In today’s complex financial landscape, investment compliance monitoring has become a critical function for investment firms seeking to navigate regulatory requirements while maximizing returns.
Investment compliance monitoring is the systematic process of ensuring that investment portfolios adhere to regulatory mandates, internal policies, and client-specific guidelines through pre-trade, post-trade, and end-of-day batch monitoring.
As regulatory scrutiny intensifies globally, effective compliance monitoring not only helps firms avoid costly penalties but also enhances operational efficiency and builds client trust.
Key Takeaways
- Proactive compliance monitoring significantly reduces financial and legal risks – Organizations implementing robust monitoring systems can detect potential violations before they occur, avoiding hefty fines like the £7.2 million penalty imposed on Aberdeen Asset Management by the UK’s FCA for compliance failures.
- Technology-driven compliance solutions deliver measurable ROI – Investment in automated compliance systems has shown to reduce rule inventory by up to 50% while improving monitoring accuracy, as evidenced by firms achieving 95% data accuracy rates through implementation of advanced monitoring tools.
- Cross-border investment activities require sophisticated compliance frameworks – With regulations varying significantly across jurisdictions, investment managers working with international clients must implement multi-layered compliance systems that can adapt to different regulatory environments, from Europe’s stringent transparency requirements to the varied state-level regulations in the US.
Table of Contents
Understanding Investment Compliance Monitoring
Definition and Scope
Investment compliance monitoring is a critical risk mitigation practice that ensures investment activities align with applicable laws, regulations, and client-specific mandates. It serves as a crucial line of defense in maintaining compliance with regulatory regimes and internal policies. The scope of investment compliance monitoring encompasses pre-trade approval processes, post-trade verification, and continuous monitoring of portfolio positions against established guidelines.
The monitoring process typically includes verification of investment limits, asset allocation parameters, prohibited investments, and various risk metrics. It also extends to ensuring adherence to specific regulatory frameworks such as NAIC, Solvency II, IFRS, and other region-specific regulations that govern investment activities.
Historical Context and Evolution
The field of investment compliance monitoring has undergone significant transformation over the past few decades. Prior to the 2008 financial crisis, compliance was primarily viewed as an advisory function with limited enforcement capabilities. The crisis marked a pivotal shift, leading to increased regulatory scrutiny and transforming compliance into an active risk management and monitoring function.
In response to the crisis, numerous regulatory frameworks were introduced or strengthened, including the Dodd-Frank Act in the United States and enhanced oversight by the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA). These changes demanded more robust compliance monitoring systems and processes from investment firms.
The evolution continued with the advent of technology-driven solutions, moving from manual spreadsheet-based monitoring to sophisticated automated systems capable of real-time monitoring and reporting. This technological progression has enabled compliance departments to handle increasingly complex regulatory requirements while improving efficiency and accuracy.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory landscape governing investment compliance monitoring varies across jurisdictions but generally includes multiple layers of oversight:
| Regulatory Level | Examples | Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Global | FATF, Basel Committee | Anti-money laundering, capital requirements |
| Regional | EU’s MiFID II, AIFMD | Market transparency, investor protection |
| National | SEC (US), FCA (UK), ASIC (Australia) | Registration, reporting, conduct |
| Industry-specific | NAIC, IFRS | Insurance, accounting standards |
| Self-regulatory | FINRA | Broker-dealer conduct |
These regulatory bodies establish requirements for various aspects of investment operations, including:
- Client suitability assessments
- Disclosure obligations
- Risk management practices
- Reporting and documentation
- Conflict of interest management
- Anti-money laundering procedures
Compliance with these diverse regulatory frameworks necessitates a comprehensive monitoring system that can adapt to evolving requirements and detect potential violations across multiple dimensions.
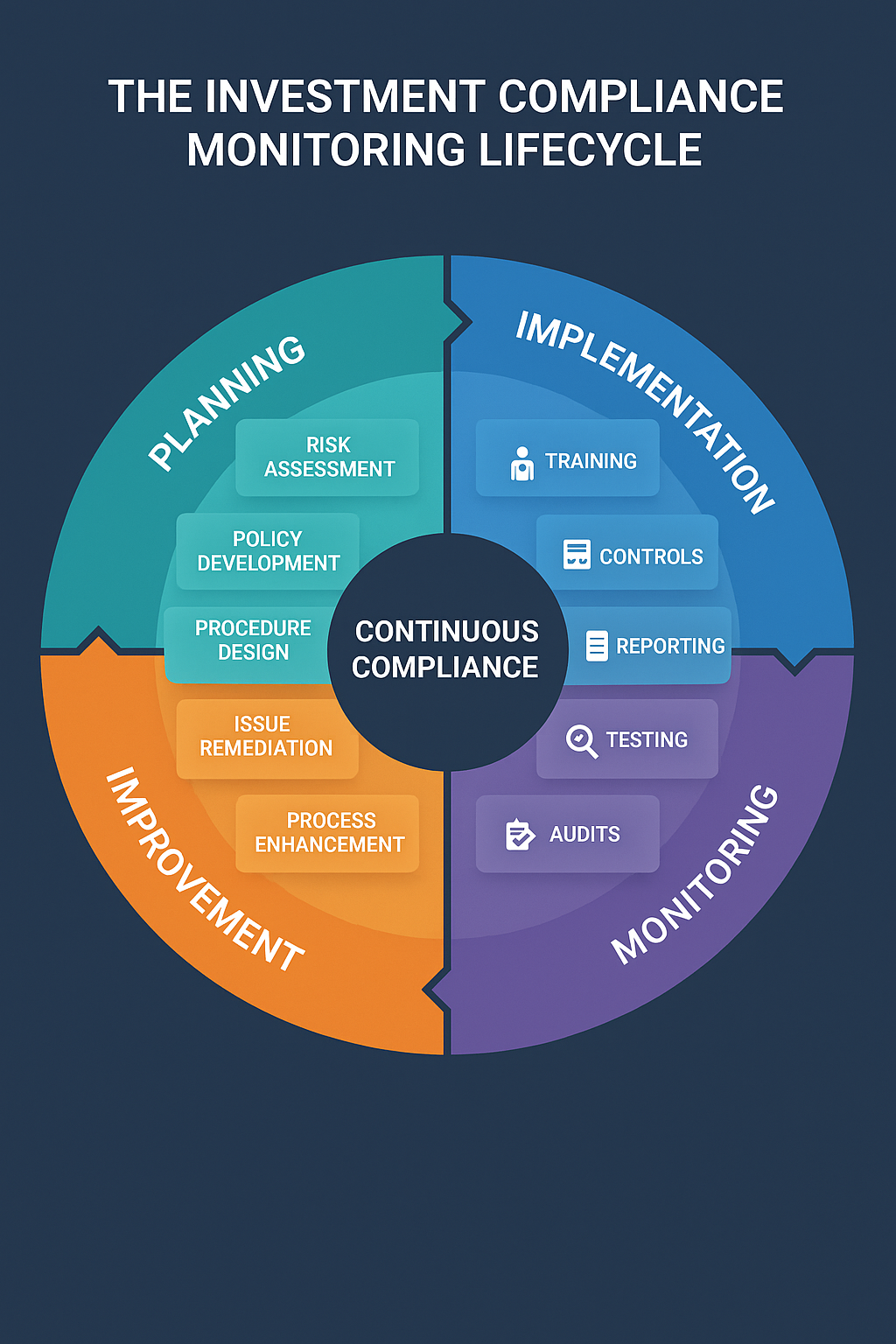
Types of Investment Compliance Monitoring
Pre-Trade Compliance
Pre-trade compliance monitoring occurs before an investment transaction is executed. This proactive approach serves as the first line of defense against potential violations by screening proposed trades against established guidelines and restrictions. Key components include:
- Order validation: Verifying that proposed orders align with investment mandates before execution
- Risk assessment: Evaluating potential transactions against risk parameters
- Restriction checking: Screening against prohibited securities or sectors
- Limit verification: Ensuring transactions won’t breach concentration or exposure limits
Pre-trade compliance systems typically integrate with order management systems to provide real-time feedback to portfolio managers, allowing them to adjust orders before execution if compliance issues are identified.
Post-Trade Compliance
Post-trade compliance monitoring reviews completed transactions to verify their adherence to applicable rules and guidelines. This process includes:
- Transaction review: Examining executed trades against compliance parameters
- Breach identification: Flagging transactions that violate investment restrictions
- Root cause analysis: Determining why compliance breaches occurred
- Remediation planning: Developing action plans to address violations
- Documentation: Recording compliance issues and resolution steps
Post-trade monitoring serves as a verification mechanism to catch any issues that might have slipped through pre-trade screens, particularly for complex transactions or when market conditions change rapidly during execution.
Continuous Monitoring
Continuous monitoring represents an ongoing surveillance approach that extends beyond specific transaction points. Elements include:
- Portfolio composition analysis: Regular review of holdings against guidelines
- Threshold monitoring: Tracking exposure levels against established limits
- Regulatory updates: Assessing portfolio compliance as regulations change
- Client guideline verification: Ensuring ongoing adherence to client-specific requirements
- Market event impact analysis: Evaluating how market shifts affect compliance status
Continuous monitoring has become increasingly important as regulatory expectations have shifted toward more active oversight and as portfolio compositions can change due to market movements even without new transactions.
Automated vs. Manual Monitoring
The comparison between automated and manual monitoring approaches reveals significant differences in efficiency and effectiveness:
| Aspect | Automated Monitoring | Manual Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Real-time or near-real-time | Delayed, often daily or weekly |
| Accuracy | Consistent application of rules | Vulnerable to human error |
| Coverage | Comprehensive across all holdings | Often sampling-based |
| Scalability | Easily handles large portfolios | Resource constraints with volume |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower ongoing | Lower setup, higher ongoing resource needs |
| Adaptability | Requires programming for changes | Can be more flexible for unique cases |
| Audit trail | Systematic documentation | Often less structured |
While automated systems have clear advantages in handling the volume and complexity of modern investment operations, many firms implement hybrid approaches that combine technology with human oversight for exception handling and judgment-based assessments.
Benefits of Effective Compliance Monitoring
Risk Mitigation
Effective investment compliance monitoring significantly reduces several types of risks:
- Regulatory risk: Minimizing the probability of violating regulations that could lead to penalties, sanctions, or license revocations
- Reputational risk: Protecting the firm’s standing with clients, partners, and the market
- Operational risk: Reducing errors and inefficiencies in investment processes
- Financial risk: Preventing losses from non-compliant investments or regulatory penalties
By implementing robust monitoring systems, investment firms create a structured approach to identifying and addressing risks before they materialize into actual compliance breaches or financial losses.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency
Well-designed compliance monitoring processes contribute to operational efficiency through:
- Standardization: Establishing consistent procedures across the organization
- Automation: Reducing manual intervention in routine compliance tasks
- Resource optimization: Allowing compliance staff to focus on higher-value activities
- Reduced redundancy: Eliminating duplicate compliance checks across departments
- Streamlined reporting: Generating required documentation efficiently
Many organizations have reported substantial efficiency gains after implementing advanced compliance monitoring systems, with some achieving up to 50% reduction in their rule inventory and significant time savings in compliance processes.
Improved Investor Confidence
Investment compliance monitoring builds investor trust through:
- Transparency: Demonstrating commitment to following rules and guidelines
- Accountability: Showing responsibility for investment decisions
- Consistency: Providing reliable adherence to stated investment policies
- Protection: Safeguarding client assets through proper governance
Investors increasingly consider the strength of a firm’s compliance framework when selecting investment managers, making effective monitoring a competitive advantage in attracting and retaining clients.
Competitive Advantage
A robust compliance monitoring program can create competitive differentiation by:
- Facilitating faster time to market for new investment products through streamlined compliance reviews
- Enabling entry into highly regulated markets with demanding compliance requirements
- Supporting customized client solutions with tailored compliance parameters
- Reducing compliance-related costs that impact investment performance
- Building a reputation for reliability and trustworthiness
Forward-thinking investment firms leverage their compliance capabilities as a selling point, particularly when serving institutional clients with strict due diligence requirements.
Challenges in Investment Compliance Monitoring
Regulatory Complexity
Investment firms face significant challenges navigating the intricate web of regulations:
- Multiple jurisdictions: Managing compliance across different countries with varying requirements
- Overlapping regulations: Reconciling potentially conflicting rules from different regulatory bodies
- Frequent updates: Keeping pace with regulatory changes and amendments
- Interpretation ambiguity: Understanding how broadly written regulations apply to specific situations
- Proportionality concerns: Determining appropriate compliance measures based on firm size and activities
The complexity is particularly challenging for global investment managers who must navigate regulations from numerous authorities simultaneously while ensuring consistent compliance approaches.
Data Management Issues
Effective compliance monitoring depends heavily on data quality and accessibility:
- Data fragmentation: Information stored across multiple systems and formats
- Inconsistent data standards: Variations in how data is captured and categorized
- Real-time availability: Ensuring timely access to data for monitoring purposes
- Historical preservation: Maintaining adequate records for lookback analysis
- Data governance: Establishing clear ownership and quality control for compliance data
These challenges are compounded by the volume and velocity of data generated in modern investment operations, requiring sophisticated data management capabilities.
Resource Constraints
Many investment firms struggle with limited resources for compliance functions:
- Budget limitations: Insufficient funding for technology and personnel
- Talent shortages: Difficulty recruiting and retaining compliance specialists
- Competing priorities: Balancing compliance needs against other business objectives
- Training requirements: Keeping staff current on regulatory developments and monitoring techniques
- Technology investments: Securing capital for compliance system upgrades
Resource constraints often force difficult trade-offs between the thoroughness of compliance and operational efficiency, particularly for smaller investment firms.
Technology Integration
Implementing and integrating compliance technology presents numerous hurdles:
- Legacy system compatibility: Connecting modern compliance tools with existing infrastructure
- Customization requirements: Adapting generic compliance solutions to firm-specific needs
- Vendor management: Coordinating across multiple technology providers
- System validation: Ensuring automated monitoring produces accurate results
- Change management: Training staff and adapting processes for new technologies
Despite these challenges, technology integration remains essential for scaling compliance monitoring capabilities to match growing regulatory demands and business complexity.
Implementing an Effective Compliance Monitoring Program
Program Design and Structure
Creating an effective investment compliance monitoring program begins with thoughtful design:
- Governance framework: Establish clear roles, responsibilities, and reporting lines
- Risk-based approach: Focus monitoring intensity on areas of highest regulatory risk
- Coverage mapping: Ensure all relevant regulations and guidelines are addressed
- Escalation protocols: Define procedures for handling compliance breaches
- Documentation standards: Establish requirements for recording monitoring activities
The program structure should align with the organization’s size, complexity, and risk profile while maintaining sufficient independence for compliance functions.
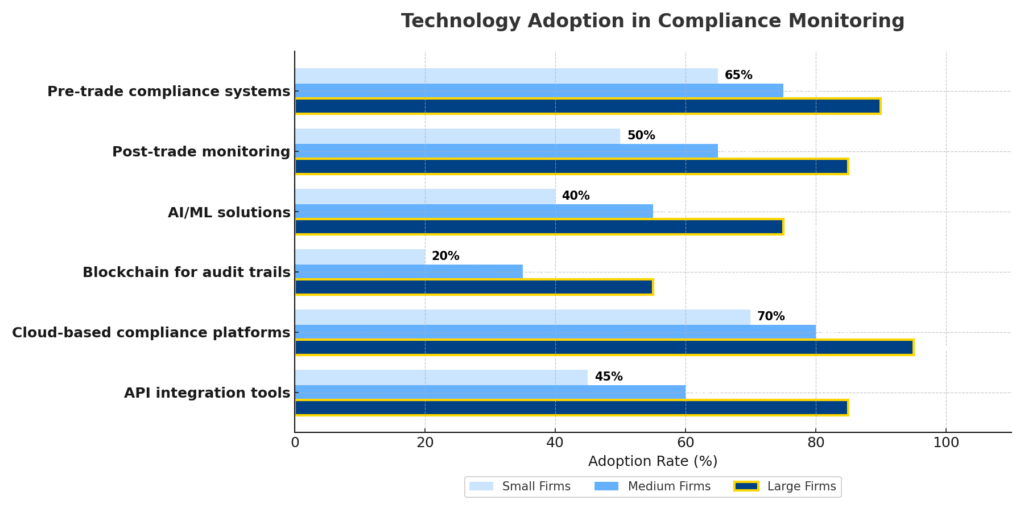
Technology Solutions
Modern compliance monitoring relies heavily on specialized technology:
- Order management system integration: Pre-trade compliance screening within trading platforms
- Rules-based engines: Codified compliance parameters for automated checking
- Exception management tools: Workflow systems for handling compliance alerts
- Dashboard reporting: Visual representations of compliance status
- Audit trail capabilities: Comprehensive recordkeeping of monitoring activities
Leading compliance technology solutions include Bloomberg AIM, Charles River Compliance, BlackRock’s Aladdin, and Ion’s (Latent Zero) Sentinel, which offer varying capabilities for different types of investment operations.
Best Practices for Implementation
Successful implementation of compliance monitoring programs typically follows these best practices:
- Phased approach: Rolling out capabilities incrementally rather than all at once
- Early stakeholder involvement: Engaging investment teams in design and testing
- Clear policies and procedures: Documenting monitoring processes comprehensively
- Regular testing: Validating monitoring effectiveness through periodic checks
- Continuous improvement: Refining approaches based on operational experience
- Executive sponsorship: Securing leadership support for compliance initiatives
- Cross-functional collaboration: Working across departments to ensure comprehensive coverage
Organizations should also consider implementation timelines that take into account regulatory deadlines, technology deployment cycles, and business priorities.
Training and Staff Development
Human expertise remains crucial even in highly automated compliance environments:
- Role-specific training: Tailored education for different compliance functions
- Regulatory updates: Regular briefings on relevant regulatory changes
- Technology proficiency: Ensuring staff can effectively use monitoring systems
- Scenario exercises: Practice handling different compliance situations
- Professional certifications: Supporting advanced compliance qualifications
- Knowledge sharing: Creating mechanisms for exchanging compliance insights
Investment in staff development pays dividends through more effective monitoring, better regulatory relationships, and reduced dependence on key individuals.
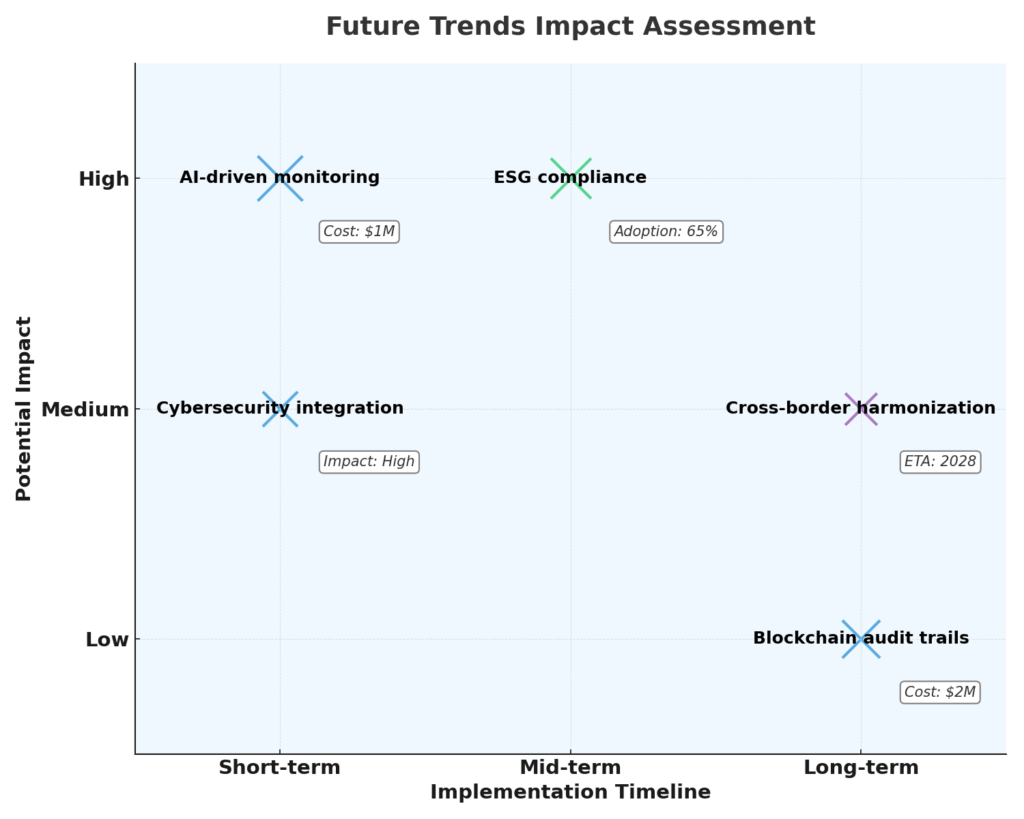
Future Trends in Investment Compliance Monitoring
Technological Innovations
Emerging technologies are transforming the compliance monitoring landscape:
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning: Advanced pattern recognition for identifying potential violations and reducing false positives
- Natural language processing: Automated interpretation of regulatory texts and investment guidelines
- Blockchain solutions: Immutable audit trails for compliance activities
- Cloud-based platforms: Scalable compliance infrastructure with reduced maintenance
- API-driven architecture: Seamless integration across multiple systems and data sources
These innovations are enabling more proactive, comprehensive, and efficient compliance monitoring while reducing the burden on compliance professionals.
Regulatory Evolution
Regulatory trends shaping the future of compliance monitoring include:
- Risk-based supervision: Regulatory focus on firms’ comprehensive risk management
- Real-time oversight expectations: Moving from periodic to continuous monitoring
- Cross-border harmonization efforts: Attempts to standardize requirements across jurisdictions
- Principles-based approaches: Emphasis on outcomes rather than prescriptive rules
- Individual accountability regimes: Personal liability for senior managers regarding compliance
As regulators leverage their own advanced analytics, investment firms must evolve their monitoring capabilities to stay ahead of examination approaches.
ESG Compliance Considerations
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors are creating new compliance monitoring requirements:
- Sustainability disclosures: Monitoring portfolio alignment with stated ESG objectives
- Greenwashing prevention: Verifying the authenticity of ESG investment claims
- Impact measurement: Tracking and reporting on non-financial outcomes
- Regulatory divergence: Managing different ESG standards across regions
- Data verification: Ensuring the quality of ESG metrics used in investment decisions
The integration of ESG factors into compliance monitoring is one of the fastest-growing areas in the field, particularly as regulations like the EU’s Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) take effect.
Cybersecurity and Data Privacy
Compliance monitoring increasingly encompasses data security dimensions:
- Personal data protection: Ensuring compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR
- Information security standards: Meeting requirements for safeguarding financial data
- Third-party oversight: Monitoring vendor compliance with security standards
- Cyber incident response: Preparing for compliance implications of security breaches
- Cross-border data transfers: Managing compliance with restrictions on data movement
As investment operations become more digitized, the intersection between compliance monitoring and cybersecurity will continue to grow in importance.
FAQs – Investment Compliance Monitoring
1. What is investment compliance monitoring?
Investment compliance monitoring is the systematic process of ensuring that investment portfolios and activities adhere to regulatory requirements, internal policies, and client-specific guidelines. It involves pre-trade screening, post-trade verification, and continuous surveillance of investments to prevent violations that could result in regulatory penalties, financial losses, or reputational damage.
2. Why is investment compliance monitoring important?
Investment compliance monitoring is crucial because it helps firms avoid regulatory penalties, builds investor trust, reduces operational risks, and improves investment decision-making. Effective monitoring serves as a protective mechanism against violations that could result in significant fines, such as the record-breaking $6.4 billion in penalties imposed by the SEC in recent years. It also demonstrates to clients that their investments are being managed responsibly within agreed parameters.
3. What are the key components of an effective compliance monitoring program?
An effective program includes well-defined policies and procedures, appropriate technology systems, clear governance structures, regular testing and validation, comprehensive documentation, escalation protocols for violations, and ongoing training. The program should cover pre-trade approvals, post-trade verification, continuous monitoring, and periodic audits to provide multiple layers of protection against compliance breaches.
4. How has technology changed investment compliance monitoring?
Technology has transformed compliance monitoring from a manual, sample-based process to a comprehensive, often real-time surveillance system. Modern compliance platforms can automatically check thousands of rules across entire portfolios, generate alerts for potential violations, maintain detailed audit trails, and produce regulatory reports. Advanced technologies, such as AI and machine learning, are further enhancing capabilities by identifying patterns and reducing false positives.
5. What challenges do firms face in implementing compliance monitoring?
Common challenges include managing regulatory complexity across multiple jurisdictions, integrating compliance systems with existing technology infrastructures, maintaining data quality and accessibility, allocating sufficient resources, keeping pace with regulatory changes, and striking a balance between thorough monitoring and operational efficiency. Firms also struggle with talent shortages in specialized compliance roles.
6. How do compliance monitoring needs differ across different types of investment firms?
Monitoring requirements vary based on firm size, investment strategies, asset classes, client types, and regulatory jurisdictions. For example, hedge funds may focus on trading restrictions and disclosures, while pension fund managers might emphasize adherence to long-term investment guidelines. Global firms need systems that can handle multiple regulatory regimes, whereas regional players may have more focused but deeper compliance needs.
7. What are the consequences of inadequate compliance monitoring?
Inadequate monitoring can lead to regulatory fines, enforcement actions, reputational damage, client losses, operational disruptions, and legal expenses. In severe cases, firms may face license suspensions or revocations, criminal penalties for executives, and class-action lawsuits. Beyond these direct impacts, compliance failures can undermine market confidence and lead to stricter regulatory oversight for the entire industry.
8. How can firms measure the effectiveness of their compliance monitoring?
Effectiveness can be measured through key metrics including the number and severity of violations, false positive rates, time to resolution for compliance issues, audit findings, regulatory examination outcomes, and operational efficiency improvements. Firms should also conduct periodic testing of monitoring systems using “red team” approaches to identify potential blind spots or weaknesses.
9. What role does the compliance department play versus portfolio managers?
While portfolio managers are responsible for investment decisions within compliance parameters, the compliance department designs monitoring frameworks, implements control systems, oversees testing, and provides advisory support. Effective programs balance clear separation of duties with collaborative approaches that integrate compliance considerations into the investment process rather than treating them as after-the-fact checkpoints.
10. How is ESG changing compliance monitoring requirements?
ESG is introducing new dimensions to compliance monitoring, including the verification of sustainability claims, alignment with specialized ESG frameworks and regulations, integrating non-financial metrics into compliance processes, and enhanced disclosure requirements. Firms must now monitor not only traditional investment restrictions but also adherence to stated ESG objectives and an evolving landscape of sustainability-focused regulations.
Conclusion
Investment compliance monitoring has evolved from a peripheral function to a critical component of successful investment management operations. As regulatory complexity continues to increase globally, effective monitoring systems have become essential not just for avoiding penalties but for creating operational advantages. The most successful investment firms now treat compliance not as a cost center but as a strategic function that enables business growth and enhances client relationships.
Looking ahead, the future of investment compliance monitoring will be shaped by technological innovation, particularly in artificial intelligence and automation, allowing for more proactive and comprehensive oversight with reduced manual intervention. Regulatory focus areas will continue to evolve, with ESG compliance and data privacy emerging as key priorities alongside traditional concerns about investor protection and market integrity.
For investment professionals and organizations, the message is clear: investing in robust compliance monitoring capabilities is not merely about staying legal – it’s about creating a foundation for sustainable growth and competitive advantage in an increasingly complex financial landscape. Those who master this balance between compliance rigor and operational efficiency will be best positioned to thrive in the years ahead.
For your reference, recently published articles include:
- Portfolio Attribution Analysis: The Ultimate Guide
- Protect Your Wealth: Investment Risk Mitigation Secrets of the Rich
- Trading Strategy Backtesting: The Ultimate Path To Profits
- Investment Decision Support: Best Secrets For Your Success
- Market Intelligence Platforms – All You Need To Know
- Never Lose Money Again: Investment Scenario Analysis Magic
………………………………………………..
Important Notice: The information in this article is for general and public information purposes only. It solely reflects Didi Somm’s or his Staff’s opinion, and no responsibility can be assumed for errors or omissions in the service’s contents. For details, please check the Disclaimer at the bottom of the homepage.

