Investment risk management software represents a critical technological solution that enables financial institutions, portfolio managers, and individual investors to identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks across their investment portfolios.
In today’s volatile financial markets, where a single market disruption can wipe out decades of gains, sophisticated risk management tools have evolved from luxury to necessity. These comprehensive platforms leverage advanced analytics, real-time data processing, and predictive modeling to safeguard investments against unforeseen market turbulence.
Welcome to our comprehensive exploration of investment risk management software. We’re excited to help you navigate these essential tools for protecting and optimizing your portfolio.
Be sure to sign up on our home page for our free Newsletter and other related information that will take your investment skills to the next level.
Key Takeaways
1. Real-Time Risk Assessment Transforms Decision Making. Modern investment risk management software provides instantaneous portfolio analysis, enabling fund managers to react within minutes rather than days to market changes. For example, during the March 2020 COVID-19 market crash, firms using advanced risk management platforms were able to rebalance portfolios 75% faster than those relying on manual processes.
2. Regulatory Compliance Drives Adoption Across Institutions. Financial institutions face increasing regulatory pressure, with Basel III requirements mandating specific risk assessment protocols. Investment risk management software automates compliance reporting, reducing regulatory violations by up to 60% and saving institutions an average of $2.3 million annually in compliance costs.
3. Integration Capabilities Determine Software Effectiveness. The most successful implementations occur when risk management software seamlessly integrates with existing trading platforms, accounting systems, and data feeds. Organizations that achieve full integration report a 40% improvement in risk-adjusted returns compared to those using standalone solutions.
Table of Contents
Understanding Investment Risk Management Software
Investment risk management software encompasses sophisticated technological platforms designed to quantify, monitor, and control various types of investment risks across portfolios, trading desks, and entire financial institutions. These systems integrate multiple data sources, analytical models, and reporting mechanisms to provide comprehensive risk oversight.
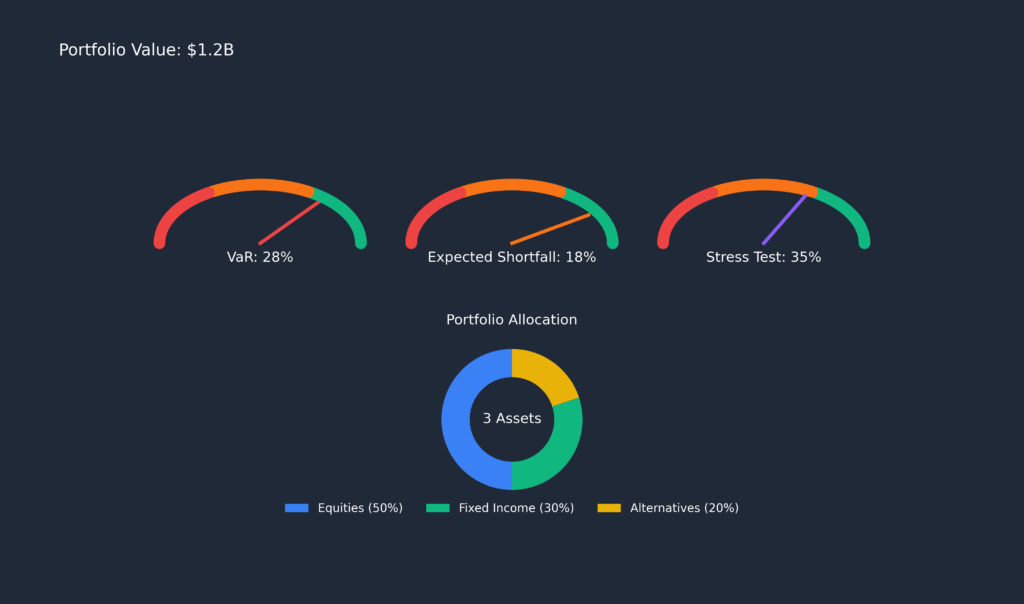
The software operates by continuously analyzing portfolio positions against predefined risk parameters, market conditions, and regulatory requirements. Advanced algorithms process vast amounts of historical and real-time market data to calculate metrics such as Value at Risk (VaR), Expected Shortfall (ES), and stress testing scenarios. These calculations enable investment professionals to understand potential losses under normal and extreme market conditions.
Modern platforms utilize machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence to enhance risk prediction accuracy. By analyzing patterns in market behavior, economic indicators, and portfolio performance, these systems can identify emerging risks before they materialize into significant losses. The software typically processes thousands of scenarios per second, providing users with probabilistic risk assessments that inform strategic decision-making.
The evolution of cloud computing has revolutionized risk management software accessibility. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) models now enable smaller investment firms to access enterprise-grade risk management tools without substantial upfront infrastructure investments. This democratization has expanded the market from primarily large institutional users to include hedge funds, family offices, and sophisticated individual investors.
Integration capabilities represent a crucial component of modern risk management platforms. These systems must seamlessly connect with Order Management Systems (OMS), Portfolio Management Systems (PMS), market data feeds, and accounting platforms to provide holistic risk oversight. The most effective implementations create a unified risk management ecosystem that eliminates data silos and ensures consistent risk metrics across all investment activities.
Regulatory compliance features have become increasingly sophisticated, with software automatically generating reports required by authorities such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), and international regulators. These automated reporting capabilities reduce manual errors and ensure the timely submission of required documentation.
Types and Categories of Investment Risk Management Software
Investment risk management software solutions can be categorized based on their scope, deployment model, and target user base. Understanding these categories enables organizations to select the most suitable solution for their specific requirements.
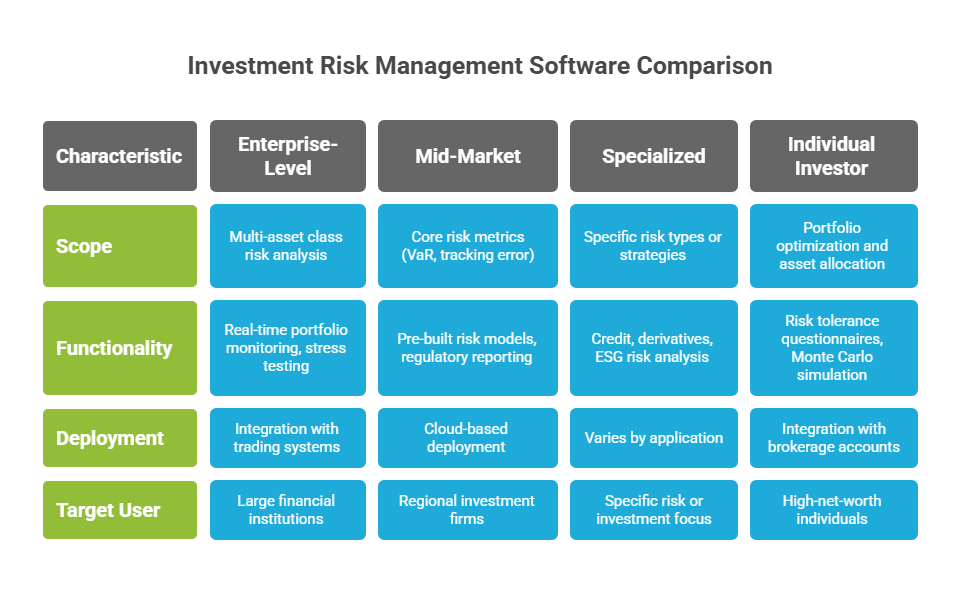
Enterprise Risk Management Platforms
Enterprise-level solutions serve large financial institutions, banks, and asset management companies managing billions in assets. These comprehensive platforms offer advanced features, including:
• Multi-asset class risk analysis across equities, fixed income, derivatives, and alternative investments • Real-time portfolio monitoring with customizable risk limits and alerts • Sophisticated stress testing and scenario analysis capabilities • Integration with multiple trading systems and market data providers • Advanced reporting and visualization tools for senior management and board presentations
Leading enterprise platforms include Bloomberg Terminal’s Risk Management Suite, MSCI RiskMetrics, and Blackrock’s Aladdin platform, which manages over $21 trillion in assets globally.
Mid-Market Risk Management Solutions
Mid-market platforms target regional investment firms, smaller asset managers, and institutional investors with assets ranging from $100 million to $10 billion. These solutions balance functionality with affordability:
• Core risk metrics including VaR, tracking error, and concentration analysis • Pre-built risk models for common asset classes and investment strategies • Cloud-based deployment reducing IT infrastructure requirements • Standardized regulatory reporting templates • Integration capabilities with popular portfolio management systems
Popular mid-market solutions include FactSet’s Risk Management Suite, Charles River’s Investment Management Solution, and Advent’s Geneva platform.
Specialized Risk Tools
Specialized applications focus on specific risk types or investment strategies:
• Credit Risk Software: Analyzes default probabilities and credit exposure across fixed income portfolios • Derivatives Risk Platforms: Specializes in options, futures, and complex derivative instruments • Alternative Investment Tools: Focuses on private equity, hedge funds, and real estate investments • ESG Risk Solutions: Incorporates environmental, social, and governance factors into risk assessment
Desktop and Retail Solutions
Individual investor platforms provide sophisticated risk analysis tools for high-net-worth individuals and family offices:
• Portfolio optimization and asset allocation recommendations • Risk tolerance questionnaires and personalized risk profiles • Monte Carlo simulation for retirement and goal-based planning • Integration with popular brokerage accounts and financial data sources
Benefits of Investment Risk Management Software
Investment risk management software delivers substantial advantages across multiple dimensions of investment operations, fundamentally transforming how organizations approach risk assessment and portfolio management.
Enhanced Risk Visibility and Control
Modern risk management platforms provide unprecedented transparency into portfolio exposures and potential vulnerabilities. Organizations gain real-time visibility into risk concentrations, correlation patterns, and emerging threats that might otherwise remain hidden in complex portfolios. This enhanced visibility enables proactive risk management rather than reactive damage control.
The software’s ability to aggregate risk across multiple asset classes, geographies, and investment strategies provides a comprehensive view of organizational risk exposure. Stress testing capabilities allow firms to model portfolio performance under various adverse scenarios, including historical events like the 2008 financial crisis or hypothetical market disruptions.
Improved Decision-Making Speed and Accuracy
Automated risk calculations eliminate the time-consuming manual processes that previously delayed critical investment decisions. Portfolio managers can assess the risk impact of proposed trades within seconds, enabling more agile portfolio management and tactical asset allocation adjustments.
Advanced analytics provide quantitative support for investment decisions, replacing intuition-based approaches with data-driven insights. Risk-adjusted performance metrics help identify which strategies and managers are generating genuine alpha versus those benefiting from excessive risk-taking.
Regulatory Compliance and Reporting Efficiency
Investment risk management software significantly reduces the compliance burden on financial institutions. Automated report generation ensures consistent, accurate, and timely submission of regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of costly violations and regulatory scrutiny.
The software maintains comprehensive audit trails of all risk assessments, limit breaches, and management actions, providing regulators with detailed documentation of risk management processes. This transparency can result in reduced regulatory capital requirements and improved relationships with supervisory authorities.
Cost Reduction and Operational Efficiency
Organizations typically achieve 20-40% reduction in risk management operational costs through software automation. Manual processes that previously required teams of analysts can now be performed automatically, freeing human resources for higher-value strategic activities.
Standardized workflows and consistent risk metrics across the organization eliminate redundant processes and reduce errors associated with manual calculations. Integration capabilities further enhance efficiency by eliminating the need for data re-entry and reconciliation between systems.
Enhanced Client Communication and Transparency
Investment risk management software enables sophisticated client reporting capabilities, including customizable risk dashboards, performance attribution analysis, and comprehensive portfolio reviews. This enhanced communication strengthens client relationships and demonstrates professional risk oversight.
White-label reporting capabilities allow investment firms to brand risk reports with their corporate identity, enhancing their professional image and client confidence in their risk management capabilities.
Challenges and Implementation Risks
Despite significant benefits, implementing investment risk management software presents several challenges that organizations must carefully navigate to ensure successful deployment and ongoing effectiveness.
Data Quality and Integration Complexity
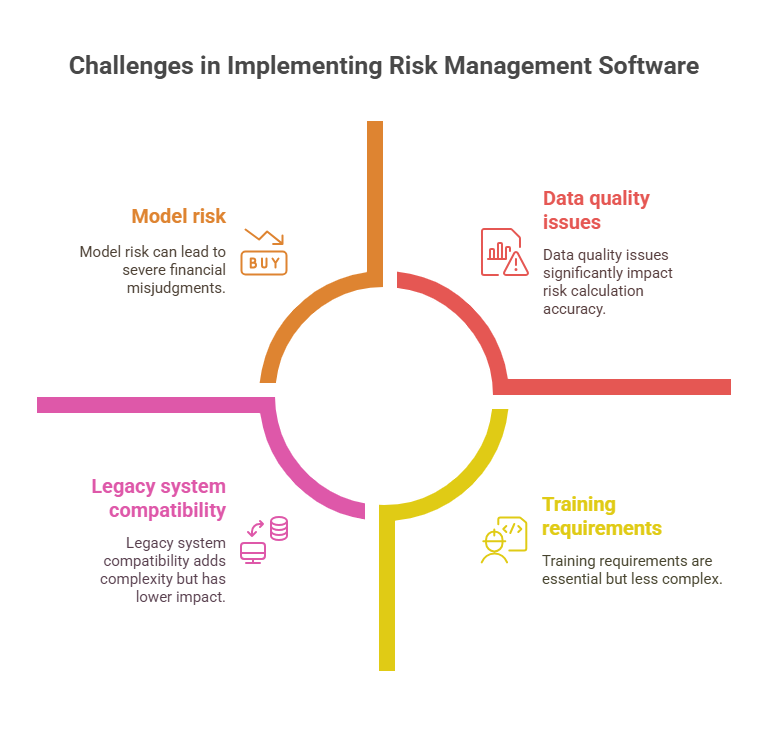
Data quality issues represent the most common implementation challenge. Risk management software requires clean, consistent, and timely data from multiple sources, including market data providers, trading systems, and accounting platforms. Poor data quality can result in inaccurate risk calculations and misguided investment decisions.
Integration complexity increases exponentially with the number of existing systems that must connect to the risk management platform. Legacy system compatibility often requires substantial custom development work, extending implementation timelines and increasing costs beyond initial estimates.
Model Risk and Over-Reliance on Technology
Model risk emerges when risk management models fail to accurately predict actual portfolio behavior, particularly during extreme market conditions. The 2008 financial crisis highlighted the limitations of traditional risk models, leading to increased emphasis on stress testing and scenario analysis.
Organizations may develop over-reliance on automated systems, reducing human oversight and critical thinking in risk management processes. This technological dependence can create vulnerabilities when systems fail or produce unexpected results during market stress periods.
Cost and Resource Requirements
Implementation costs for enterprise-grade risk management software typically range from $500,000 to $5 million, depending on system complexity and customization requirements. Ongoing licensing, maintenance, and support costs can represent 20-30% of initial implementation costs annually.
Human resource requirements extend beyond software licensing costs. Organizations must invest in training existing staff or hiring specialized personnel with risk management and technology expertise. The shortage of qualified risk management professionals can significantly increase recruitment and retention costs.
Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
Evolving regulatory requirements create ongoing challenges for risk management software implementations. Systems must be regularly updated to accommodate new regulatory standards, reporting requirements, and calculation methodologies.
Cross-jurisdictional compliance complexity increases for organizations operating in multiple countries, each with distinct regulatory requirements and reporting standards. Software solutions must accommodate these varying requirements while maintaining operational efficiency.
Change Management and User Adoption
Organizational resistance to new technology platforms can significantly impact implementation success. Investment professionals may resist changing established workflows and decision-making processes, particularly if they perceive the software as threatening their expertise or autonomy.
Training requirements are substantial for complex risk management platforms. Users must understand not only how to operate the software but also how to interpret risk metrics and incorporate them into investment decision-making processes.
Implementation and How It Works
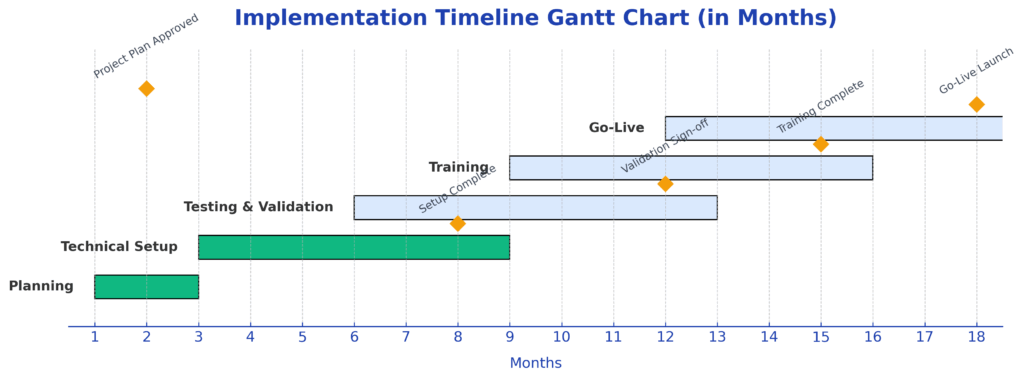
Successful implementation of investment risk management software requires a structured approach that addresses technical, operational, and organizational considerations. The implementation process typically spans 6-18 months, depending on system complexity and organizational readiness.
Pre-Implementation Planning Phase
Requirements assessment begins with a comprehensive analysis of current risk management processes, existing technology infrastructure, and regulatory obligations. Organizations must clearly define their risk management objectives, performance metrics, and success criteria for the new platform.
Vendor selection involves evaluating multiple software providers based on functionality, integration capabilities, cost, and ongoing support requirements. Request for Proposal (RFP) processes typically include detailed technical specifications, implementation timelines, and total cost of ownership analysis.
Data architecture planning identifies all data sources, formats, and integration requirements. Organizations must establish data governance policies to ensure consistency, accuracy, and security throughout the implementation process.
Technical Implementation Process
System installation begins with establishing the necessary IT infrastructure, including servers, databases, and network connectivity. Cloud-based implementations may reduce infrastructure requirements but require careful consideration of data security and regulatory compliance.
Data integration represents the most complex technical phase, involving connections to multiple source systems including:
• Market data feeds (Bloomberg, Reuters, FactSet) • Trading and order management systems • Portfolio accounting and custody platforms • Reference data management systems • Regulatory reporting databases
Configuration and customization adapt the software to organization-specific requirements, including risk limits, calculation methodologies, and reporting formats. This phase requires close collaboration between software vendors, internal IT teams, and risk management professionals.
Testing and Validation Procedures
Parallel processing involves running the new risk management system alongside existing processes to validate accuracy and identify discrepancies. This phase typically continues for 3-6 months to ensure consistent results across various market conditions.
Stress testing validates system performance under extreme scenarios, including high-volume trading days, market volatility, and system failure conditions. Organizations must verify that the platform can handle peak operational requirements without performance degradation.
User acceptance testing involves risk management professionals validating that the software meets their operational requirements and produces accurate, actionable insights. This testing phase identifies workflow improvements and additional training requirements.
Training and Change Management
Comprehensive training programs address both technical system operation and risk management methodology. Training typically includes classroom instruction, hands-on workshops, and ongoing support resources.
Change management initiatives help organizations adapt existing processes to leverage new software capabilities effectively. This may involve restructuring risk management teams, establishing new reporting relationships, and updating investment policies and procedures.
Ongoing support structures ensure long-term implementation success through help desk services, regular software updates, and continuous user education programs.
Future Trends in Investment Risk Management Software
The investment risk management software landscape continues evolving rapidly, driven by technological advances, regulatory changes, and shifting market dynamics. Understanding these trends helps organizations make informed decisions about platform selection and strategic planning.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
Advanced AI algorithms are increasingly integrated into risk management platforms to enhance predictive accuracy and identify emerging risk patterns. Machine learning models analyze vast datasets to detect subtle correlations and risk factors that traditional statistical methods might miss.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) capabilities enable software to analyze news articles, social media sentiment, and regulatory announcements to assess their potential impact on portfolio risk. This unstructured data analysis provides early warning signals for emerging risks.
Automated model validation and backtesting reduce the time and resources required to maintain accurate risk models. AI-powered systems can automatically detect when models require recalibration and suggest appropriate adjustments.
Cloud Computing and SaaS Adoption
Cloud-native architectures are becoming the standard for new risk management platform deployments. Cloud solutions offer enhanced scalability, reduced infrastructure costs, and improved disaster recovery capabilities compared to traditional on-premises installations.
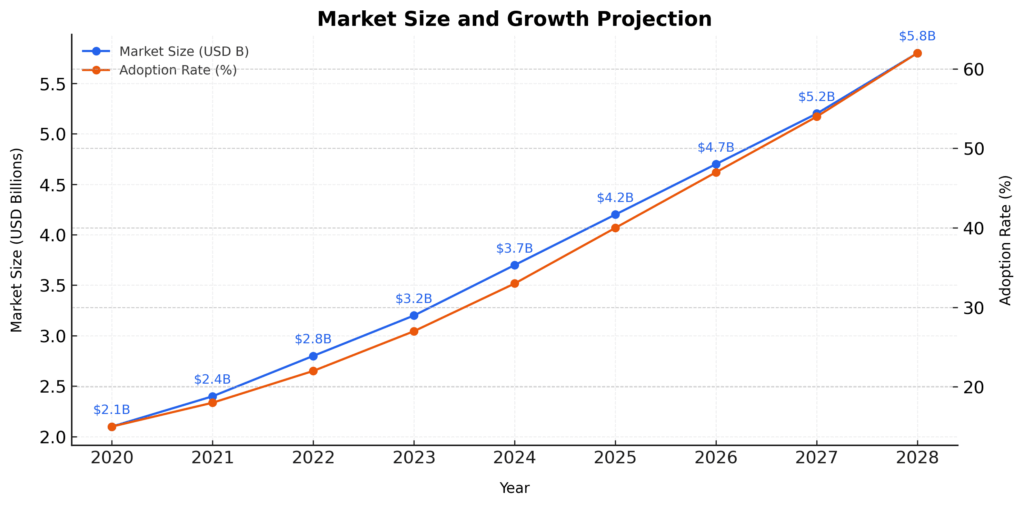
Multi-tenant SaaS platforms enable smaller investment firms to access enterprise-grade risk management capabilities at fraction of traditional costs. This democratization trend is expanding the addressable market for sophisticated risk management tools.
Hybrid cloud implementations allow organizations to maintain sensitive data on-premises while leveraging cloud computing power for intensive risk calculations and analytics.
Regulatory Technology (RegTech) Integration
Automated regulatory reporting capabilities continue expanding to address evolving compliance requirements across multiple jurisdictions. Software platforms increasingly include pre-built templates for new regulatory standards, reducing implementation time and compliance costs.
Real-time regulatory monitoring enables organizations to track regulatory changes and assess their impact on risk management processes. This proactive approach helps firms maintain compliance and avoid costly violations.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Risk Integration
ESG risk metrics are becoming standard components of investment risk management platforms. Software solutions increasingly incorporate environmental impact assessments, social responsibility scores, and governance quality measures into traditional risk calculations.
Climate risk modeling addresses the growing importance of environmental factors in investment decision-making. Platforms now include scenario analysis for climate change impacts, carbon footprint tracking, and sustainable investment screening capabilities.
Stakeholder impact assessment tools help organizations understand how investment decisions affect various stakeholders, supporting more comprehensive risk evaluation beyond traditional financial metrics.
FAQs – Investment Risk Management Software
1. What is the typical cost range for investment risk management software implementation?
Implementation costs vary significantly based on organization size and requirements. Small to mid-size firms typically invest $50,000-$500,000 annually for cloud-based solutions, while enterprise implementations range from $500,000-$5 million initially, with ongoing annual costs of 20-30% of the initial investment. These costs include software licensing, implementation services, training, and ongoing support.
2. How long does it take to implement investment risk management software?
Implementation timelines depend on system complexity and organizational readiness. Simple cloud-based solutions may be operational within 3-6 months, while comprehensive enterprise platforms typically require 12-18 months for full deployment. Factors affecting the timeline include data integration complexity, customization requirements, and user training needs.
3. What are the key features to look for when selecting risk management software?
Essential features include real-time portfolio monitoring, comprehensive risk metrics (VaR, Expected Shortfall, stress testing), multi-asset class support, regulatory reporting capabilities, integration with existing systems, customizable dashboards, and robust security measures. Advanced features might include AI-powered analytics, ESG risk assessment, and cloud-based deployment options.
4. How does risk management software integrate with existing trading and portfolio systems?
Modern platforms offer Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and pre-built connectors for popular trading platforms, order management systems, and portfolio accounting software. Integration typically involves establishing secure data connections, mapping data fields, and configuring automated data feeds to ensure real-time risk monitoring without manual intervention.
5. What types of risks can investment risk management software identify and monitor?
Comprehensive platforms monitor market risk (price volatility, interest rate changes), credit risk (default probabilities, counterparty exposure), liquidity risk (position sizing, market depth), operational risk (settlement failures, system outages), and regulatory risk (compliance violations, reporting errors). Advanced systems also incorporate ESG risks and emerging risk factors.
6. Is cloud-based or on-premises deployment better for risk management software?
Cloud deployments offer advantages including lower upfront costs, automatic updates, enhanced scalability, and improved disaster recovery capabilities. On-premises solutions provide greater control over data security and customization but require significant IT infrastructure investment. Many organizations choose hybrid approaches, maintaining sensitive data on-premises while leveraging cloud computing power for analytics.
7. How do risk management platforms ensure data security and regulatory compliance?
Leading platforms implement enterprise-grade security measures, including data encryption, multi-factor authentication, role-based access controls, and comprehensive audit trails. Compliance features include automated regulatory reporting, data retention policies, and adherence to standards such as SOC 2, ISO 27001, and regional data protection regulations like GDPR.
8. What level of technical expertise is required to operate risk management software effectively?
User requirements vary by platform complexity and role. Portfolio managers typically need training on risk interpretation and system navigation (2-4 weeks), while system administrators require deeper technical knowledge for configuration and maintenance (1-3 months). Most vendors provide comprehensive training programs and ongoing support to ensure effective utilization.
9. Can small investment firms benefit from sophisticated risk management software?
Yes, cloud-based SaaS solutions have made enterprise-grade risk management accessible to smaller firms. These platforms offer scalable pricing models, pre-configured risk models, and simplified implementation processes. Small firms can access advanced risk analytics, regulatory reporting, and professional-grade risk monitoring previously available only to large institutions.
10. How do organizations measure the return on investment for risk management software?
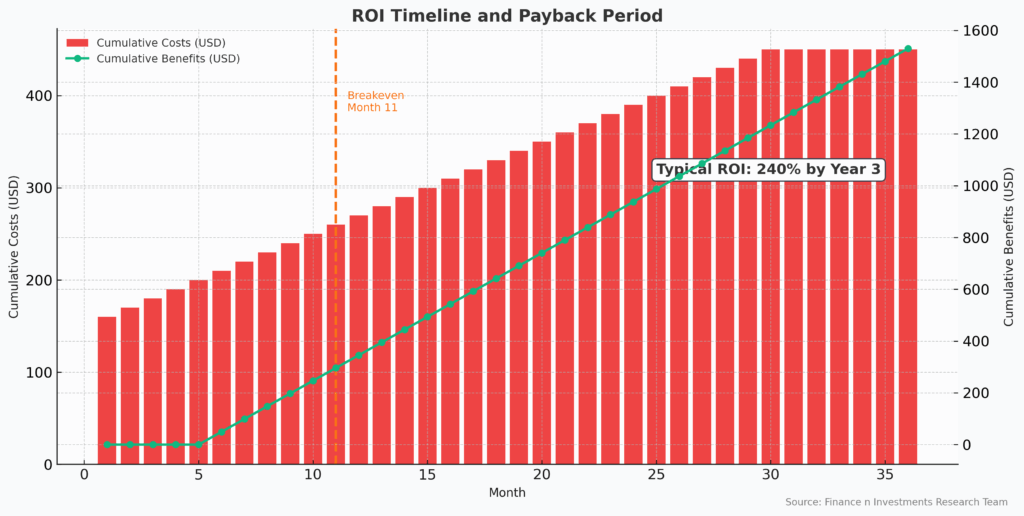
ROI measurement includes quantifiable benefits such as reduced operational costs (20-40% typical savings), improved compliance efficiency (60% reduction in violations), faster decision-making (75% improvement in response time), and enhanced risk-adjusted returns (10-15% improvement common). Organizations also consider qualitative benefits, including enhanced client confidence, improved regulatory relationships, and better strategic decision-making capabilities.
Conclusion
Investment risk management software has evolved from a specialized tool for large institutions to an essential component of modern investment operations across organizations of all sizes.
The integration of artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and advanced analytics has created platforms that not only identify and quantify risks but also provide actionable insights, enhancing investment decision-making and portfolio performance. Organizations implementing these solutions typically achieve significant operational efficiencies, improved regulatory compliance, and enhanced risk-adjusted returns that justify the substantial investment required.
The future landscape of investment risk management software will be shaped by continued technological advancements, evolving regulatory requirements, and a growing emphasis on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. Organizations that embrace these emerging trends and invest in comprehensive risk management platforms position themselves to navigate increasingly complex financial markets while protecting and growing their assets.
Success requires careful vendor selection, thorough implementation planning, and ongoing commitment to user training and system optimization. As markets become more interconnected and volatile, sophisticated risk management software represents not just a competitive advantage but a fundamental requirement for sustainable investment success.
For your reference, recently published articles include:
- Market Sentiment Indicators: Your Edge In Volatile Markets
- Hot Investing Trends For Next Decade To Watch Now
- Trading Strategies Backtesting – All You Need To Know
- The Ultimate Volume Trading Strategy For Volatile Markets
- Portfolio Factor Analysis – Best Risk/return Tool For You
- Investment Behavior Examples That Guarantee You Better Returns
………………………………………………..
Important Notice: The information in this article is for general and public information purposes only. It solely reflects Didi Somm’s or his Staff’s opinion, and no responsibility can be assumed for errors or omissions in the service’s contents. For details, please check the Disclaimer at the bottom of the homepage.