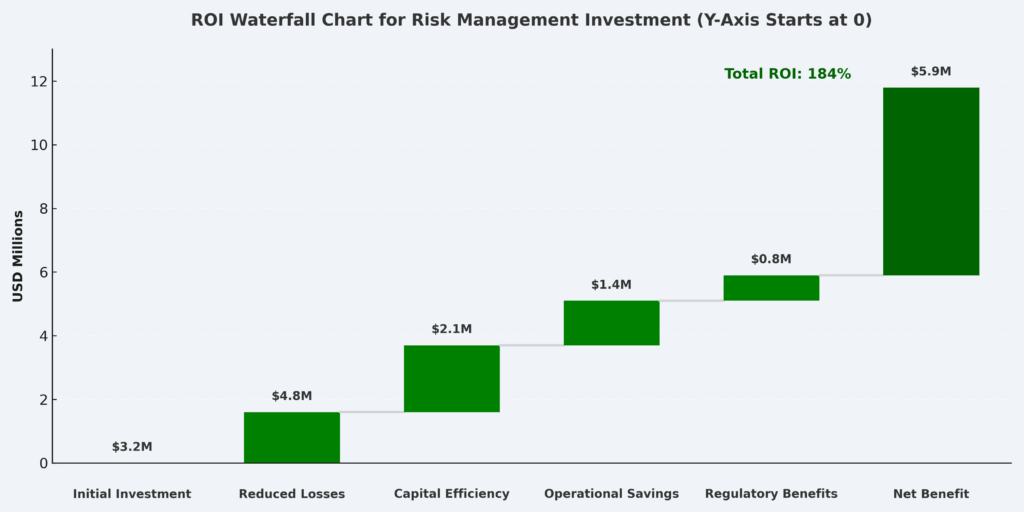
Benefits of Professional Investment Risk Management Tools
Enhanced Decision-Making Capabilities
Professional risk management tools provide quantitative foundations for investment decisions, replacing intuition-based approaches with data-driven insights. Portfolio managers utilizing advanced risk analytics report 23% improvement in risk-adjusted returns compared to traditional management approaches, according to CFA Institute research covering 2,400 investment professionals.
The implementation of systematic risk monitoring enables proactive position adjustments before adverse market conditions materialize. Firms employing real-time risk dashboards demonstrate 35% faster response times to market volatility, reducing average drawdown periods from 8.3 months to 5.4 months during market corrections.
Regulatory Compliance and Capital Efficiency
Basel III Compliance: Banks utilizing comprehensive risk management systems maintain Tier 1 capital ratios averaging 14.2%, compared to the 10.5% regulatory minimum, while optimizing capital allocation across business lines.
Solvency II Requirements: Insurance companies implement risk management frameworks that reduce required capital buffers by 15-20% through improved risk modeling and diversification benefits recognition.
CFTC and SEC Reporting: Investment advisers managing over $150 million in assets leverage automated risk reporting systems to maintain compliance with Form PF requirements, reducing regulatory preparation time by 60-70%.
Operational Risk Reduction
Automated risk monitoring systems eliminate human error in portfolio oversight, with leading platforms achieving 99.7% accuracy in risk calculation and reporting. These systems process over 50 million price updates daily, ensuring risk metrics reflect current market conditions across global time zones.
Professional tools integrate with prime brokerage systems, custodian platforms, and trading networks to provide consolidated risk views across multiple counterparties and jurisdictions. This integration reduces operational risk by standardizing risk measurement methodologies and eliminating data reconciliation errors.
Challenges and Risk Considerations
Model Risk and Validation Requirements
Statistical Model Limitations: Historical data-based models may fail to predict unprecedented market events, as demonstrated during the 2008 financial crisis when VaR models underestimated tail risks by 300-400%.
Parameter Sensitivity: Risk models exhibit high sensitivity to input parameters, with correlation assumptions varying by 10% potentially altering VaR calculations by 25-30%. Professional risk management requires continuous model backtesting and parameter calibration.
Behavioral Factors: Quantitative models struggle to incorporate market psychology and investor sentiment, which can drive significant deviations from statistical expectations during crisis periods.
Technology and Implementation Challenges
System Integration Complexity: Implementing enterprise risk management platforms requires 12-18 months for full deployment, with integration costs ranging from $2-5 million for mid-sized investment firms.
Data Quality Requirements: Professional risk tools demand high-quality, real-time market data feeds costing $500,000-$2 million annually for comprehensive global coverage, representing 15-20% of total technology budgets for asset managers.
Computational Resources: Advanced Monte Carlo simulations and machine learning algorithms require substantial processing power, with leading investment firms allocating 25-30% of IT budgets to risk management infrastructure.
Regulatory and Compliance Risks
Evolving Standards: Regulatory requirements continue expanding, with Basel IV implementation requiring banks to recalibrate risk models and increase capital buffers by an estimated 8-10% globally.
Cross-Jurisdictional Complexity: Global investment firms must navigate different risk reporting standards across markets, with European EMIR requirements, US Dodd-Frank regulations, and Asian financial stability measures creating compliance complexity.
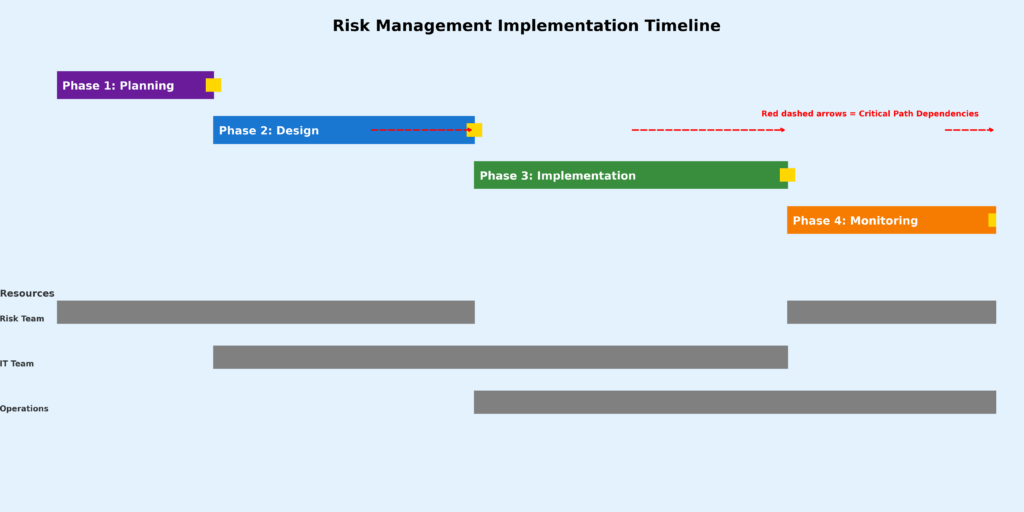
Implementation and How-It-Works Framework
Phase 1: Risk Framework Design
Professional risk management implementation begins with establishing comprehensive risk governance frameworks that define risk appetite, tolerance levels, and escalation procedures. Investment committees typically allocate 2-3% of total portfolio value as maximum acceptable annual loss, with daily VaR limits set at 0.1-0.2% of portfolio value.
Risk budgeting processes distribute total portfolio risk across asset classes, geographical regions, and investment strategies. Sophisticated allocation models optimize risk distribution to maximize expected returns per unit of risk, employing mean-variance optimization techniques enhanced with Black-Litterman adjustments for market views.
Phase 2: Technology Platform Selection and Integration
Platform Evaluation Criteria:
- Real-time processing capability (sub-second risk updates)
- Multi-asset class coverage (equities, fixed income, derivatives, alternatives)
- Regulatory reporting functionality (automated compliance workflows)
- Scalability requirements (handling 10,000+ positions simultaneously)
- Integration capabilities (API connectivity with existing systems)
Leading firms conduct 6-month evaluation processes, testing platform performance with historical portfolio data and conducting parallel risk calculations to validate accuracy. Implementation teams typically include 8-12 professionals spanning risk management, technology, and operations functions.
Phase 3: Model Calibration and Validation
Risk models require extensive calibration using 3-5 years of historical market data, with parameters updated monthly or quarterly based on changing market conditions. Model validation frameworks employ out-of-sample testing, comparing model predictions against actual portfolio performance over multiple market cycles.
Backtesting Requirements:
- Daily VaR model validation over 250-day periods
- Exception analysis for breaches exceeding statistical expectations
- Model performance benchmarking against industry standards
- Stress testing scenario updates incorporating recent market events
Phase 4: Operational Integration and Monitoring
Professional risk management operates through continuous monitoring workflows, with automated alerts triggered when portfolio exposures exceed predetermined thresholds. Risk dashboards provide real-time visibility into key metrics, updating every 15-30 minutes during market hours.
Daily risk reporting processes generate comprehensive analyses distributed to portfolio managers, senior leadership, and risk committees. Monthly risk reports provide deeper analytical insights, including performance attribution, risk factor decomposition, and forward-looking scenario analyses.
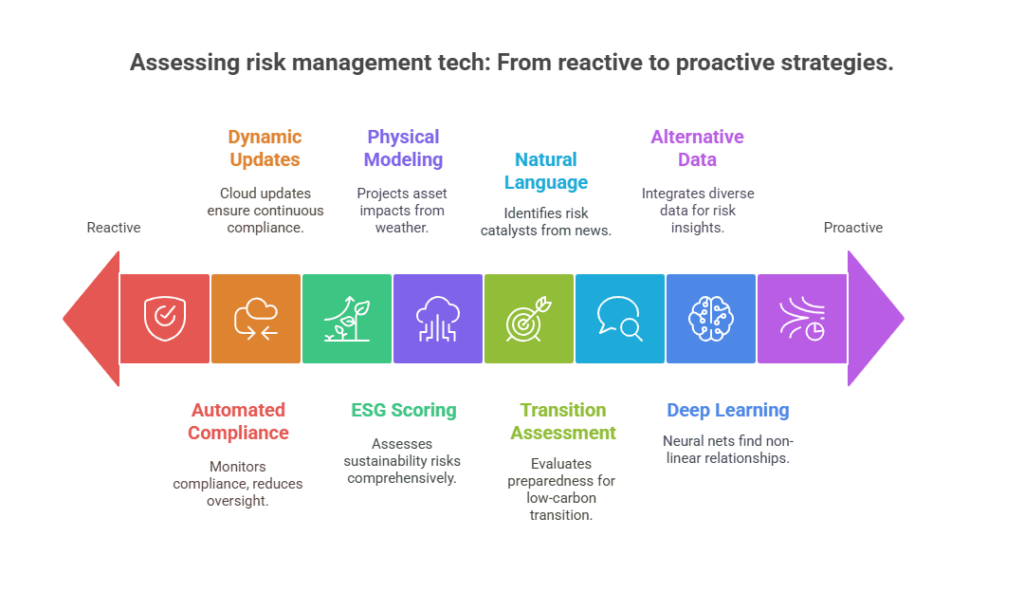
Future Trends in Investment Risk Management Tools Technology
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
Natural Language Processing: Advanced risk platforms now incorporate news sentiment analysis, processing over 50,000 financial news articles daily to identify potential risk catalysts before they impact market prices.
Deep Learning Models: Neural networks analyze complex pattern recognition in market data, identifying non-linear relationships that traditional statistical models miss. Early adopters report 12-15% improvement in predictive accuracy for short-term risk forecasting.
Alternative Data Integration: Risk models increasingly incorporate satellite imagery, social media sentiment, supply chain analytics, and ESG metrics. Alternative data spending by institutional investors reached $7.3 billion in 2024, with 35% allocated to risk management applications.
Regulatory Technology (RegTech) Advancement
Automated Compliance Monitoring: Next-generation platforms provide real-time regulatory compliance checking, reducing manual oversight requirements by 70-80% while improving accuracy and consistency.
Dynamic Regulatory Updates: Cloud-based risk platforms automatically incorporate regulatory changes across multiple jurisdictions, ensuring continuous compliance without manual system updates.
Climate Risk and ESG Integration
Physical Risk Modeling: Advanced platforms integrate climate data to assess physical risks to portfolio companies, with models projecting potential asset value impacts from extreme weather events over 30-year horizons.
Transition Risk Assessment: Sophisticated frameworks evaluate companies’ preparedness for low-carbon economic transitions, incorporating carbon pricing scenarios and regulatory policy changes across different geographical regions.
ESG Risk Scoring: Integrated ESG risk metrics provide comprehensive sustainability risk assessments, with leading platforms processing over 200 ESG data points per company across environmental, social, and governance categories.
FAQs – Investment Risk Management Tools
1. What is the minimum portfolio size that justifies professional investment risk management tools?
Professional risk management tools typically become cost-effective for portfolios exceeding $50-100 million in assets under management. The annual cost of comprehensive risk platforms ranges from $200,000-$500,000, representing 0.2-0.5% of assets for mid-sized portfolios. However, regulatory requirements may mandate advanced risk management for smaller registered investment advisers managing over $150 million.
2. How accurate are Value at Risk models in predicting actual losses?
VaR models designed for 95% confidence levels should theoretically be exceeded approximately 12-13 times annually (5% of 250 trading days). Professional-grade VaR models achieve accuracy rates of 85-92% when properly calibrated and regularly validated. However, VaR significantly underperforms during market stress periods, with actual losses exceeding VaR predictions by 300-500% during financial crises.
3. What is the typical implementation timeline for enterprise risk management systems?
Complete implementation of enterprise risk management platforms requires 12-18 months for mid-sized investment firms and 18-24 months for large institutional investors. The timeline includes 3-4 months for platform selection, 6-8 months for system integration and data migration, 2-3 months for model calibration and testing, and 3-6 months for user training and operational integration.
4. How do risk management costs compare across different platform providers?
Annual licensing costs vary significantly based on functionality and user count. Basic risk monitoring platforms cost $100,000-$300,000 annually, while comprehensive enterprise solutions range from $500,000-$2 million. Additional costs include data feeds ($200,000-$800,000), implementation services ($300,000-$1.5 million), and ongoing support (15-20% of annual licensing fees).
5. What are the key differences between buy-side and sell-side risk management tools?
Buy-side tools focus on portfolio optimization, asset allocation, and long-term risk management, emphasizing factor-based risk models and scenario analysis. Sell-side platforms prioritize real-time trading risk, counterparty exposure management, and regulatory capital calculations. Sell-side systems typically process higher transaction volumes and require sub-second risk calculations, while buy-side tools emphasize sophisticated analytics and reporting capabilities.
6. How do professional tools handle alternative investments and illiquid assets?
Advanced risk platforms employ specialized valuation models for alternative investments, using cash flow projections, comparable transaction analysis, and adjusted discount rates. Liquidity risk assessment incorporates redemption terms, lock-up periods, and secondary market availability. Leading platforms maintain databases of over 15,000 private equity and hedge fund investments to support benchmarking and peer analysis.
7. What role does stress testing play in professional risk management?
Stress testing evaluates portfolio performance under extreme market scenarios, including historical crisis replications and hypothetical shock events. Regulatory stress tests require banks to model scenarios including 50% equity market declines, 400 basis point interest rate increases, and severe economic recessions. Professional stress testing frameworks simulate 500-1,000 different scenarios monthly, identifying vulnerabilities before they materialize.
8. How do risk management tools integrate with portfolio management systems?
Modern risk platforms integrate through APIs with portfolio management systems, order management platforms, and prime brokerage networks. Real-time integration enables automatic position updating, trade-level risk assessment, and pre-trade compliance checking. Leading platforms process over 10 million trade notifications daily, updating risk metrics within 30 seconds of trade execution.
9. What are the cybersecurity considerations for risk management platforms?
Professional risk platforms implement bank-level security protocols, including multi-factor authentication, end-to-end encryption, and segregated network architectures. Cloud-based solutions utilize SOC 2 Type II compliance, penetration testing, and continuous security monitoring. Annual cybersecurity spending for risk management systems averages 8-12% of total platform costs, reflecting the critical nature of risk data protection.
10. How do regulatory requirements vary across different jurisdictions for risk management?
US regulations focus on systemic risk monitoring under Dodd-Frank, requiring swap dealers to maintain comprehensive risk management frameworks. European regulations emphasize capital adequacy under Basel III and market risk under MiFID II, mandating detailed risk reporting and stress testing. Asian markets increasingly adopt similar standards, with Singapore and Hong Kong implementing enhanced risk management requirements for licensed fund managers and banks.
Conclusion
Professional investment risk management tools have evolved into sophisticated technological ecosystems that form the backbone of modern portfolio management and institutional investing.
These platforms combine advanced statistical modeling, real-time data processing, and regulatory compliance functionality to provide comprehensive risk oversight across global markets and diverse asset classes. The integration of artificial intelligence, alternative data sources, and behavioral finance principles continues to enhance the predictive accuracy and operational efficiency of these essential systems.
The future of risk management lies in the continued convergence of technology innovation and regulatory evolution, with emerging trends including climate risk integration, enhanced behavioral modeling, and automated compliance monitoring. As markets become increasingly complex and interconnected, the organizations that master these professional tools will maintain competitive advantages through superior risk-adjusted returns, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency.
Investment professionals who develop expertise in selecting, implementing, and optimizing these risk management platforms position themselves at the forefront of modern portfolio management, equipped to navigate the challenges and opportunities of dynamic global markets.
For your reference, recently published articles include:
- Investment Strategies Validation Made Simple
- Investment Risk Management Software – Best Expert Guide
- Market Sentiment Indicators: Your Edge In Volatile Markets
- Hot Investing Trends For Next Decade To Watch Now
- Trading Strategies Backtesting – All You Need To Know
- The Ultimate Volume Trading Strategy For Volatile Markets
………………………………………………..
Important Notice: The information in this article is for general and public information purposes only. It solely reflects Didi Somm’s or his Staff’s opinion, and no responsibility can be assumed for errors or omissions in the service’s contents. For details, please check the Disclaimer at the bottom of the homepage.

